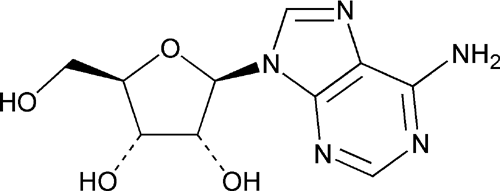
Adenosine
» Adenosine contains not less than 99.0 percent and not more than 101.0 percent of C10H13N5O4, calculated on the dried basis.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in tight, light-resistant containers, and store at controlled room temperature.
USP Reference standards  11
11 —
—
USP Adenosine RS.
USP Adenosine RS.
Identification, Infrared Absorption  197M
197M .
.
Specific rotation  781S
781S :
between
:
between 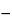 68.0
68.0 and
and 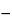 72.0
72.0 .
.
Test solution:
20 mg per mL in sodium hydroxide solution (1 in 20), determined on a test specimen previously dried at 105 for 2 hours.
for 2 hours.
Acidity or alkalinity—
Suspend 1 g in 20 mL of carbon dioxide-free water. Stir for 30 seconds, and pass through a coarse filter. To each of two 10-mL portions of the filtrate add 0.1 mL of bromocresol purple TS. Not more than 0.3 mL of 0.01 N sodium hydroxide is required to produce a blue-violet color in one portion, and not more than 0.1 mL of 0.01 N hydrochloric acid is required to produce a yellow color in the other portion.
Loss on drying  731
731 —
Dry it at 105
—
Dry it at 105 for 2 hours: it loses not more than 0.5% of its weight.
for 2 hours: it loses not more than 0.5% of its weight.
Residue on ignition  281
281 :
not more than 0.1%.
:
not more than 0.1%.
Heavy metals, Method II  231
231 :
0.001%.
:
0.001%.
Limit of ammonia—
Suspend 0.5 g in 10 mL of water. Stir for 30 seconds, and pass through a coarse filter. Dilute the filtrate with water to 15 mL, mix, and use the filtrate as the test solution. Dilute 1 mL of ammonium chloride solution (314 mg in 1000 mL) with 100 mL of water. Mix 2 mL of this ammonia standard solution with 13 mL of water, and use this as the reference solution. To the test solution and the reference solution add 0.3 mL of alkaline mercuric-potassium iodide TS, cap the test tubes, and allow to stand for about 5 minutes: the test solution does not exhibit a more intense yellow color than that of the reference solution (not more than 0.0004% ammonia).
Limit of chloride—
Suspend 0.2 g in 10 mL of water. Stir for 30 seconds, pass through a coarse filter, and use the filtrate as the test solution. Prepare a chloride standard solution by diluting 1 mL of sodium chloride solution (231 mg in 1000 mL) with 100 mL of water. To the test solution and 10 mL of the chloride standard solution add 1 mL of nitric acid and 1 mL of silver nitrate TS, dilute each solution with water to 40 mL, and mix. Allow the solutions to stand for 5 minutes, protected from light. When viewed against a dark background, the test solution is not more turbid than the standard solution (not more than 0.007% chloride).
Limit of sulfate—
Suspend 0.75 g in 15 mL of water. Stir for 30 seconds, pass through a coarse filter, and use the filtrate as the test solution. Prepare a sulfate standard solution by adding 0.15 mL of 0.020 N sulfuric acid to 15 mL of water. To the test solution and the standard solution add 2 mL of barium chloride TS and 1 mL of 3 N hydrochloric acid, dilute each solution with water to 30 mL, and mix. Allow the solutions to stand for 5 minutes: the test solution is not more turbid than the standard solution (not more than 0.02% sulfate).
Chromatographic purity—
Sulfate buffer—
Dissolve 6.8 g of potassium hydrogen sulfate and 3.4 g of tetrabutylammonium hydrogen sulfate in water, dilute with water to 1000 mL, and mix. Adjust with 2 N potassium hydroxide to a pH of 6.5.
Mobile phase—
Prepare a filtered and degassed mixture of Sulfate buffer and a solution (1 in 10,000) of sodium azide (60:40). Make adjustments if necessary (see System Suitability under Chromatography  621
621 ).
).
System suitability solution—
Transfer about 20 mg of Adenosine and 20 mg of inosine, each accurately weighed, to a 100-mL volumetric flask. Dissolve in and dilute with Mobile phase to volume, and mix.
Test solution—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of Adenosine in Mobile phase, and dilute with Mobile phase to obtain a solution having a concentration of about 1 mg per mL.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 254-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 25-cm column that contains 5-µm packing L1. The flow rate is about 1.5 mL per minute. Chromatograph the System suitability solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the resolution, R, between adenosine and inosine is not less than 9.0; the tailing factor is not more than 2.5; and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 2.0%. Chromatograph the Test solution, and adjust the run time to at least twice the retention time of the major peak.
)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 254-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 25-cm column that contains 5-µm packing L1. The flow rate is about 1.5 mL per minute. Chromatograph the System suitability solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the resolution, R, between adenosine and inosine is not less than 9.0; the tailing factor is not more than 2.5; and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 2.0%. Chromatograph the Test solution, and adjust the run time to at least twice the retention time of the major peak.
Procedure—
Inject a volume (about 20 µL) of the Test solution into the chromatograph, record the chromatogram, and measure the peak responses. Determine the percentage of each impurity in the portion of Adenosine taken: not more than 0.1% each of guanosine, inosine, and uridine is found; not more than 0.2% of adenine is found; and not more than 0.5% of total impurities is found.
Assay—
Dissolve about 200 mg of Adenosine, previously dried at 105 for 2 hours and accurately weighed, in 50 mL of glacial acetic acid. Titrate with 0.1 N perchloric acid VS, determining the endpoint potentiometrically. Perform a blank determination, and make any necessary correction. Each mL of 0.1 N perchloric acid is equivalent to 26.72 mg of C10H13N5O4.
for 2 hours and accurately weighed, in 50 mL of glacial acetic acid. Titrate with 0.1 N perchloric acid VS, determining the endpoint potentiometrically. Perform a blank determination, and make any necessary correction. Each mL of 0.1 N perchloric acid is equivalent to 26.72 mg of C10H13N5O4.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
Chromatographic Column—
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
| Monograph | Ian DeVeau, Ph.D.
Director, Veterinary Drugs and Radiopharmaceuticals 1-301-816-8178 |
(RMI05) Radiopharmaceuticals and Medical Imaging Agents 05 |
| Reference Standards | Lili Wang, Technical Services Scientist 1-301-816-8129 RSTech@usp.org |
USP32–NF27 Page 1432
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 29(6) Page 1834
Chromatographic columns text is not derived from, and not part of, USP 32 or NF 27.