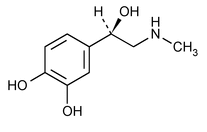
Epinephrine
(ep'' i nef' rin).
1,2-Benzenediol, 4-[1-hydroxy-2-(methylamino)ethyl]-, (R)-.
(
» Epinephrine contains not less than 97.0 percent and not more than 100.5 percent of C9H13NO3, calculated on the dried basis.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in tight, light-resistant containers.
Identification—
To 5 mL of pH 4.0 acid phthalate buffer (see Buffer Solutions in the section Reagents, Indicators, and Solutions) add 0.5 mL of a slightly acid solution of Epinephrine (1 in 1000) and 1.0 mL of 0.1 N iodine. Mix, and allow to stand for 5 minutes. Add 2 mL of sodium thiosulfate solution (1 in 40): a deep red color is produced.
Specific rotation  781S
781S :
between –50.0
:
between –50.0 and –53.5
and –53.5 .
.
Test solution:
20 mg per mL, in 0.6 N hydrochloric acid.
Loss on drying  731
731 —
Dry it in vacuum over silica gel for 18 hours: it loses not more than 2.0% of its own weight.
—
Dry it in vacuum over silica gel for 18 hours: it loses not more than 2.0% of its own weight.
Residue on ignition  281
281 :
negligible, from 100 mg.
:
negligible, from 100 mg.
Limit of adrenalone—
Its absorptivity (see Spectrophotometry and Light-scattering  851
851 ) at 310 nm, determined in a solution in dilute hydrochloric acid (1 in 200) containing 2 mg per mL, is not more than 0.2.
) at 310 nm, determined in a solution in dilute hydrochloric acid (1 in 200) containing 2 mg per mL, is not more than 0.2.
Limit of norepinephrine—
Epinephrine standard solution—
Dilute with methanol an accurately measured volume of a solution of USP Epinephrine Bitartrate RS in formic acid containing about 364 mg per mL to obtain a solution having a concentration of about 20 mg per mL.
Norepinephrine standard solution—
Dilute with methanol an accurately measured volume of a solution of USP Norepinephrine Bitartrate RS in formic acid containing 16 mg per mL to obtain a solution having a known concentration of 1.6 mg per mL.
Test solution—
Dissolve 200 mg of Epinephrine in 1.0 mL of formic acid, dilute with methanol to 10.0 mL, and mix.
Procedure—
Apply 5-µL portions of Epinephrine standard solution, Norepinephrine standard solution, and Test solution to a suitable thin-layer chromatographic plate (see Chromatography  621
621 ) coated with a 0.25-mm layer of chromatographic silica gel mixture. Allow the spots to dry, and develop the chromatogram in an unsaturated tank using a solvent system consisting of a mixture of n-butanol, water, and formic acid (7:2:1) until the solvent front has moved about three-fourths of the length of the plate. Remove the plate from the developing chamber, mark the solvent front, and allow the solvent to evaporate in warm circulating air. Spray with Folin-Ciocalteu Phenol TS, followed by sodium carbonate solution (1 in 10): the RF value of the principal spot obtained from the Test solution corresponds to that obtained from the Epinephrine standard solution. Any spot obtained from the Test solution is not larger nor more intense than the spot with the same RF value obtained from the Norepinephrine standard solution, corresponding to not more than 4.0% of norepinephrine.
) coated with a 0.25-mm layer of chromatographic silica gel mixture. Allow the spots to dry, and develop the chromatogram in an unsaturated tank using a solvent system consisting of a mixture of n-butanol, water, and formic acid (7:2:1) until the solvent front has moved about three-fourths of the length of the plate. Remove the plate from the developing chamber, mark the solvent front, and allow the solvent to evaporate in warm circulating air. Spray with Folin-Ciocalteu Phenol TS, followed by sodium carbonate solution (1 in 10): the RF value of the principal spot obtained from the Test solution corresponds to that obtained from the Epinephrine standard solution. Any spot obtained from the Test solution is not larger nor more intense than the spot with the same RF value obtained from the Norepinephrine standard solution, corresponding to not more than 4.0% of norepinephrine.
Assay—
Dissolve about 300 mg of Epinephrine, accurately weighed, in 50 mL of glacial acetic acid, warming slightly if necessary to effect solution. Add crystal violet TS, and titrate with 0.1 N perchloric acid VS. Perform a blank determination, and make any necessary correction. Each mL of 0.1 N perchloric acid is equivalent to 18.32 mg of C9H13NO3.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Domenick Vicchio, Ph.D.
Senior Scientific Liaison 1-301-998-6828 |
(SM42010) Monographs - Small Molecules 4 |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP35–NF30 Page 3052
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 37(2)