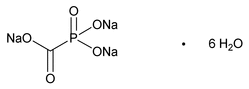Foscarnet Sodium
(fos kar' net soe' dee um).
Phosphinecarboxylic acid, dihydroxy-, oxide, trisodium salt, hexahydrate.
Phosphonoformic acid, trisodium salt, hexahydrate
» Foscarnet Sodium contains not less than 98.5 percent and not more than 101.0 percent of CNa3O5P, calculated on the dried basis.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in tight, light-resistant containers. Store at room temperature.
USP Reference standards  11
11 —
—
USP Foscarnet Sodium RS
USP Foscarnet Related Compound B RS
Disodium (ethoxyoxidophosphanyl)formate.
C3H5Na2O5P 198.02
Disodium (ethoxyoxidophosphanyl)formate.
C3H5Na2O5P 198.02
USP Foscarnet Related Compound D RS
O,O-Diethyl ethoxycarbonylphosphonate.
C7H15O5P 210.16
O,O-Diethyl ethoxycarbonylphosphonate.
C7H15O5P 210.16
Identification—
B:
It meets the requirements of the test for Sodium  191
191 .
.
pH  791
791 :
between 9.0 and 11.0, in a carbon dioxide-free aqueous solution containing 20 mg of Foscarnet Sodium per mL.
:
between 9.0 and 11.0, in a carbon dioxide-free aqueous solution containing 20 mg of Foscarnet Sodium per mL.
Loss on drying  731
731 —
Dry about 0.1 g at 150
—
Dry about 0.1 g at 150 for at least 15 minutes and weigh: it loses between 35.0% and 37.0% of its weight.
for at least 15 minutes and weigh: it loses between 35.0% and 37.0% of its weight.
Heavy metals—
Lead standard stock solution (1000 ppm)—
Dissolve 0.4 g of lead nitrate in 250 mL of water. Prepare and store this solution in glass containers free from soluble lead salts.
Lead standard solution—
Immediately before use, dilute Lead standard stock solution (1000 ppm), quantitatively and stepwise if necessary, with water to obtain a solution having a known concentration of 1 ppm of lead.
Sodium sulfide solution—
Dissolve 12 g of disodium sulfide nonahydrate with heating in 45 mL of a mixture of 10 volumes of water and 29 volumes of 85% glycerol, allow to cool, and dilute with the same mixture of solvents to 100 mL.
Acetate buffer—
Dissolve 25.0 g of ammonium acetate in 25 mL of water, and add 38.0 mL of 6 N hydrochloric acid. Adjust, if necessary, with 6 N ammonium hydroxide or 6 N hydrochloric acid to a pH of 3.5, dilute with water to 100 mL, and mix.
Test solution—
Dissolve 1.25 g in 12.5 mL of 1 M hydrochloric acid. Heat on a boiling water bath for 3 minutes and cool to room temperature. Transfer to a beaker, adjust with 6 N ammonium hydroxide to a pH of about 3.5, and dilute with water to 25 mL.
Standard solution—
Prepare a mixture of 5.0 mL of Lead standard solution, 5.0 mL of water, 2.0 mL of the Test solution, and 2.0 mL of Acetate buffer. Rapidly pour the solution into a test tube containing 1 drop of Sodium sulfide solution.
Procedure—
To 12 mL of the Test solution add 2.0 mL of Acetate buffer. Rapidly pour the mixture into a test tube containing 1 drop of Sodium sulfide solution. The solution is not more intensely colored than the Standard solution prepared simultaneously (10 ppm).
Limit of foscarnet related compound B, unknown impurities, and total impurities—
Solution A—
Dissolve 3.2 g of sodium sulfate decahydrate in water, add 3 mL of glacial acetic acid and 6 mL of 0.1 M sodium pyrophosphate, and dilute with water to 1000 mL.
Solution B—
Dissolve 3.2 g of sodium sulfate decahydrate in water, add 6.8 g of sodium acetate and 6 mL of 0.1 M sodium pyrophosphate, and dilute with water to 1000 mL.
Mobile phase—
Prepare a mixture of Solution A and Solution B (70:30). [note—The pH of this solution is about 4.4. ] To 1000 mL of this solution, add 0.25 g of tetrahexylammonium hydrogen sulfate and 100 mL of methanol, and mix.
Test solution—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of Foscarnet Sodium in Mobile phase to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 2.5 mg per mL.
Standard solution—
Accurately dilute the Test solution in Mobile phase, stepwise if necessary, to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 5.0 µg per mL.
Resolution solution—
Transfer 2.0 mL of the Test solution into a 50-mL volumetric flask, add 5.0 mg of USP Foscarnet Related Compound B RS, and dilute with Mobile phase to volume.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 230-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 10-cm column that contains 3-µm packing L1. The flow rate is about 1.0 mL per minute. Chromatograph the Resolution solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the resolution, R, between foscarnet and foscarnet related compound B is not less than 7.
)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 230-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 10-cm column that contains 3-µm packing L1. The flow rate is about 1.0 mL per minute. Chromatograph the Resolution solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the resolution, R, between foscarnet and foscarnet related compound B is not less than 7.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 20 µL) of the Standard solution and the Test solution into the chromatograph, allow the chromatogram to run for 2.5 times of the retention time of foscarnet, record the chromatograms, and measure the peak responses: the area of any peak, apart from the major peak, in the chromatogram obtained with the Test solution is not greater than the area of the major peak in the chromatogram obtained with the Standard solution (0.2%); the sum of the areas of all the peaks, apart from the major peak, is not greater than twice the area of the major peak in the chromatogram obtained with the Standard solution (0.4%). Disregard any peak with a relative retention time less than 0.6 and any peak with an area less than 0.2 times that of the peak in the chromatogram obtained with the Standard solution.
Limit of foscarnet related compound D—
Test solution—
Dissolve 0.25 g of Foscarnet Sodium in 9 mL of 0.1 M acetic acid. Add 1 mL of alcohol, and mix.
Standard solution—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of USP Foscarnet Related Compound D RS in alcohol, stepwise if necessary, to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 25 µg per mL.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
The gas chromatograph is equipped with a flame-ionization detector and a 0.31-mm × 25-m column coated with a 0.5-µm phase G27. The carrier gas is helium, flowing at a rate of 1 mL per minute. The split ratio is 1:20. The chromatograph is programmed as follows. The temperature of the column is increased from 100
)—
The gas chromatograph is equipped with a flame-ionization detector and a 0.31-mm × 25-m column coated with a 0.5-µm phase G27. The carrier gas is helium, flowing at a rate of 1 mL per minute. The split ratio is 1:20. The chromatograph is programmed as follows. The temperature of the column is increased from 100 to 180
to 180 at a rate of 10
at a rate of 10 per minute. The injection port temperature is maintained at 200
per minute. The injection port temperature is maintained at 200 , and the detector temperature is maintained at 250
, and the detector temperature is maintained at 250 .
.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 3 µL) of the Standard solution and the Test solution into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the peak responses: the area of the peak due to foscarnet related compound D in the chromatogram obtained with the Test solution is not greater than the area of the peak in the chromatogram obtained with the Standard solution (0.1%).
Limit of phosphate and phosphite—
Mobile phase—
Dissolve about 0.1 g of potassium phthalate monobasic in water, add 2.5 mL of 1 M nitric acid, and dilute with water to 1000 mL.
Test solution—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of Foscarnet Sodium in water to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 2.4 mg per mL.
Standard stock solution 1—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of sodium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate in water to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 0.28 mg per mL.
Standard stock solution 2—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of sodium phosphite pentahydrate in water to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 0.43 mg per mL.
Standard solution—
Transfer 1 mL each of Standard stock solution 1 and Standard stock solution 2 to a 25-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 290-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 5-cm column that contains packing L23 (see Chromatographic Reagents). The flow rate is about 1.4 mL per minute. Chromatograph the Standard solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the resolution, R, between phosphate and phosphite is not less than 2.0.
)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 290-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 5-cm column that contains packing L23 (see Chromatographic Reagents). The flow rate is about 1.4 mL per minute. Chromatograph the Standard solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the resolution, R, between phosphate and phosphite is not less than 2.0.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 20 µL) of the Standard solution and the Test solution into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the peak responses: the area of any peak due to phosphate and phosphite in the chromatogram obtained with the Test solution is not greater than the area of the corresponding peak in the chromatogram obtained with the Standard solution (0.3% of phosphate and 0.3% of phosphite).
Assay—
Dissolve about 0.2 g of Foscarnet Sodium, accurately weighed, in 50 mL of water. Titrate with 0.05 M sulfuric acid, determining the endpoint potentiometrically at the first inflection point. Each mL of 0.05 M sulfuric acid is equivalent to 19.20 mg of CNa3O5P.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Behnam Davani, Ph.D., M.B.A.
Senior Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8394 |
(SM12010) Monographs - Small Molecules 1 |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP35–NF30 Page 3279
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 34(1) Page 97