Rubidium Chloride Rb 82 Injection
» Rubidium Chloride Rb 82 Injection is a sterile solution, suitable for intravenous administration. It contains not less than 90.0 percent and not more than 110.0 percent of the labeled amount of 82Rb expressed in megabecquerels (or in millicuries) per mL at the time indicated in the labeling. It is obtained by elution from a strontium 82-rubidium 82 generator system. 82Rb, with a half-life of 76 seconds, is a short-lived positron-emitting radionuclide formed by the radioactive decay of the parent nuclide 82Sr. Strontium Sr 82 with a half-life of 25.5 days is produced by the proton irradiation of rubidium or spallation of molybdenum. The chemical form of the Injection is 82RbCl. [note—Elute with additive-free Sodium Chloride Injection only. Discard the first 50 mL of the eluate each day the generator is eluted.]
Packaging, storage, and labeling—
Requirements for packaging, storage, and labeling do not apply; Rubidium Chloride Rb 82 Injection is obtained by elution from the generator and is administered by direct infusion.
Bacterial endotoxins  85
85 —
It contains not more than 175/V USP Endotoxin Unit per mL of the Injection, when compared with the USP Endotoxin RS, in which V is the maximum recommended total dose, in mL, at the expiration date or time.
—
It contains not more than 175/V USP Endotoxin Unit per mL of the Injection, when compared with the USP Endotoxin RS, in which V is the maximum recommended total dose, in mL, at the expiration date or time.
Radionuclide identification (see Radioactivity  821
821 )—
[note—Perform this test quickly, because of the rapid decay of the 82Rb.] The gamma-ray spectrum of eluted 82Rb exhibits photopeaks at 511 and 777 keV.
)—
[note—Perform this test quickly, because of the rapid decay of the 82Rb.] The gamma-ray spectrum of eluted 82Rb exhibits photopeaks at 511 and 777 keV.
pH  791
791 :
between 4.0 and 8.0.
:
between 4.0 and 8.0.
Radionuclidic purity—
Using a suitable counting assembly (see Selection of a Counting Assembly under Radioactivity  821
821 ), determine the radioactivity of each radionuclidic impurity, in kBq per MBq (or µCi per mCi), of Rb 82 in the generator eluate by use of a calibrated system as directed under Radioactivity
), determine the radioactivity of each radionuclidic impurity, in kBq per MBq (or µCi per mCi), of Rb 82 in the generator eluate by use of a calibrated system as directed under Radioactivity  821
821 . [note—For the following tests, use the generator eluate containing 82Rb that has been allowed to decay for 1 hour after the end of elution.]
. [note—For the following tests, use the generator eluate containing 82Rb that has been allowed to decay for 1 hour after the end of elution.]
Sr 82 and Rb 83—
Obtain a gamma-ray spectrum of the hour-old eluate, and measure the activities of the radionuclidic impurities directly from the spectrum. Sr 82 exhibits photopeaks at 511 and 777 keV and decays with a radioactive half-life of 25.5 days. Rb 83 exhibits a photopeak at 530 keV and decays with a radioactive half-life of 86.2 days. The activity levels of Sr 82 and Rb 83 are not more than 0.02 kBq per MBq (0.02 µCi per mCi) and not more than 0.05 kBq per MBq (0.05 µCi per mCi) of Rb 82 at the end of elution, respectively.
Sr 85—
Obtain a gamma spectrum of the hour-old eluate, and, using the same system and geometry, obtain a gamma spectrum of a pure Rb 82 specimen (generator eluate containing 82Rb taken within 10 minutes of elution). Sr 85 exhibits a major photopeak at 514 keV and decays with a radioactive half-life of 64.8 days. Sr 85 may be determined by subtraction of the 511 and 777 keV peaks in the pure Rb 82, from the 511–514 keV and 777 keV peaks in the hour-old eluate. The activity level of Sr 85 is not more than 0.2 kBq per MBq (0.2 µCi per mCi) of Rb 82 at the end of elution.
Other gamma-ray emitters—
The total of other gamma-ray emitting radionuclidic impurities does not exceed 0.005 kBq per MBq (0.005 µCi per mCi) of Rb 82 at the end of elution.
Chemical purity—
Electrolyte solution—
Transfer 107 g of ammonium chloride, 25 g of gelatin, and 42 mL of hydrochloric acid to a 500-mL volumetric flask. Add about 450 mL of water, and sonicate until a clear solution is obtained. Dilute with water to volume, and mix.
Tin stock standard solution—
Dissolve 100 mg of metallic tin (Sn), accurately weighed, in 10 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid (1 in 2), and dilute with water to 100 mL.
Tin standard solution A—
Transfer 0.5 mL of Tin stock standard solution to a 50-mL volumetric flask and dilute with 0.1 N hydrochloric acid to volume.
Tin standard solution B—
Transfer 1.0 mL of Tin standard solution A to a 50-mL volumetric flask. Add 10.0 mL of 0.9% sodium chloride solution, dilute with Electrolyte solution to volume, and mix.
Test solution—
Obtain a 50-mL eluate from the generator, and allow to stand for at least 1 hour to allow for the complete decay of 82Rb. Transfer 10.0 mL of the eluate to a 50-mL volumetric flask, dilute with the Electrolyte solution to volume, and mix.
Procedure—
Transfer a portion of the Test solution to a polarographic cell, and deaerate by bubbling nitrogen through the solution for 5 minutes. Insert the dropping mercury electrode of a suitable polarograph, and obtain the differential pulse polarogram from 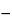 0.15 to
0.15 to 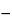 0.75 volts, at a current range of 0.5 µA, using a saturated calomel electrode as the reference electrode and a platinum wire as the auxiliary electrode (see Polarography
0.75 volts, at a current range of 0.5 µA, using a saturated calomel electrode as the reference electrode and a platinum wire as the auxiliary electrode (see Polarography  801
801 ). Similarly, transfer a portion of the Tin standard solution to a polarographic cell and obtain the polarogram. A peak at
). Similarly, transfer a portion of the Tin standard solution to a polarographic cell and obtain the polarogram. A peak at 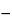 0.52 volts indicates the presence of tin. The peak height of the Test solution is not greater than that of the Tin standard solution (1 µg per mL).
0.52 volts indicates the presence of tin. The peak height of the Test solution is not greater than that of the Tin standard solution (1 µg per mL).
Other requirements—
It meets the requirements under Injections  1
1 , except that the Injection may be distributed or dispensed prior to completion of the test for Sterility, the latter test being started on the day of final manufacture, and except that it is not subject to the recommendation for Volume in Container under Injections
, except that the Injection may be distributed or dispensed prior to completion of the test for Sterility, the latter test being started on the day of final manufacture, and except that it is not subject to the recommendation for Volume in Container under Injections  1
1 .
.
Assay for radioactivity—
Using a suitable counting assembly (see Selection of a Counting Assembly under Radioactivity  821
821 ), determine the radioactivity, in MBq (or in µCi) per mL, of the Injection by use of a calibrated system as directed under Radioactivity
), determine the radioactivity, in MBq (or in µCi) per mL, of the Injection by use of a calibrated system as directed under Radioactivity  821
821 .
.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
| Monograph | Ian DeVeau, Ph.D.
Director, Veterinary Drugs and Radiopharmaceuticals 1-301-816-8178 |
(RMI05) Radiopharmaceuticals and Medical Imaging Agents 05 |
| Reference Standards | Lili Wang, Technical Services Scientist 1-301-816-8129 RSTech@usp.org |
|
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Senior Scientist 1-301-816-8339 |
(MSA05) Microbiology and Sterility Assurance |
USP32–NF27 Page 3526