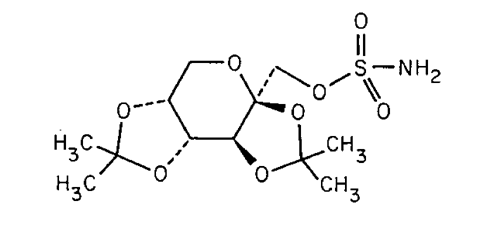
Topiramate
2,3:4,5-Di-O-isopropylidene-
» Topiramate contains not less than 98.0 percent and not more than 102.0 percent of C12H21NO8S, calculated on the anhydrous basis.
Caution—Great care must be exercised in handling Topiramate because it is a suspected teratogen.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in tight, light-resistant containers, and store at controlled room temperature.
Labeling—
If a test for Related compounds by HPLC other than Test 1 is used, then the labeling states the test with which the article complies. The label also states that it is a suspected teratogen.
USP Reference standards  11
11 —
—
USP Fructose RS .
.
USP Topiramate RS .
.
USP Topiramate Related Compound A RS .
.
USP Fructose RS
 .
.
USP Topiramate RS
 .
. USP Topiramate Related Compound A RS
 .
.
Identification—
B:
The retention time of the major peak in the chromatogram of the Assay preparation corresponds to that in the chromatogram of the Standard preparation, as obtained in the Assay.
Specific rotation  781S
781S :
between
:
between 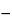 28.6
28.6 and
and 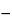 35.0
35.0 , measured at 20
, measured at 20 .
.
Test solution:
4 to 10 mg per mL, in methanol.
Water, Method I  921
921 :
not more than 0.5%.
:
not more than 0.5%.
Residue on ignition  281
281 :
not more than 0.2%.
:
not more than 0.2%.
Heavy metals, Method II  231
231 :
0.001%.
:
0.001%.
Related compounds by TLC—
[note—Perform this test only if N-methyltopiramate is a potential related compound.]
Adsorbent:
0.20-mm layer of chromatographic silica gel mixture, prewashed with methanol and air-dried.
Test solution—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of Topiramate in methanol to obtain a solution containing approximately 40 mg per mL.
Identification solution—
Dissolve a weighed quantity of USP Topiramate Related Compound A RS in methanol to obtain a solution containing about 0.2 mg per mL.
Standard solution A—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of USP Topiramate RS in methanol to obtain a final solution having a known concentration of about 40 mg per mL of topiramate.
Standard solution B—
Quantitatively dilute Standard solution A with methanol to obtain a solution containing 0.08 mg per mL of topiramate.
Standard solution C—
Quantitatively dilute Standard solution A with methanol to obtain a solution containing 0.04 mg per mL of topiramate.
Spray reagent—
Prepare a 30 mg per mL solution of phenol in a mixture of alcohol and concentrated sulphuric acid (95:5, v/v).
Application volume:
20 µL.
Developing solvent system—
Prepare a mixture of 0.5 M sodium chloride, acetonitrile, and methanol (50:35:15).
Procedure—
Proceed as directed for Thin-Layer Chromatography under Chromatography  621
621 . After elution, air-dry the plate, spray the plate with the Spray reagent, and let the plate air-dry. Then dry the plate for 10 minutes in an oven at 125
. After elution, air-dry the plate, spray the plate with the Spray reagent, and let the plate air-dry. Then dry the plate for 10 minutes in an oven at 125 . Examine the plate using visible light, and estimate the percentage of all secondary spots observed in the chromatogram of the Test solution by comparing each spot with the principal spot obtained from the chromatograms of the Standard solutions. [note—Appoximate RF values for topiramate and topiramate related compound A are 0.65 and 0.70, respectively. Disregard any spots observed at the origins of the chromatograms. Disregard any spot corresponding to topiramate related compound A because this impurity should be quantified using the test for Related compounds by HPLC. ]: any single spot is not greater in size and intensity than the spot for Standard solution C; not more than 0.1% of any individual impurity is found; and not more than 0.5% of total impurities by TLC is found.
. Examine the plate using visible light, and estimate the percentage of all secondary spots observed in the chromatogram of the Test solution by comparing each spot with the principal spot obtained from the chromatograms of the Standard solutions. [note—Appoximate RF values for topiramate and topiramate related compound A are 0.65 and 0.70, respectively. Disregard any spots observed at the origins of the chromatograms. Disregard any spot corresponding to topiramate related compound A because this impurity should be quantified using the test for Related compounds by HPLC. ]: any single spot is not greater in size and intensity than the spot for Standard solution C; not more than 0.1% of any individual impurity is found; and not more than 0.5% of total impurities by TLC is found.
Related compounds by HPLC—
[note—On the basis of the synthetic route, perform either Test 1 or Test 2. Test 2 is recommended if N-methyltopiramate is a potential related compound.]
test 1—
Mobile phase—
Proceed as directed in the Assay.
note—Prepare all solutions fresh before use.
Test solution—
Transfer about 1 g of Topiramate, accurately weighed, to a 25-mL volumetric flask, and dissolve in Mobile phase with the aid of sonication. Cool to room temperature, dilute with Mobile phase to volume, and mix.
System suitability solution—
Transfer about 3 mg each of USP Fructose RS and USP Topiramate Related Compound A RS, accurately weighed, to a 10-mL volumetric flask. Dissolve in and dilute with Test solution to volume, and mix.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a refractive index detector and a 4.6-mm × 25-cm column that contains packing L1. The column and the detector temperatures are maintained at 55
)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a refractive index detector and a 4.6-mm × 25-cm column that contains packing L1. The column and the detector temperatures are maintained at 55 . The flow rate is about 0.6 mL per minute. Chromatograph the System suitability solution, and record the peak areas as directed for Procedure: the relative retention times are about 0.45 for fructose, 0.9 for topiramate related compound A, and 1.0 for topiramate; the resolution, R, between topiramate related compound A and topiramate is not less than 1.0; and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 2.0% for the topiramate peak.
. The flow rate is about 0.6 mL per minute. Chromatograph the System suitability solution, and record the peak areas as directed for Procedure: the relative retention times are about 0.45 for fructose, 0.9 for topiramate related compound A, and 1.0 for topiramate; the resolution, R, between topiramate related compound A and topiramate is not less than 1.0; and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 2.0% for the topiramate peak.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 50 µL) of the Test solution and the Mobile phase into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure all of the peak areas. Record the chromatogram for a period of time equivalent to not less than five times the retention time of the topiramate peak. Calculate the percentage of each of the impurities in the portion of Topiramate taken by the formula:
100(1/F)(rU / rs)
in which F is the relative response factor and is equal to 1.2 for topiramate related compound A and 1.0 for all the other peaks; rU is the area of any impurity peak; and rs is the sum of the areas of all of the impurity peaks and the topiramate peak. Not more than 0.3% of fructose is found; not more than 0.3% of topiramate related compound A is found; not more than 0.1% of any other individual impurity is found; and not more than 0.5% of total impurities detected by Test 1 is found.
test 2—
Mobile phase—
Prepare a mixture of water and methanol (68:32). Make adjustments if necessary (see System Suitability under Chromatography  621
621 ).
).
Standard solution—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of USP Topiramate RS and USP Topiramate Related Compound A RS in Mobile phase, and dilute quantitatively, and stepwise if necessary, to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 10 mg of topiramate and 0.04 mg of topiramate related compound A per mL.
Test solution—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of Topiramate in Mobile phase, and dilute quantitatively, and stepwise if necessary, to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 10 mg per mL.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a refractive index detector and a 4.6-mm × 15-cm column that contains 5-µm packing L15. The column temperature is maintained at 35
)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a refractive index detector and a 4.6-mm × 15-cm column that contains 5-µm packing L15. The column temperature is maintained at 35 . The flow rate is about 1.5 mL per minute. Chromatograph the Standard solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the resolution, R, between topiramate and topiramate related compound A is not less than 1.0; and the relative standard deviation for six replicate injections is not more than 2.0% for topiramate.
. The flow rate is about 1.5 mL per minute. Chromatograph the Standard solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the resolution, R, between topiramate and topiramate related compound A is not less than 1.0; and the relative standard deviation for six replicate injections is not more than 2.0% for topiramate.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 50 µL) of the Standard solution and the Test solution into the chromatograph, and measure the responses for all of the peaks. Calculate the percentage of each impurity in the portion of Topiramate taken by the formula:
100(1/F)(CS /CU)(ri / rS)
in which F is the relative response factor, which has a value of 1.1 for topiramate related compound A and 1.0 for all other impurities; CS and CU are the concentrations of topiramate in the Standard solution and the Test solution, respectively; ri is the peak response for each impurity in the Test solution; and rS is the peak response of topiramate in the Standard solution: not more than 0.3% of topiramate related compound A is found; not more than 0.10% of any other individual impurity is found; and not more than 0.5% of total impurities detected by Test 2 is found.
Limit of sulfamate and sulfate—
[note—Use Purified Water (resistivity not less than 18 megohm-cm) for Mobile phase and all solution preparations.]
Diluent—
Prepare a mixture of Purified Water and acetonitrile (80:20).
Solution A—
Transfer about 4 g of sodium hydroxide to a 1000-mL volumetric flask. Dissolve in and dilute with water (see Reagents in Chemical Resistance under Containers—Glass  660
660 ) to volume, filter, and degas.
) to volume, filter, and degas.
Solution B—
Use filtered and degassed water.
Solution C—
Dilute 50 mL of Solution A with water to 100 mL, filter, and degas.
Mobile phase—
Use variable mixtures of Solution A, Solution B, and Solution C as directed for Chromatographic system. Make adjustments if necessary (see System Suitability under Chromatography  621
621 ).
).
Sulfamic acid stock solution—
Transfer about 60 mg, accurately weighed, of sulfamic acid to a 100-mL volumetric flask. Dissolve in and dilute with Diluent to volume.
Sulfate stock solution—
Transfer about 90.7 mg, accurately weighed, of potassium sulfate to a 100-mL volumetric flask. Dissolve in and dilute with Diluent to volume.
Standard solution—
Transfer 3.0 mL each of Sulfamic acid stock solution and Sulfate stock solution to a 50-mL volumetric flask, dilute with Diluent to volume, and mix.
Test solution—
Transfer about 100 mg, accurately weighed, of Topiramate to a 10-mL volumetric flask. Dissolve in and dilute with Diluent to volume.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a conductivity detector, a 4.0-mm × 5-cm guard column that contains packing L46 and a 4.0-mm × 25-cm column that contains packing L46. The flow rate is about 2.0 mL per minute. The chromatograph is programmed as follows.
)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a conductivity detector, a 4.0-mm × 5-cm guard column that contains packing L46 and a 4.0-mm × 25-cm column that contains packing L46. The flow rate is about 2.0 mL per minute. The chromatograph is programmed as follows.
Chromatograph the Standard solution, and record the peak areas as directed for Procedure: the relative retention time is 1.0 for the sulfate peak and about 0.27 for the sulfamate peak; and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 2.0% for both the sulfate and sulfamate peaks.
| Time (minutes) |
Solution
A (%) |
Solution
B (%) |
Solution
C (%) |
|
| 0 | 0 | 95 | 5 | equilibration |
| 0–7.0 | 0 | 95 | 5 | isocratic |
| 7.0–15.0 | 0®20 | 95®0 | 5®80 | linear gradient |
| 15.0–20.0 | 20 | 0 | 80 | isocratic |
| 20.0–20.1 | 20®0 | 0®95 | 80®5 | linear gradient |
| 20.1–25.0 | 0 | 95 | 5 | re-equilibration |
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 20 µL) of the Standard solution and the Test solution into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the peak areas for the sulfate and sulfamate peaks. Calculate the percentage of sulfate in the portion of Topiramate taken by the formula:
1000(96.06/174.25)(C/W)(ri / rS)
in which 96.06 and 174.25 are the molecular weights of the sulfate ion and potassium sulfate, respectively; C is the concentration, in mg per mL, of potassium sulfate in the Standard solution; W is the weight, in mg, of Topiramate taken; and ri and rS are the peak areas of the sulfate ion obtained from the Test solution and the Standard solution, respectively: not more than 0.10% of sulfate ion is found. Calculate the percentage of sulfamate in the portion of Topiramate taken by the formula:
1000(96.08/97.09)(C/W)(ri / rS)
in which 96.08 and 97.09 are the molecular weights of sulfamate ion and sulfamic acid, respectively; C is the concentration, in mg per mL, of sulfamic acid in the Standard solution; W is the weight, in mg, of Topiramate taken; and ri and rS are the peak areas of the sulfamate ion obtained from the Test solution and the Standard solution, respectively: not more than 0.10% of sulfamate ion is found.
Assay—
Mobile phase—
Prepare a filtered and degassed mixture of acetonitrile and water (1:1). Make adjustments if necessary (see System Suitability under Chromatography  621
621 ).
).
Standard preparation—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of USP Topiramate RS in Mobile phase, and dilute quantitatively, and stepwise if necessary, with Mobile phase to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 2.0 mg per mL.
Assay preparation—
Transfer about 50 mg of Topiramate, accurately weighed, to a 25-mL volumetric flask, and dissolve in and dilute with Mobile phase to volume.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a refractive index detector and a 4.6-mm × 25-cm column that contains 5-µm packing L1. The flow rate is about 0.6 mL per minute. The detector and column temperatures are maintained at 50
)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a refractive index detector and a 4.6-mm × 25-cm column that contains 5-µm packing L1. The flow rate is about 0.6 mL per minute. The detector and column temperatures are maintained at 50 . Chromatograph the Standard preparation, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the column efficiency is not less than 1500 theoretical plates; the tailing factor is not more than 2.0; and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 2.0%.
. Chromatograph the Standard preparation, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the column efficiency is not less than 1500 theoretical plates; the tailing factor is not more than 2.0; and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 2.0%.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 20 µL) of the Standard preparation and the Assay preparation into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the responses for the major peaks. Calculate the quantity, in percentage, of C12H21NO8S in the portion of Topiramate taken by the formula:
100(CS / CU)(rU / rS)
in which CS is the concentration, in mg per mL, of USP Topiramate RS in the Standard preparation; CU is the concentration, in mg per mL, of Topiramate in the Assay preparation; and rU and rS are the peak areas for topiramate obtained from the Assay preparation and the Standard preparation, respectively.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
Chromatographic Column—
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
| Monograph | Ravi Ravichandran, Ph.D.
Senior Scientist 1-301-816-8330 |
(MDPP05) Monograph Development-Psychiatrics and Psychoactives |
| Reference Standards | Lili Wang, Technical Services Scientist 1-301-816-8129 RSTech@usp.org |
USP32–NF27 Page 3773
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 33(3) Page 461
Chromatographic columns text is not derived from, and not part of, USP 32 or NF 27.