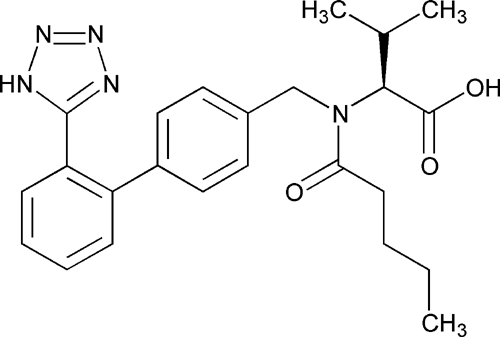
Valsartan
» Valsartan contains not less than 98.0 percent and not more than 102.0 percent of C24H29N5O3, calculated on the anhydrous basis.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in tight containers, and store at 25 , excursions permitted between 15
, excursions permitted between 15 and 30
and 30 . Protect from moisture and heat.
. Protect from moisture and heat.
USP Reference standards  11
11 —
—
USP Valsartan RS .
.
USP Valsartan Related Compound A RS .
.
USP Valsartan Related Compound B RS .
.
USP Valsartan Related Compound C RS .
.
USP Valsartan RS
 .
.
USP Valsartan Related Compound A RS
 .
.
USP Valsartan Related Compound B RS
 .
.
USP Valsartan Related Compound C RS
 .
.
Identification—
B:
The retention time of the major peak in the chromatogram of the Assay preparation corresponds to that in the chromatogram of the Standard preparation, as obtained in the Assay.
Absorbance—
Prepare a 1 in 20 solution in methanol, and determine the absorbance at 420 nm. The absorbance divided by the path length is not more than 0.02.
Water, Method I  921
921 :
not more than 2.0%.
:
not more than 2.0%.
Residue on ignition  281
281 :
not more than 0.1%.
:
not more than 0.1%.
Heavy metals, Method II  231
231 :
0.001%.
:
0.001%.
Related compounds—
test 1 (limit of valsartan related compound a)—
Mobile phase—
Prepare a mixture of n-hexane, 2-propanol, and trifluoroacetic acid (85:15:0.1). Make adjustments if necessary (see System Suitability under Chromatography  621
621 ).
).
Standard solution—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of USP Valsartan Related Compound A RS in Mobile phase, and dilute quantitatively, and stepwise if necessary, to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 0.01 mg per mL.
System suitability solution—
Dissolve accurately weighed quantities of USP Valsartan RS and USP Valsartan Related Compound A RS in Mobile phase to obtain a solution having known concentrations of about 0.04 mg per mL each of valsartan and valsartan related compound A.
Test solution—
Transfer about 50 mg of Valsartan, accurately weighed, to a 50-mL volumetric flask, add about 40 mL of Mobile phase, and sonicate for 5 minutes. Dilute with Mobile phase to volume, and mix.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 230-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 25-cm column that contains 5-µm packing L40. The flow rate is about 0.8 mL per minute. Chromatograph the System suitability solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the resolution, R, between valsartan related compound A and valsartan is not less than 2.0; and the relative standard deviation, determined from the valsartan related compound A peak, for replicate injections is not more than 5%.
)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 230-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 25-cm column that contains 5-µm packing L40. The flow rate is about 0.8 mL per minute. Chromatograph the System suitability solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the resolution, R, between valsartan related compound A and valsartan is not less than 2.0; and the relative standard deviation, determined from the valsartan related compound A peak, for replicate injections is not more than 5%.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 10 µL) of the Standard solution and the Test solution into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the areas for the major peaks. Calculate the percentage of valsartan related compound A in the portion of Valsartan taken by the formula:
100(CS / CU)(rU / rS)
in which CS is the concentration, in mg per mL, of USP Valsartan Related Compound A RS in the Standard solution; CU is the concentration, in mg per mL, of valsartan in the Test solution; and rU and rS are the peak responses for valsartan related compound A obtained from the Test solution and Standard solution, respectively: not more than 1.0% is found.
test 2 (limit of valsartan related compound b, valsartan related compound c, and other related compounds)—
Mobile phase—
Proceed as directed in the Assay.
Standard solution—
Dissolve accurately weighed quantities of USP Valsartan RS, USP Valsartan Related Compound B RS, and USP Valsartan Related Compound C RS in Mobile phase, and dilute quantitatively, and stepwise if necessary, with Mobile phase to obtain a solution having known concentrations of about 0.001 mg of valsartan per mL, 0.001 mg of valsartan related compound B per mL, and 0.001 mg of valsartan related compound C per mL.
Test solution—
Transfer about 50 mg of Valsartan, accurately weighed, to a 100-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in and dilute with Mobile phase to volume, and mix.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
Prepare as directed in the Assay, except to use a 225-nm detector. Chromatograph the Standard solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the resolution, R, between valsartan related compound B and valsartan is not less than 1.8; the relative standard deviation, determined from the valsartan related compound B peaks, for replicate injections is not more than 10.0%; and the relative standard deviation, determined from the valsartan peaks, for replicate injections is not more than 2.0%.
)—
Prepare as directed in the Assay, except to use a 225-nm detector. Chromatograph the Standard solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the resolution, R, between valsartan related compound B and valsartan is not less than 1.8; the relative standard deviation, determined from the valsartan related compound B peaks, for replicate injections is not more than 10.0%; and the relative standard deviation, determined from the valsartan peaks, for replicate injections is not more than 2.0%.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 10 µL) of the Standard solution and the Test solution into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the areas for the major peaks. Calculate the percentage of valsartan related compound B and valsartan related compound C in the portion of Valsartan taken by the formula:
100(CS / CU)(ri / rS)
in which CS is the concentration, in mg per mL, of the appropriate USP Valsartan Related Compound RS in the Standard solution; CU is the concentration, in mg per mL, of valsartan in the Test solution; ri is the peak response for the impurity obtained from the Test solution; and rS is the peak response for the appropriate valsartan related compound obtained from the Standard solution. Calculate the percentage of each other impurity in the portion of Valsartan taken by the same formula, in which CS is the concentration, in mg per mL, of USP Valsartan RS in the Standard solution; rS is the peak response for valsartan obtained from the Standard solution; and the other terms are as defined above: not more than 0.2% of valsartan related compound B is found; not more than 0.1% of valsartan related compound C is found; not more than 0.1% of any other individual impurity, excluding valsartan related compound A, is found; and not more than 0.3% of total impurities, excluding valsartan related compound A, is found.
Assay—
Mobile phase—
Prepare a filtered and degassed mixture of water, acetonitrile, and glacial acetic acid (500:500:1). Make adjustments if necessary (see System Suitability under Chromatography  621
621 ).
).
Standard preparation—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of USP Valsartan RS in Mobile phase, and dilute quantitatively, and stepwise if necessary, with Mobile phase to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 0.5 mg per mL.
Assay preparation—
Transfer about 50 mg of Valsartan, accurately weighed, to a 100-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in and dilute with Mobile phase to volume, and mix.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 273-nm detector and a 3.0-mm × 12.5-cm column that contains 5-µm packing L1. The flow rate is about 0.4 mL per minute. Chromatograph the Standard preparation, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 2.0%.
)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 273-nm detector and a 3.0-mm × 12.5-cm column that contains 5-µm packing L1. The flow rate is about 0.4 mL per minute. Chromatograph the Standard preparation, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 2.0%.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 10 µL) of the Standard preparation and the Assay preparation into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the areas for the major peaks. Calculate the quantity, in mg, of C24H29N5O3 in the portion of Valsartan taken by the formula:
100C(rU / rS)
in which C is the concentration, in mg per mL, of USP Valsartan RS in the Standard preparation; and rU and rS are the peak responses obtained from the Assay preparation and the Standard preparation, respectively.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
Chromatographic Column—
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
| Monograph | Sujatha Ramakrishna, Ph.D.
Scientist 1-301-816-8349 |
(MDCV05) Monograph Development-Cardiovascular |
| Reference Standards | Lili Wang, Technical Services Scientist 1-301-816-8129 RSTech@usp.org |
USP32–NF27 Page 3842
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 33(3) Page 467
Chromatographic columns text is not derived from, and not part of, USP 32 or NF 27.