Sodium Phosphates Rectal Solution
» Sodium Phosphates Rectal Solution is a solution of Dibasic Sodium Phosphate and Monobasic Sodium Phosphate, or Dibasic Sodium Phosphate and Phosphoric Acid, in Purified Water. It contains, in each 100 mL, not less than 5.4 g and not more than 6.6 g of dibasic sodium phosphate (Na2HPO4·7H2O), and not less than 14.4 g and not more than 17.6 g of monobasic sodium phosphate (NaH2PO4·H2O).
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in tight, single-unit containers, at controlled room temperature.
Specific gravity  841
841 :
between 1.112 and 1.136.
:
between 1.112 and 1.136.
pH  791
791 :
between 5.0 and 5.8.
:
between 5.0 and 5.8.
Assay—
Pipet 5.0 mL of Rectal Solution into a 250-mL beaker, and add 15.0 mL of 0.5 N sodium hydroxide VS and 95 mL of water. Titrate the excess base potentiometrically with 0.5 N hydrochloric acid VS to the first inflection point, at a pH of about 9.2. Record the volume, A, in mL, of 0.5 N hydrochloric acid consumed. Continue the titration to the second inflection point, at a pH of about 4.4, and record the total volume, B, in mL, of 0.5 N hydrochloric acid required in the titration. For a blank determination, transfer 15.0 mL of 0.5 N sodium hydroxide into a 250-mL beaker, add 100 mL of water, and immediately titrate potentiometrically with 0.5 N hydrochloric acid VS. Record the volume, C, in mL, of 0.5 N hydrochloric acid consumed. Each mL of the volume (C 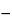 A) of 0.5 N hydrochloric acid is equivalent to 69.0 mg of monobasic sodium phosphate (NaH2PO4·H2O). Each mL of the volume (B
A) of 0.5 N hydrochloric acid is equivalent to 69.0 mg of monobasic sodium phosphate (NaH2PO4·H2O). Each mL of the volume (B 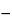 C) of 0.5 N hydrochloric acid is equivalent to 134.0 mg of dibasic sodium phosphate (Na2HPO4·7H2O).
C) of 0.5 N hydrochloric acid is equivalent to 134.0 mg of dibasic sodium phosphate (Na2HPO4·7H2O).
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
| Monograph | Elena Gonikberg, Ph.D.
Senior Scientist 1-301-816-8251 |
(MDGRE05) Monograph Development-Gastrointestinal Renal and Endocrine |
USP32–NF27 Page 3583
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 31(5) Page 1403