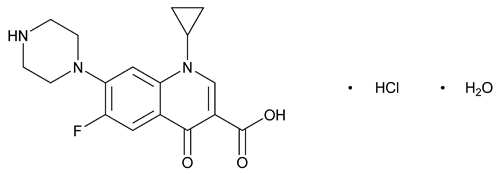
Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride
C17H18FN3O3·HCl·H2O 385.82
3-Quinolinecarboxylic acid, 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-, monohydrochloride, monohydrate;
1-Cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid, monohydrochloride, monohydrate

 [86393-32-0].
[86393-32-0].
(sip'' roe flox' a sin hye'' droe klor' ide).
C17H18FN3O3·HCl·H2O 385.82
3-Quinolinecarboxylic acid, 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-, monohydrochloride, monohydrate;
1-Cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid, monohydrochloride, monohydrate
DEFINITION
Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride contains NLT 98.0% and NMT 102.0% of C17H18FN3O3·HCl, calculated on the anhydrous basis.
IDENTIFICATION
• B.
The retention time of the major peak of the Sample solution corresponds to that of the Standard solution, as obtained in the Assay.
ASSAY
• Procedure
Solution A:
0.025 M phosphoric acid. Adjust with triethylamine to a pH of 3.0 ± 0.1.
Mobile phase:
Acetonitrile and Solution A (13:87)
Standard solution:
0.5 mg/mL of USP Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride RS in Mobile phase
System suitability solution:
0.025 mg/mL of USP Ciprofloxacin Ethylenediamine Analog RS in Mobile phase. Transfer 1.0 mL of this solution to a 10-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with Standard solution to volume.
Sample solution:
0.5 mg/mL of Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride in Mobile phase
Chromatographic system
Mode:
LC
Detector:
UV 278 nm
Column:
4.6-mm × 25-cm; packing L1
Column temperature:
30 ± 1
Flow rate:
1.5 mL/min
Injection size:
10 µL
System suitability
Samples:
Standard solution and System suitability solution
[Note—The relative retention times for ciprofloxacin ethylenediamine analog and ciprofloxacin are 0.7 and 1.0, respectively. ]
Suitability requirements
Resolution:
NLT 6 between the ciprofloxacin ethylenediamine analog peak and the ciprofloxacin peak, System suitability solution
Column efficiency:
NLT 2500 theoretical plates from the ciprofloxacin peak, Standard solution
Tailing factor:
NMT 2.5 for the ciprofloxacin peak, Standard solution
Relative standard deviation:
NMT 1.5%, Standard solution
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of C17H18FN3O3 ·HCl in the portion of Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × 100
| rU | = | = peak area response from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak area response from the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of USP Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL) |
| CU | = | = concentration of Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride in the Sample solution (mg/mL) |
Acceptance criteria:
98.0%–102.0% on the anhydrous basis
IMPURITIES
Inorganic Impurities
• Residue on Ignition  281
281 :
NMT 0.1%
:
NMT 0.1%
• Chloride and Sulfate, Sulfate  221
221 :
A 375-mg portion shows no more sulfate than corresponds to 0.15 mL of 0.020 N sulfuric acid (0.04%).
:
A 375-mg portion shows no more sulfate than corresponds to 0.15 mL of 0.020 N sulfuric acid (0.04%).
• Heavy Metals, Method II  231
231 :
NMT 20 ppm
:
NMT 20 ppm
Organic Impurities
• Procedure 1: Limit of Fluoroquinolonic Acid
Standard solution:
Transfer 5.0 mg of USP Fluoroquinolonic Acid RS to a 50-mL volumetric flask containing 0.05 mL of 6 N ammonium hydroxide, add water to volume, and mix. Transfer 2.0 mL of this solution to a 10.0-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume.
Sample solution:
10 mg/mL of Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride in water
Chromatographic system
Mode:
TLC
Adsorbent:
0.25-mm layer of silica gel mixture
Application volume:
5 µL
Developing solvent system:
Methylene chloride, methanol, acetonitrile, and ammonium hydroxide (4:4:1:2)
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Proceed as directed in the chapter. Place a beaker containing 50 mL of ammonium hydroxide in a suitable chamber, and then place the plate in the chamber. After 15 min, transfer the plate to a suitable chromatographic chamber, and develop the chromatogram in the Developing solvent system until the solvent front has moved about three-fourths of the length of the plate. Remove the plate from the chamber, mark the solvent front, and allow the plate to air-dry for about 15 min. Examine the plate under short-wavelength UV light.
Acceptance criteria:
Any spot from the Sample solution, at an RF value corresponding to the principal spot from the Standard solution, is not greater in size or intensity than the principal spot from the Standard solution (0.2%).
• Procedure 2
Mobile phase, Standard solution, System suitability solution, Sample solution, Chromatographic system, and System suitability:
Proceed as directed in the Assay.
Analysis
Sample:
Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of each impurity in the portion of Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride taken:
Result = (rU/rT) × 100
| rU | = | = peak response of each impurity |
| rT | = | = sum of the responses of all the peaks |
Acceptance criteria
Individual impurities:
NMT 0.2% for the ciprofloxacin ethylenediamine analog or any other individual impurity peak
Total impurities:
NMT 0.5%
SPECIFIC TESTS
• pH  791
791 :
3.0–4.5, in a 25 mg/mL solution
:
3.0–4.5, in a 25 mg/mL solution
• Water Determination, Method I  921
921 :
4.7%–6.7%
:
4.7%–6.7%
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
• Packaging and Storage:
Preserve in tight, light-resistant containers. Store at 25 , excursions permitted between 15
, excursions permitted between 15 and 30
and 30 .
.
• USP Reference Standards  11
11
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Behnam Davani, Ph.D., M.B.A.
Senior Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8394 |
(SM12010) Monographs - Small Molecules 1 |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP35–NF30 Page 2670
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 35(4) Page 839