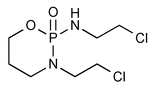
Ifosfamide
(eye fos' fa mide).
2H-1,3,2-Oxazaphosphorin-2-amine,N,3-bis(2-chloroethyl)tetrahydro-, 2-oxide.
3-(2-Chloroethyl)-[(2-chloroethyl)amino]tetrahydro-2H-1,3,2-oxazaphosphorine 2-oxide
» Ifosfamide contains not less than 98.0 percent and not more than 102.0 percent of C7H15Cl2N2O2P.
[Caution—Great care should be taken in handling Ifosfamide, as it is a potent cytotoxic agent and suspected carcinogen.
]
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in tight containers at a temperature not exceeding 25 .
.
Labeling—
Where it is intended for use in preparing injectable dosage forms, the label states that it is sterile or must be subjected to further processing during the preparation of injectable dosage forms.
Identification—
B:
The retention time of the major peak in the chromatogram of the Assay preparation corresponds to that of the Standard preparation, both relative to the internal standard, as obtained in the Assay.
pH  791
791 :
between 4.0 and 7.0 in a solution (1 in 10).
:
between 4.0 and 7.0 in a solution (1 in 10).
Water, Method I  921
921 :
not more than 0.3%.
:
not more than 0.3%.
Heavy metals, Method I  231
231 :
not more than 0.002%.
:
not more than 0.002%.
Ionic chloride—
Standard sodium chloride solution—
Transfer about 118.7 mg of sodium chloride, accurately weighed, to a 200-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in and dilute with water to volume, and mix. This solution contains 360 ppm of ionic chloride.
Procedure—
Pipet 10 mL of Standard sodium chloride solution into a beaker, and add 90 mL of water and 10 mL of acetic acid. Titrate with 0.01 N silver nitrate VS (prepared fresh daily), determining the endpoint potentiometrically using silver and silver-silver chloride electrodes. Record the volume, V1, of 0.01 N silver nitrate VS consumed. Transfer about 2.0 g of Ifosfamide, accurately weighed, into a beaker, and add 90 mL of water and 10 mL of acetic acid. Pipet 10 mL of Standard sodium chloride solution into the beaker, and stir, if necessary, until solution is complete. Titrate with 0.01 N silver nitrate VS as directed above, and record the volume, V2, of 0.01 N silver nitrate VS consumed. Calculate the difference in volume, V, of 0.01 N silver nitrate VS consumed between the two determinations by subtracting V1 from V2: a difference of not more than 1.0 mL corresponding to not more than 0.018% of ionic chloride is found.
Chloroform-insoluble phosphorus—
Ammonium molybdate solution—
[note—Prepare fresh on the day of use. ] Dissolve 25 g of ammonium molybdate in 300 mL of water (Solution A). Cautiously add 75 mL of sulfuric acid to 100 mL of water, cool to room temperature, and dilute with water to 200.0 mL (Solution B). Mix Solution A and Solution B to obtain Ammonium molybdate solution.
Hydroquinone solution—
Dissolve 0.5 g of hydroquinone in 100 mL of water, and add one drop of concentrated sulfuric acid. [note—When this solution darkens, discard it and prepare fresh. ]
Sodium sulfite solution—
Prepare a solution of sodium sulfite in water having a concentration of 200 mg per mL. [note—Prepare fresh at the time of use. ]
Phosphorus stock solution—
Transfer 0.1824 g of monobasic potassium phosphate, accurately weighed, to a 1000-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in and dilute with water to volume, and mix.
Phosphorus intermediate solution—
Transfer 10.0 mL of Phosphorus stock solution to a 100-mL volumetric flask, dilute with water to volume, and mix. Prepare this solution fresh on the day of use.
Phosphorus standard solution—
Transfer 10.0 mL of Phosphorus intermediate solution to a 100-mL volumetric flask, dilute with water to volume, and mix.
Test preparation—
Transfer 1 g of Ifosfamide, accurately weighed, to a 100-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in 50 mL of water, dilute with water to volume, and mix. Transfer 10.0 mL of this solution to a separatory funnel, and add 5 mL of water. Add 15 mL of chloroform, shake vigorously for 30 seconds, allow the layers to separate and drain, and discard the lower chloroform layer. Repeat this extraction four times, each time with 15 mL of chloroform, discarding the chloroform layer after each extraction. Transfer the aqueous portion to a conical flask, wash the separatory funnel with two 5-mL portions of water, and collect all the aqueous washings in the same flask. Add 3 mL of sulfuric acid, and heat under a hood until white fumes appear. Remove the flask from the heat, and with swirling, add 0.6 mL of hydrogen peroxide. Heat until white fumes reappear. If the solution is not colorless, repeat additions of hydrogen peroxide followed by heating until all color is gone. Cool to room temperature, add 25 mL of water, and cautiously add 10 mL of ammonium hydroxide solution. Cool to room temperature, add 2 drops of phenolphthalein TS, and then add hydrochloric acid dropwise until all pink color has disappeared. Transfer the contents of the flask to a 100-mL flask, dilute with water to volume, and mix.
Blank solution—
To 3 mL of sulfuric acid in a second conical flask, adding 0.6 mL of hydrogen peroxide, proceed as directed for the Test preparation, beginning with “Heat until white fumes reappear.”
Procedure—
Transfer 15.0 mL each of the Test preparation, the Blank solution, and the Phosphorus standard solution to three separate 25-mL volumetric flasks. Add 2.5 mL of Ammonium molybdate solution to each of the flasks, swirl, and allow to stand for about 30 seconds. To each of the three flasks in order, rapidly add 2.5 mL each of Hydroquinone solution and Sodium sulfite solution. Dilute the contents of each flask with water to volume, mix, and allow the flasks to stand for 30 minutes. Concomitantly determine the absorbances of the solutions obtained from the Test preparation and the Phosphorus standard solution in 1-cm cells at the wavelength of maximum absorbance at about 730 nm, with a suitable spectrophotometer, using the solution obtained from the Blank solution as the blank. Calculate the percentage of chloroform-insoluble phosphorus in the portion of Ifosfamide taken by the formula:
100(C / W)(AU / AS)
in which C is the concentration, in µg per mL, of phosphorus in the Phosphorus standard solution;W is the weight, in mg, of Ifosfamide taken; and AU and AS are the absorbances from the solutions obtained from the Test preparation and the Phosphorus standard solution, respectively: not more than 0.0415% is found.
Limit of 2-chloroethylamine hydrochloride—
Standard solution—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of 2-chloroethylamine hydrochloride in N,N-dimethylacetamide, and dilute quantitatively, and stepwise if necessary, with the same solvent to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 0.025 mg per mL.
Test solution—
Transfer about 100 mg of Ifosfamide, accurately weighed, to a flask, add 10.0 mL of N,N-dimethylacetamide, and shake until dissolved.
Chromatographic system—
The gas chromatograph is equipped with a flame-ionization detector and contains a 2-mm × 1.8-m column packed with 10% liquid phase G16 containing 2% potassium hydroxide on 80- to 100-mesh support S1A. The injection port is maintained at a temperature of about 200 , the detector is maintained at a temperature of about 300
, the detector is maintained at a temperature of about 300 , the oven is maintained at a temperature of about 140
, the oven is maintained at a temperature of about 140 , and nitrogen is used as the carrier gas at a flow rate of about 25 mL per minute.
, and nitrogen is used as the carrier gas at a flow rate of about 25 mL per minute.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 1.0 µL) of the Test solution and the Standard solution into the gas chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the areas of the peaks due to 2-chloroethylamine hydrochloride. Calculate the percentage of 2-chloroethylamine hydrochloride in the portion of Ifosfamide taken by the formula:
1000(C / W)(rU / rS)
in which C is the concentration, in mg per mL, of 2-chloroethylamine hydrochloride in the Standard solution;W is the weight, in mg, of Ifosfamide taken; and rU and rS are the areas of the 2-chloroethylamine peaks obtained from the Test solution and the Standard solution, respectively: not more than 0.25% of 2-chloroethylamine hydrochloride is found.
Other requirements—
Where the label states that Ifosfamide is sterile, it meets the requirements for Sterility Tests  71
71 and for Bacterial endotoxins under Ifosfamide for Injection. Where the label states that Ifosfamide must be subjected to further processing during the preparation of injectable dosage forms, it meets the requirements for Bacterial endotoxins under Ifosfamide for Injection.
and for Bacterial endotoxins under Ifosfamide for Injection. Where the label states that Ifosfamide must be subjected to further processing during the preparation of injectable dosage forms, it meets the requirements for Bacterial endotoxins under Ifosfamide for Injection.
Assay—
[note—Ifosfamide degrades in solution. Prepare solutions of Ifosfamide fresh daily and do not store for more than 24 hours. Prepare the Standard preparation and the Assay preparation simultaneously. ]
Mobile phase—
Prepare a filtered and degassed mixture of water and acetonitrile (70:30). Make adjustments if necessary (see System Suitability under Chromatography  621
621 ).
).
Internal standard solution—
Transfer about 50 mg of ethylparaben, accurately weighed, to a 100-mL volumetric flask, and add 25 mL of alcohol to dissolve. Dilute with water to volume, and mix.
Standard preparation—
Transfer about 15 mg of USP Ifosfamide RS, accurately weighed, to a 25-mL volumetric flask, add 1.0 mL of Internal standard solution, dilute with water to volume, and mix.
Assay preparation—
Transfer about 150 mg of Ifosfamide, accurately weighed, to a 250-mL volumetric flask, add 10.0 mL of Internal standard solution, dilute with water to volume, and mix.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 195-nm detector and a 3.9-mm × 30-cm column that contains packing L1. The flow rate is about 1.5 mL per minute. Chromatograph the Standard preparation, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the resolution, R, between ifosfamide and ethylparaben is not less than 6.0, and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 2.0%.
)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 195-nm detector and a 3.9-mm × 30-cm column that contains packing L1. The flow rate is about 1.5 mL per minute. Chromatograph the Standard preparation, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the resolution, R, between ifosfamide and ethylparaben is not less than 6.0, and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 2.0%.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 25 µL) of the Standard preparation and the Assay preparation into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the areas for the major peaks. Calculate the quantity, in mg, of C7H15Cl2N2O2P in the portion of Ifosfamide taken by the formula:
250C(RU / RS)
in which C is the concentration, in mg per mL, of USP Ifosfamide RS in the Standard preparation; and RU and RS are the ratios of the responses of the ifosfamide peak to the ethylparaben peak obtained from the Assay preparation and the Standard preparation, respectively.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Feiwen Mao, M.S.
Senior Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8320 |
(SM32010) Monographs - Small Molecules 3 |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP35–NF30 Page 3477