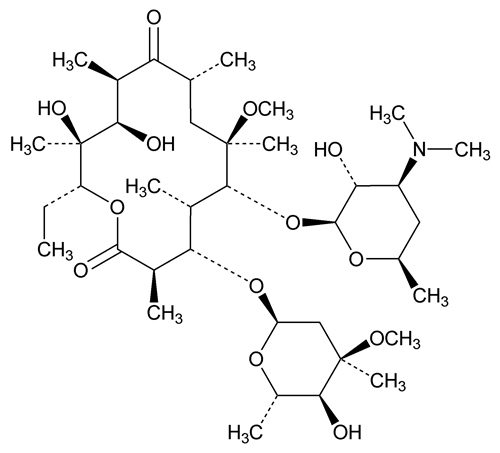
Clarithromycin
(kla rith'' roe mye' sin).
» Clarithromycin contains not less than 96.0 percent and not more than 102.0 percent of C38H69NO13, calculated on the anhydrous basis.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in tight containers.
Identification, Infrared Absorption  197K
197K .
.
Specific rotation  781S
781S :
between
:
between  94
94 and
and  102
102 (t = 20
(t = 20 ).
).
Test solution:
10 mg per mL, in methylene chloride.
Crystallinity  695
695 :
meets the requirements.
:
meets the requirements.
pH  791
791 :
between 8.0 and 10.0, determined in a 1 in 500 suspension of it in a mixture of water and methanol (19:1).
:
between 8.0 and 10.0, determined in a 1 in 500 suspension of it in a mixture of water and methanol (19:1).
Water, Method I  921
921 :
not more than 2.0%.
:
not more than 2.0%.
Residue on ignition  281
281 :
not more than 0.2%, 0.5 g of it being taken, the charred residue being moistened with 1 mL of sulfuric acid.
:
not more than 0.2%, 0.5 g of it being taken, the charred residue being moistened with 1 mL of sulfuric acid.
Heavy metals:
not more than 0.002%.
Test solution—
Dissolve 1.0 g of it in an 85% (v/v) solution of dioxane in water, and dilute with the same diluent to 20 mL. Transfer 12 mL of this solution to a color-comparison tube.
Blank—
Add 10 mL of an 85% (v/v) solution of dioxane in water and 2 mL of the Test solution to a color-comparison tube.
Standard solution—
Prepare using standard lead solution (1 ppm Pb) obtained by diluting standard lead solution (100 ppm Pb) with an 85% (v/v) solution of dioxane in water. Add 10 mL of this solution (1 ppm Pb) and 2 mL of the Test solution to a color-comparison tube. To each of the three tubes containing the Test solution, the Blank, and the Standard solution add 2 mL of pH 3.5 acetate buffer, mix, add 1.2 mL of thioacetamide–glycerin base TS, and mix. Compared to the Blank, the Standard solution shows a slight brown color. After 2 minutes, any brown color in the Test solution is not more intense than that in the Standard solution.
Related substances—
Solution A—
Prepare a solution containing 4.76 g of monobasic potassium phosphate per L. Adjust with dilute phosphoric acid (l in 10) or potassium hydroxide (45% w/v) to a pH of 4.4. Pass this solution through a C18 filtration kit.
Solution B—
Use acetonitrile.
Mobile phase—
Use variable mixtures of Solution A and Solution B as directed under Chromatographic system. Make adjustments if necessary (see System Suitability under Chromatography  621
621 ).
).
Diluting solution—
Prepare a mixture of acetonitrile and water (50:50).
Standard solution A—
Transfer about 75 mg of USP Clarithromycin RS, accurately weighed, to a 50-mL volumetric flask, and dissolve in 25 mL of acetonitrile. Dilute with water to volume, and mix.
Standard solution B—
Transfer 5.0 mL of Standard solution A to a 100-mL volumetric flask, dilute with Diluting solution to volume, and mix.
Standard solution C—
Transfer 1.0 mL of Standard solution B to a 10-mL volumetric flask, dilute with Diluting solution to volume, and mix. This solution contains about 0.0075 mg of USP Clarithromycin RS per mL.
Standard solution D—
Transfer about 15 mg of USP Clarithromycin Identity RS, accurately weighed, to a 10-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in 5.0 mL of acetonitrile, dilute with water to volume, and mix.
Test solution—
Transfer about 75 mg of Clarithromycin, accurately weighed, to a 50-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in 25 mL of acetonitrile, dilute with water to volume, and mix.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 205-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 10-cm column that contains packing L1 and is maintained at a constant temperature of about 40
)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 205-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 10-cm column that contains packing L1 and is maintained at a constant temperature of about 40 . The flow rate is about 1.1 mL per minute. The chromatograph is programmed as follows.
. The flow rate is about 1.1 mL per minute. The chromatograph is programmed as follows.
Relative retention times with reference to clarithromycin (retention time = about 11 minutes) include the following: impurity I = about 0.38; impurity C = about 0.89; impurity F = about 1.33; impurity A = about 0.42; impurity D = about 0.96; impurity P = about 1.35; impurity J = about 0.63; impurity N = about 1.15; impurity K = about 1.59; impurity L = about 0.74; impurity E = about 1.27; impurity G = about 1.72; impurity B = about 0.79; impurity 0 = about 1.38; impurity H = about 1.82; and impurity M = about 0.81.
| Time (minutes) |
Solution A
(%) |
Solution B
(%) |
Elution |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0®32 | 75®40 | 25®60 | linear gradient |
| 32®34 | 40 | 60 | isocratic |
| 34®36 | 40®75 | 60®25 | linear gradient |
| 36®42 | 75 | 25 | isocratic |
System suitability—
Chromatograph Standard solution B, and record the responses as directed for Procedure: the tailing factor for the main clarithromycin peak is not more than 1.7. Chromatograph Standard solution D, and record the responses as directed for Procedure: the peak-to-valley ratio (HP / HV) of impurity D and clarithromycin is not less than 3.0, where HP is the height above the baseline of the peak due to impurity D; and HV is the height above the baseline of the lowest point of the curve separating this peak from the peak due to clarithromycin.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 10 µL) of the Diluting solution, Standard solution B, Standard solution D, Standard solution C, and the Test solution into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the peak area responses. Calculate the percentage of each impurity in the Clarithromycin taken by the formula:
50(CC / W)(riF/rC)P
in which CC is the concentration, in mg per mL, of USP Clarithromycin RS in Standard solution C; W is the weight, in mg, of Clarithromycin taken to prepare the Test solution; ri is the peak area response for any individual impurity observed in the chromatogram obtained from the Test solution; F is 1.0, or the correction factor of 0.27, and 0.15 applied to the responses for peaks at relative retention times in relation to that of clarithromycin of about 1.72, and 1.82, corresponding to related compound G and related compound H, respectively; rC is the peak area response of the main clarithromycin peak in the chromatogram obtained from Standard solution C; and P is the purity of USP Clarithromycin RS taken to prepare Standard solution A. Not more than 1.0% of any single related compound is found, not more than four related compounds exceed the limit of 0.4%, and the total of all related compounds is not more than 3.5%.
Assay—
Solution A, Solution B, Diluting solution, and Standard solution D—
Proceed as directed in the test for Related substances.
Standard preparation—
Use Standard solution A, prepared as directed in the test for Related substances.
Assay preparation—
Use the Test solution, prepared as directed in the test for Related substances.
Chromatographic system—
Proceed as directed in the test for Related substances. In addition, the relative standard deviation for replicate injections of the Standard preparation is not more than 1.5%.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 10 µL) of the Standard preparation and the Assay preparation into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the peak area responses for the major peaks. Calculate the percentage of C38H69NO13 in the portion of Clarithromycin taken by the formula:
50(CS / W)(rU / rS)P
in which CS is the concentration, in mg per mL, of USP Clarithromycin RS in the Standard preparation; W is the weight, in mg, of Clarithromycin taken to prepare the Assay preparation; rU and rS are the clarithromycin peak area responses obtained from the chromatograms of the Assay preparation and the Standard preparation, respectively; and P is the purity of USP Clarithromycin RS taken to prepare the Standard preparation.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Ahalya Wise, M.S.
Senior Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8161 |
(SM12010) Monographs - Small Molecules 1 |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP35–NF30 Page 2690
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 30(4) Page 1179