Alfadex
(al' fa dex).
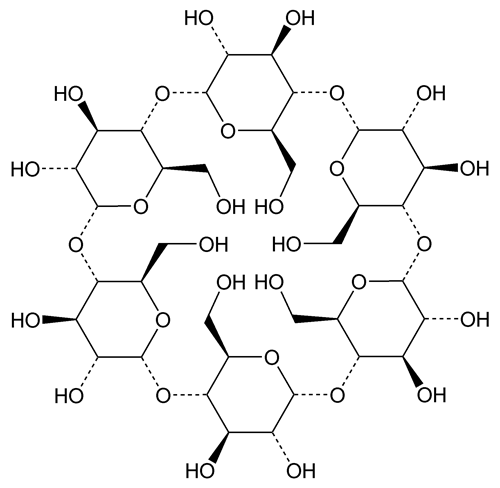
» Alfadex is composed of six alpha-(1-4) linked d-glucopyranosyl units. It contains not less than 98.0 percent and not more than 101.0 percent of (C6H10O5)6, calculated on the anhydrous basis.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in tight containers. No storage requirements specified.
Clarity of solution—
Dissolve 1.0 g in 100.0 mL of previously boiled and cooled water: the resulting solution is clear.
Identification—
A:
The retention time of the major peak in the chromatogram of the Assay preparation corresponds to that in the chromatogram of the Standard preparation, as obtained in the Assay.
B:
It meets the requirements of the test for Specific rotation.
C:
Mix 0.2 g with 2 mL of iodine TS, warm in a water bath to dissolve the test specimen, and allow to stand at room temperature: a yellow-brown precipitate is formed.
Specific rotation  781S
781S :
between +147
:
between +147 and +152
and +152 , determined at 20
, determined at 20 .
.
Test solution:
10 mg per mL, in water.
Microbial enumeration tests  61
61 and Tests for specified microorganisms
and Tests for specified microorganisms  62
62 —
It meets the requirements of the tests for absence of Salmonella species and Escherichia coli. The total aerobic bacterial count does not exceed 1000 cfu per g. The total combined molds and yeasts count does not exceed 100 cfu per g.
—
It meets the requirements of the tests for absence of Salmonella species and Escherichia coli. The total aerobic bacterial count does not exceed 1000 cfu per g. The total combined molds and yeasts count does not exceed 100 cfu per g.
pH  791
791 —
The pH of the mixture of 30 mL of its aqueous solution (1 in 100) and 1 mL of Potassium chloride solution is 5.0 to 8.0.
—
The pH of the mixture of 30 mL of its aqueous solution (1 in 100) and 1 mL of Potassium chloride solution is 5.0 to 8.0.
Potassium chloride solution—
Transfer 22.4 g of potassium chloride into a 100-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume.
Water, Method I  921
921 :
not more than 11.0%.
:
not more than 11.0%.
Residue on ignition  281
281 :
not more than 0.1%, determined on 1.0 g.
:
not more than 0.1%, determined on 1.0 g.
Heavy metals, Method II  231
231 :
not more than 10 µg per g.
:
not more than 10 µg per g.
Reducing sugars—
Cupric solution—
Dissolve 15 g of cupric sulfate in water to make 100 mL.
Tartrate solution—
Dissolve 2.5 g of anhydrous sodium carbonate, 2.5 g of potassium sodium tartrate, 2.0 g of sodium bicarbonate, and 20 g of anhydrous sodium sulfate in water to make 100 mL.
Cupric–tartaric solution—
Immediately before use, mix 1 part of Cupric solution with 25 parts of Tartrate solution.
Ammonium molybdate reagent—
Mix 10 mL of a solution of disodium arsenate (6 in 100), 50 mL of a solution of ammonium molybdate (1 in 10), and 90 mL of diluted sulfuric acid, and dilute with water to 200 mL.
Test solution—
Transfer about 1.0 g of Alfadex, accurately weighed, and calculated on the anhydrous basis, to a 100-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in and dilute with water that has been previously boiled and cooled to room temperature, to volume, and mix. To 1 mL of this solution add 1 mL of Cupric–tartaric solution. Heat on a water bath for 10 minutes, then cool to room temperature. Add 10 mL of Ammonium molybdate reagent, and allow to stand for 15 minutes.
Standard stock solution—
Prepare a solution having a known concentration of 20 mg per L for USP Dextrose RS, calculated on the anhydrous basis.
Standard solution—
Prepare as directed for the Test solution, at the same time, except to use 1 mL of Standard stock solution in place of 1.0 g anhydrous Alfadex.
Procedure—
Measure the absorbance of the Test solution and the Standard solution at the wavelength of maximum absorbance at 740 nm relative to that of water, with a suitable spectrophotometer. The absorbance of the Test solution is not greater than that of the Standard solution (0.2%).
Related compounds—
System suitability solution—
Prepare as directed for System suitability preparation in the Assay.
Standard solution—
Transfer 5.0 mL of the System suitability solution into a 50-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume.
Test solution—
Use the Assay stock preparation prepared as directed in the Assay.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
Proceed as directed in the Assay.
)—
Proceed as directed in the Assay.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 50 µL) of the Standard solution and the Test solution into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the responses for the major peaks. For the Test solution, the areas of any peaks corresponding to beta cyclodextrin or to gamma cyclodextrin are not greater than half of the area of the corresponding peaks in the chromatogram of the Standard solution (0.25%), and the sum of the areas of all the peaks, excluding the principal peak and the peaks corresponding to beta cyclodextrin or to gamma cyclodextrin, is not greater than the area of the peak corresponding to alpha cyclodextrin in the chromatogram of the Standard solution (0.5%).
Light-absorbing impurities—
Test solution—
Transfer about 1.0 g of Alfadex, accurately weighed, and calculated on the anhydrous basis, to a 100-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in and dilute with water, which has been previously boiled and cooled to room temperature, to volume, mix, and pass through a 0.2-µm filter.
Procedure—
Determine the absorbance of the Test solution in a 1-cm cell with a suitable spectrophotometer, after correcting for the blank: between 230 nm and 350 nm, the absorbance is not greater than 0.10; and between 350 nm and 750 nm, the absorbance is not greater than 0.05.
Assay—
Mobile phase—
Prepare a filtered and degassed mixture of water and methanol (93:7). Make adjustments if necessary (see System Suitability under Chromatography  621
621 ).
).
Standard preparation—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of USP Alpha Cyclodextrin RS in water to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 1.0 mg per mL, calculated on the anhydrous basis.
System suitability preparation—
Dissolve accurately weighed quantities of USP Alpha Cyclodextrin RS, USP Beta Cyclodextrin RS, and USP Gamma Cyclodextrin RS in water to obtain a solution having known concentrations of about 0.5 mg of each per mL for USP Alpha Cyclodextrin RS and USP Beta Cyclodextrin RS, each calculated on the anhydrous basis, and about 0.5 mg per mL for USP Gamma Cyclodextrin RS, calculated on the dried basis.
Assay stock preparation—
Transfer 250 mg of Alfadex, accurately weighed, to a 25-mL volumetric flask, and dissolve in water with the aid of heat. Cool, and dilute with water to volume.
Assay preparation—
Transfer 5.0 mL of the Assay stock preparation to a 50-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a refractive index detector and a 4.6-mm × 15-cm column that contains 5-µm packing L1. The temperature for the refractive index detector is maintained at 40
)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a refractive index detector and a 4.6-mm × 15-cm column that contains 5-µm packing L1. The temperature for the refractive index detector is maintained at 40 , and the temperature for the analytical column is maintained at 30
, and the temperature for the analytical column is maintained at 30 . The flow rate is about 1.5 mL per minute. Chromatograph the System suitability preparation, and identify the components based on their relative retention times, which are 0.8, 1.0, and 2.0 for gamma cyclodextrin, alfadex, and betadex, respectively. Record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the resolution, R, between the gamma cyclodextrin and alfadex peaks is not less than 1.5; the tailing factors for the three cyclodextrins are between 0.8 and 2.0; and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 2.0%.
. The flow rate is about 1.5 mL per minute. Chromatograph the System suitability preparation, and identify the components based on their relative retention times, which are 0.8, 1.0, and 2.0 for gamma cyclodextrin, alfadex, and betadex, respectively. Record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the resolution, R, between the gamma cyclodextrin and alfadex peaks is not less than 1.5; the tailing factors for the three cyclodextrins are between 0.8 and 2.0; and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 2.0%.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 50 µL) of the Standard preparation and the Assay preparation into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the responses for the major peaks. Calculate the percentage of (C6H10O5)6 in the portion of Alfadex taken by the formula:
100 (10) × (25) {C / [W(1  0.01A)]}(rU / rS)
0.01A)]}(rU / rS)
in which 10 is the dilution factor for preparing the Assay preparation from the Assay stock preparation; 25 is the volume, in mL, of the Assay stock preparation; C is the concentration, in mg per mL, of alpha cyclodextrin in the Standard preparation; W is the weight, in mg, of alpha cyclodextrin taken to prepare the Assay stock preparation; A is the percentage of water in the portion of Alfadex taken; and rU and rS are the peak responses of the alpha cyclodextrin peak obtained from the Assay preparation and the Standard preparation, respectively.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Robert H. Lafaver, M.S.
Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8335 |
(EXC2010) Monographs - Excipients |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
|
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8339 |
(GCM2010) General Chapters - Microbiology | |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8339 |
(GCM2010) General Chapters - Microbiology |
USP35–NF30 Page 1689
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 34(1) Page 126