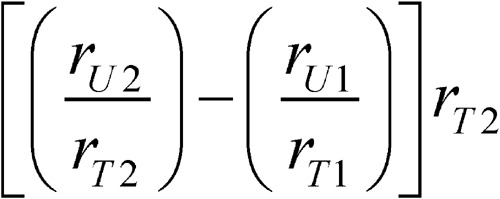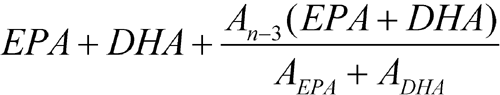Fish Oil Containing Omega-3 Acids
» Fish Oil Containing Omega-3 Acids is the purified, winterized, and deodorized fatty oil obtained from fish of the families Engraulidae, Carangidae, Clupeidae, Osmeridae, Scombroidae, and Ammodytidae. The omega-3 acids are defined as the following: alpha-linolenic acid (C18:3 n-3), moroctic acid (C18:4 n-3), eicosatetraenoic acid (C20:4 n-3), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) (C20:5 n-3), heneicosapentaenoic acid (C21:5 n-3), docosapentaenoic acid (C22:5 n-3), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) (C22:6 n-3). It contains not less than 28.0 percent (w/w) of total omega-3 acids, expressed as free acids, consisting of not less than 13.0 percent of EPA and not less than 9.0 percent of DHA. Suitable antioxidants in appropriate concentrations may be added.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in tight, light-resistant containers, and store at controlled room temperature. It may be bottled or otherwise packaged in containers from which air has been expelled by production of a vacuum or by an inert gas.
Labeling—
The label states the average content of DHA and EPA in mg per g. It also states the name and concentration of any added antioxidant.
USP Reference standards  11
11 —
—
USP Docosahexaenoic Acid Ethyl Ester RS.
USP Eicosapentaenoic Acid Ethyl Ester RS.
USP Fish Oil RS.
USP Methyl Tricosanoate RS.
USP Docosahexaenoic Acid Ethyl Ester RS.
USP Eicosapentaenoic Acid Ethyl Ester RS.
USP Fish Oil RS.
USP Methyl Tricosanoate RS.
Identification—
The retention times of the peaks for eicosapentaenoic acid methyl ester and docosahexaenoic acid methyl ester obtained in the chromatogram of Test solution 2 in the test for Content of EPA and DHA correspond to those for the respective compounds in the chromatogram of the Standard solution 1. The sum of the area for EPA and DHA methyl esters is not less than 22% of the total detected area for the methyl esters, and no other peak in the chromatogram has an area higher than 20% of the total detected area for the methyl esters. The chromatogram of Test solution 2 exhibits at least 15 additional peaks at the retention times of the methyl esters of unsaturated fatty acids exhibited in the chromatogram of Standard solution 2.
Acid value  401
401 :
not more than 3.
:
not more than 3.
Anisidine value  401
401 :
not more than 20.0.
:
not more than 20.0.
Peroxide value  401
401 :
not more than 5.0.
:
not more than 5.0.
Total oxidation value (TOTOX)  401
401 :
not more than 26, calculated by the formula:
:
not more than 26, calculated by the formula:
(2 × PV) + AV
in which PV is the Peroxide value, and AV is the Anisidine value.
Unsaponifiable matter  401
401 :
not more than 1.5%.
:
not more than 1.5%.
Stearin:
10 mL remains clear after cooling at 0 for 3 hours.
for 3 hours.
Absorbance—
Dilute 0.300 g to 50.0 mL with isooctane. Quantitatively transfer 2.0 mL of this solution to a 50-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with isooctane to volume. The absorbance is not more than 0.70, determined at 233 nm.
Limit of arsenic—
[note—For the preparation of all aqueous solutions and for the rinsing of glass, polytef, and plastic vessels before use, employ water that has been passed through a strong-acid, strong-base, mixed-bed ion-exchange resin before use. Select all reagents to have as low a content of arsenic as practicable, and store all reagent solutions in containers of borosilicate glass. Cleanse glass, polytef, and plastic vessels before use by soaking in warm 8 N nitric acid for 30 minutes and by rinsing with deionized water.]
1% Palladium stock solution—
Transfer 1 g of ultrapure palladium metal, accurately weighed, into a Teflon beaker. Add 20 mL of water and 10 mL of nitric acid, and warm on a hot plate to dissolve. Allow the solution to cool to room temperature, transfer it into a 100-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with deionized water to volume.
1% Magnesium nitrate stock solution—
Transfer 1 g of ultrapure magnesium nitrate, accurately weighed, into a Teflon beaker. Add 40 mL of water and 1 mL of nitric acid, and warm on a hot plate to dissolve the solids. Allow the solution to cool to room temperature, transfer it into a 100-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with deionized water to volume.
Modifier working solution—
Transfer 3 mL of 1% Palladium stock solution and 2 mL of 1% Magnesium nitrate stock solution into a 10-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with 2% nitric acid to volume. A volume of 5 µL provides 0.015 mg of palladium and 0.01 mg of magnesium nitrate.
Blank—
Transfer 5 mL of nitric acid to a 100-mL volumetric flask, dilute with water to volume, and mix.
Standard stock solution—
Transfer 10.0 mL of Standard Arsenic Solution, prepared as directed in the test for Arsenic  211
211 , to a 100-mL volumetric flask, add 40 mL of water and 5 mL of nitric acid, dilute with water to volume, and mix. This solution contains 0.10 µg of arsenic per mL.
, to a 100-mL volumetric flask, add 40 mL of water and 5 mL of nitric acid, dilute with water to volume, and mix. This solution contains 0.10 µg of arsenic per mL.
Standard solutions—
Dilute the Standard stock solution with the Blank to obtain solutions containing, respectively, 0.002, 0.005, 0.010, 0.025, and 0.050 µg of arsenic per mL.
Test solution—
For preparation of the Test solution, use a microwave oven with a magnetron frequency of about 2455 MHz and a selectable output power of 0 to 950 watts in 1% increments, equipped with advanced composite vessels with 100-mL polytef liners. Use rupture membranes to vent vessels should the pressure exceed 125 psi. The vessels fit into a turntable, and each vessel can be vented into an overflow container. Equip the microwave oven with an exhaust tube to ventilate fumes. [Caution—Wear proper eye protection and protective clothing and gloves.
] Transfer approximately 500 mg of Fish Oil Containing Omega-3 Acids, accurately weighed to the nearest 0.1 mg, into a Teflon digestion vessel liner. Prepare samples in duplicate. Add 15 mL of nitric acid, and swirl gently. Cover the vessels with lids, leaving the vent fitting off. Predigest overnight under a hood. Place the rupture membrane in the vent fitting, and tighten the lid. Place all vessels on the microwave oven turntable. Connect the vent tubes to the vent trap, and connect the pressure-sensing line to the appropriate vessel. Initiate a two-stage digestion procedure by heating the microwave at 15% power for 15 minutes, followed by 25% power for 45 minutes. Remove the turntable of vessels from the oven, and allow the vessels to cool to room temperature. [note—A cool water bath may be used to speed the cooling process.] Vent the vessels when they reach room temperature. Remove the lids, and slowly add 2 mL of 30 percent hydrogen peroxide to each. Allow the reactions to subside, and seal the vessels. Return the vessels on the turntable to the microwave oven, and heat for an additional 15 minutes at 30% power. Remove the vessels from the oven, and allow them to cool to room temperature. Transfer the cooled digests into 25-mL volumetric flasks, and dilute with water to volume.
Procedure—
Program the graphite furnace as follows. Dry at 115 , using a 1-second ramp, a 65-second hold, and an argon flow of 300 mL per minute; char the sample at 1000
, using a 1-second ramp, a 65-second hold, and an argon flow of 300 mL per minute; char the sample at 1000 , using a 1-second ramp, a 20-second hold, and an airflow of 300 mL per minute; cool down, and purge the air from the furnace for 10 seconds, using a 20
, using a 1-second ramp, a 20-second hold, and an airflow of 300 mL per minute; cool down, and purge the air from the furnace for 10 seconds, using a 20 set temperature and an argon flow of 300 mL per minute; atomize at 2400
set temperature and an argon flow of 300 mL per minute; atomize at 2400 , using a 0-second ramp and a 5-second hold with the argon flow stopped; and clean out at 2600
, using a 0-second ramp and a 5-second hold with the argon flow stopped; and clean out at 2600 with a 1-second ramp and a 5-second hold. Separately inject equal volumes (about 20 µL) of the Standard solutions, the Test solution, and the Blank, followed by an injection of 5 µL of the Modifier working solution for each of the samples, into the graphite tube of a suitable graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrophotometer equipped with a hollow-cathode lamp for arsenic. Determine the peak area at the arsenic emission line at 193.7 nm, corrected for background absorption. Plot the corrected peak areas of the Standard solutions versus their contents of arsenic, in µg per mL, and calculate the regression line best fitting the points. Determine the concentration, C, in µg per mL, of arsenic in each mL of the Test solution by interpolation from the regression line. Calculate the content of arsenic in the portion of Fish Oil Containing Omega-3 Acids taken by the formula:
with a 1-second ramp and a 5-second hold. Separately inject equal volumes (about 20 µL) of the Standard solutions, the Test solution, and the Blank, followed by an injection of 5 µL of the Modifier working solution for each of the samples, into the graphite tube of a suitable graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrophotometer equipped with a hollow-cathode lamp for arsenic. Determine the peak area at the arsenic emission line at 193.7 nm, corrected for background absorption. Plot the corrected peak areas of the Standard solutions versus their contents of arsenic, in µg per mL, and calculate the regression line best fitting the points. Determine the concentration, C, in µg per mL, of arsenic in each mL of the Test solution by interpolation from the regression line. Calculate the content of arsenic in the portion of Fish Oil Containing Omega-3 Acids taken by the formula:
25C/W
in which W is the weight, in g, of Fish Oil Containing Omega-3 Acids taken to prepare the Test solution: not more than 0.1 µg per g is found.
Limit of lead—
[note—For the preparation of all aqueous solutions and for the rinsing of glass, polytef, and plastic vessels before use, employ water that has been passed through a strong-acid, strong-base, mixed-bed ion-exchange resin before use. Select all reagents to have as low a content of lead as practicable, and store all reagent solutions in containers of borosilicate glass. Cleanse glass, polytef, and plastic vessels before use by soaking in warm 8 N nitric acid for 30 minutes and by rinsing with deionized water.]
10% Monobasic ammonium phosphate stock solution—
Transfer 10 g of ultrapure monobasic ammonium phosphate, accurately weighed, to a 100-mL volumetric flask. Add 40 mL of water and 1 mL of nitric acid to dissolve the phosphate. Dilute with deionized water to 100 mL.
1% Magnesium nitrate stock solution—
Transfer 1 g of ultrapure magnesium nitrate, accurately weighed, to a Teflon beaker. Add 40 mL of water and 1 mL of nitric acid, and warm on a hot plate to dissolve the solids. Allow the solution to cool to room temperature, transfer it to a 100-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with deionized water to volume.
Modifier working solution—
Transfer 4 mL of 10% Monobasic ammonium phosphate stock solution and 2 mL of 1% Magnesium nitrate stock solution to a 10-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with 2% nitric acid to volume. A volume of 5 µL provides 0.2 mg of phosphate plus 0.01 mg of magnesium nitrate.
Blank—
Transfer 5 mL of nitric acid to a 100-mL volumetric flask, dilute with water to volume, and mix.
Standard stock solution—
Transfer 10.0 mL of Lead Nitrate Stock Solution, prepared as directed in the test for Heavy Metals  231
231 , to a 100-mL volumetric flask, add 40 mL of water and 5 mL of nitric acid, dilute with water to volume, and mix. Transfer 1.0 mL of this solution to a second 100-mL volumetric flask, add 50 mL of water and 1 mL of nitric acid, dilute with water to volume, and mix. This solution contains 0.10 µg of lead per mL.
, to a 100-mL volumetric flask, add 40 mL of water and 5 mL of nitric acid, dilute with water to volume, and mix. Transfer 1.0 mL of this solution to a second 100-mL volumetric flask, add 50 mL of water and 1 mL of nitric acid, dilute with water to volume, and mix. This solution contains 0.10 µg of lead per mL.
Standard solutions—
Dilute the Standard stock solution with the Blank to obtain solutions containing, respectively, 0.002, 0.005, 0.010, 0.025, and 0.050 µg of lead per mL.
Test solution—
Prepare as directed for Test solution in the test for Limit of arsenic.
Procedure—
Program the graphite furnace as follows. Dry at 120 , using a 1-second ramp, a 55-second hold, and an argon flow of 300 mL per minute; char the sample at 850
, using a 1-second ramp, a 55-second hold, and an argon flow of 300 mL per minute; char the sample at 850 , using a 1-second ramp, a 30-second hold, and an airflow of 300 mL per minute; cool down, and purge the air from the furnace for 10 seconds, using a 20
, using a 1-second ramp, a 30-second hold, and an airflow of 300 mL per minute; cool down, and purge the air from the furnace for 10 seconds, using a 20 set temperature and an argon flow of 300 mL per minute; atomize at 2100
set temperature and an argon flow of 300 mL per minute; atomize at 2100 , using a 0-second ramp and a 5-second hold with the argon flow stopped; and clean out at 2600
, using a 0-second ramp and a 5-second hold with the argon flow stopped; and clean out at 2600 with a 1-second ramp and a 5-second hold. Separately inject equal volumes (about 20 µL) of the Standard solutions, the Test solution, and the Blank, followed by an injection of 5 µL of the Modifier working solution for each of the samples, into the graphite tube of a suitable graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrophotometer equipped with a hollow-cathode lamp for lead. Determine the peak area at the lead emission line at 283.3 nm, corrected for background absorption. Plot the corrected peak areas of the Standard solutions versus their contents of lead, in µg per mL, and calculate the regression line best fitting the points. Determine the concentration, C, in µg per mL, of lead in each mL of the Test solution by interpolation from the regression line. Calculate the content of lead in the portion of Fish Oil Containing Omega-3 Acids taken by the formula:
with a 1-second ramp and a 5-second hold. Separately inject equal volumes (about 20 µL) of the Standard solutions, the Test solution, and the Blank, followed by an injection of 5 µL of the Modifier working solution for each of the samples, into the graphite tube of a suitable graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrophotometer equipped with a hollow-cathode lamp for lead. Determine the peak area at the lead emission line at 283.3 nm, corrected for background absorption. Plot the corrected peak areas of the Standard solutions versus their contents of lead, in µg per mL, and calculate the regression line best fitting the points. Determine the concentration, C, in µg per mL, of lead in each mL of the Test solution by interpolation from the regression line. Calculate the content of lead in the portion of Fish Oil Containing Omega-3 Acids taken by the formula:
25C/W
in which W is the weight, in g, of Fish Oil Containing Omega-3 Acids taken to prepare the Test solution: not more than 0.1 µg per g is found.
Limit of cadmium—
[note—For the preparation of all aqueous solutions and for the rinsing of glass, polytef, and plastic vessels before use, employ water that has been passed through a strong-acid, strong-base, mixed-bed ion-exchange resin before use. Select all reagents to have as low a content of cadmium as practicable, and store all reagent solutions in containers of borosilicate glass. Cleanse glass, polytef, and plastic vessels before use by soaking in warm 8 N nitric acid for 30 minutes and by rinsing with deionized water.]
10% Monobasic ammonium phosphate stock solution—
Transfer 10 g of ultrapure monobasic ammonium phosphate, accurately weighed, to a 100-mL volumetric flask. Add 40 mL of water and 1 mL of nitric acid to dissolve the phosphate. Dilute with deionized water to 100 mL.
1% Magnesium nitrate stock solution—
Transfer 1 g of ultrapure magnesium nitrate, accurately weighed, to a Teflon beaker. Add 40 mL of water and 1 mL of nitric acid, and warm on a hot plate to dissolve the solids. Allow the solution to cool to room temperature, transfer it to a 100-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with deionized water to volume.
Modifier working solution—
Transfer 4 mL of 10% Monobasic ammonium phosphate stock solution and 2 mL of 1% Magnesium nitrate stock solution to a 10-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with 2% nitric acid to volume. A volume of 5 µL provides 0.2 mg of phosphate and 0.01 mg of magnesium nitrate.
Blank—
Transfer 5 mL of nitric acid to a 100-mL volumetric flask, dilute with water to volume, and mix.
Standard stock solution—
Transfer 137.2 mg of cadmium nitrate to a 1000-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in and dilute with water to volume, and mix. Transfer 2.0 mL of this solution to a second 100-mL volumetric flask, add 50 mL of water and 1 mL of nitric acid, dilute with water to volume, and mix. This solution contains 0.10 µg of cadmium per mL.
Standard solutions—
Dilute the Standard stock solution with the Blank to obtain solutions containing, respectively, 0.002, 0.005, 0.010, 0.025, and 0.050 µg of cadmium per mL.
Test solution—
Prepare as directed for Test solution in the test for Limit of arsenic.
Procedure—
Program the graphite furnace as follows. Dry at 120 , using a 1-second ramp, a 55-second hold, and an argon flow of 300 mL per minute; char the sample at 850
, using a 1-second ramp, a 55-second hold, and an argon flow of 300 mL per minute; char the sample at 850 , using a 1-second ramp, a 30-second hold, and an airflow of 300 mL per minute; cool down, and purge the air from the furnace for 10 seconds, using a 20
, using a 1-second ramp, a 30-second hold, and an airflow of 300 mL per minute; cool down, and purge the air from the furnace for 10 seconds, using a 20 set temperature and an argon flow of 300 mL per minute; atomize at 2400
set temperature and an argon flow of 300 mL per minute; atomize at 2400 , using a 0-second ramp and a 5-second hold with the argon flow stopped; and clean out at 2600
, using a 0-second ramp and a 5-second hold with the argon flow stopped; and clean out at 2600 with a 1-second ramp and a 5-second hold. Separately inject equal volumes (about 20 µL) of the Standard solutions, the Test solution, and the Blank, followed by an injection of 5 µL of the Modifier working solution for each of the samples, into the graphite tube of a suitable graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrophotometer equipped with a hollow-cathode lamp for cadmium. Determine the peak area at the cadmium emission line at 228.8 nm, corrected for background absorption. Plot the corrected peak areas of the Standard solutions versus their contents of cadmium, in µg per mL, and calculate the regression line best fitting the points. Determine the concentration, C, in µg per mL, of cadmium in each mL of the Test solution by interpolation from the regression line. Calculate the content of cadmium in the Fish Oil Containing Omega-3 Acids taken by the formula:
with a 1-second ramp and a 5-second hold. Separately inject equal volumes (about 20 µL) of the Standard solutions, the Test solution, and the Blank, followed by an injection of 5 µL of the Modifier working solution for each of the samples, into the graphite tube of a suitable graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrophotometer equipped with a hollow-cathode lamp for cadmium. Determine the peak area at the cadmium emission line at 228.8 nm, corrected for background absorption. Plot the corrected peak areas of the Standard solutions versus their contents of cadmium, in µg per mL, and calculate the regression line best fitting the points. Determine the concentration, C, in µg per mL, of cadmium in each mL of the Test solution by interpolation from the regression line. Calculate the content of cadmium in the Fish Oil Containing Omega-3 Acids taken by the formula:
25C/W
in which W is the weight, in g, of Fish Oil Containing Omega-3 Acids taken to prepare the Test solution: not more than 0.1 µg per g is found.
Limit of mercury—
Proceed as directed for Method IIa under Mercury  261
261 , except to use a Standard Mercury Solution having the equivalent of 0.1 µg of mercury per mL.
, except to use a Standard Mercury Solution having the equivalent of 0.1 µg of mercury per mL.
Test solution—
Prepare as directed for the Test solution in the test for Limit of arsenic combining the 2 duplicate cooled digests into 1.0 mL of Potassium Permanganate Solution. The limit is 0.1 µg per g.
Limit of dioxins, furans, and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs)—
Determine the content of polychlorinated dibenzo-para-dioxins (PCDDs) and polychlorinated dibenzofurans (PCDFs) by method No. 1613 revision B of the Environmental Protection Agency. Determine the content of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) by method No. 1668 revision A of the Environmental Protection Agency. The sum of PCDDs and PCDFs is not more than 2.0 pg of WHO toxic equivalents per g. The sum of PCDDs, PCDFs, and dioxin-like PCBs (polychlorinated biphenyls, non-ortho IUPAC congeners PCB-77, PCB-81, PCB-126, and PCB-169, and mono-ortho IUPAC congeners PCB-105, PCB-114, PCB-118, PCB-123, PCB-156, PCB-157, PCB-167, and PCB-189) is not more than 10.0 pg of WHO toxic equivalents per g.
Content of EPA and DHA —
Antioxidant solution—
Dissolve an accurately weighed amount of butylated hydroxytoluene in hexanes to obtain a solution having a concentration of 0.05 mg per mL.
Internal standard solution—
Transfer an accurately weighed quantity of USP Methyl Tricosanoate RS to a volumetric flask. Dissolve in Antioxidant solution, and dilute with the same solvent to obtain a solution having a concentration of about 7.0 mg per mL. [note—Guard the solution against evaporation during usage.]
Standard stock solution 1—
Transfer 0.100 g each of USP Docosahexaenoic Acid Ethyl Ester RS and USP Eicosapentaenoic Acid Ethyl Ester RS, accurately weighed, to a 10-mL volumetric flask, and dissolve in and dilute with Internal standard solution to volume.
Standard stock solution 2—
Transfer 0.300 g of USP Fish Oil RS accurately weighed to a 10.0-mL volumetric flask, and dissolve in and dilute with Internal standard solution to volume.
Standard solution 1—
Transfer 2.0 mL of Standard stock solution 1 to a glass tube, and evaporate the solvent with a gentle stream of nitrogen. Add 1.5 mL of a 2% (w/v) solution of sodium hydroxide in methanol, cap tightly with a polytetrafluoroethylene-lined cap, mix, and heat in a boiling water bath for 7 minutes. Cool, add 2 mL of boron trichloride–methanol solution (120 g in 1000 mL of methanol), cover with nitrogen, cap tightly, mix, and heat in a boiling water bath for 30 minutes. Cool to 40 to 50
to 50 , add 1 mL of 2,2,4-trimethylpentane, cap, and mix on a vortex mixer or shake vigorously for at least 30 seconds. Immediately add 5 mL of saturated sodium chloride solution containing 1 volume of sodium chloride and 2 volumes of water. [note—Shake from time to time. Before use, decant the solution from any undissolved substance and filter if necessary.] Cover with nitrogen, cap, and mix on a vortex mixer or shake thoroughly for at least 15 seconds. Allow the upper layer to become clear, and transfer to a separate tube. Shake the methanol layer once more with 1 mL of 2,2,4-trimethylpentane, and combine the 2,2,4-trimethylpentane extracts. Wash the combined extracts with two quantities, each of 1 mL of water, and dry over anhydrous sodium sulfate.
, add 1 mL of 2,2,4-trimethylpentane, cap, and mix on a vortex mixer or shake vigorously for at least 30 seconds. Immediately add 5 mL of saturated sodium chloride solution containing 1 volume of sodium chloride and 2 volumes of water. [note—Shake from time to time. Before use, decant the solution from any undissolved substance and filter if necessary.] Cover with nitrogen, cap, and mix on a vortex mixer or shake thoroughly for at least 15 seconds. Allow the upper layer to become clear, and transfer to a separate tube. Shake the methanol layer once more with 1 mL of 2,2,4-trimethylpentane, and combine the 2,2,4-trimethylpentane extracts. Wash the combined extracts with two quantities, each of 1 mL of water, and dry over anhydrous sodium sulfate.
Standard solution 2—
Proceed as directed for Standard solution 1, except to use Standard stock solution 2.
Test stock solution—
Transfer 0.300 g of Fish Oil Containing Omega-3 Acids, accurately weighed, to a 10-mL volumetric flask, and dissolve in and dilute with Antioxidant solution to volume.
Test solution 1—
Proceed as directed for Standard solution 1, except to use the Test stock solution.
Test solution 2—
Transfer 2.0 mL of the Internal standard solution into a glass tube. Then proceed as directed for Test solution 1.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
The gas chromatograph is equipped with a flame-ionization detector and a 0.25-mm × 25-m fused silica capillary column coated with a 0.2-µm film of G16. The temperature of the detector is maintained at 270
)—
The gas chromatograph is equipped with a flame-ionization detector and a 0.25-mm × 25-m fused silica capillary column coated with a 0.2-µm film of G16. The temperature of the detector is maintained at 270 and that of the injection port at 250
and that of the injection port at 250 . The column temperature is initially set at 170
. The column temperature is initially set at 170 for 2 minutes, then increased at a rate of 3
for 2 minutes, then increased at a rate of 3 per minute to 240
per minute to 240 , and is maintained at this temperature for 2.5 minutes. The carrier gas is helium with a split flow ratio of 1:200 and a flow rate of about 1 mL per minute. [note—If splitless injection mode is used, solutions should be further diluted 1 in 200.] Chromatograph Standard solution 2, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the resolution, R, between the peaks in Standard solution 2 due to methyl oleate and methyl cis-vaccinate is not less than 1.3. The number of fatty acid methyl ester peaks exceeding 0.05% of the total area in the chromatogram of Standard solution 2 is at least 24, and the 24 largest peaks of the methyl esters account for more than 90% of the total area. (These correspond, in common elution order, to: 14:0, 15:0, 16:0, 16:1 n-7, 16:4 n-1, 18:0, 18:1 n-9, 18:1 n-7, 18:2 n-6, 18:3 n-3, 18:4 n-3, 20:1 n-11, 20:1 n-9, 20:1 n-7, 20:2 n-6, 20:4 n-6, 20:3 n-3, 20:4 n-3, 20:5 n-3, 22:1 n-11, 22:1 n-9, 21:5 n-3, 22:5 n-3, 22:6 n-3). Chromatograph Standard stock solution 1 and Standard solution 1, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the derivatization efficiency for the conversion of fatty acid ethyl ester to the fatty acid methyl ester is not less than 90.0% for each (DHA and EPA).
, and is maintained at this temperature for 2.5 minutes. The carrier gas is helium with a split flow ratio of 1:200 and a flow rate of about 1 mL per minute. [note—If splitless injection mode is used, solutions should be further diluted 1 in 200.] Chromatograph Standard solution 2, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the resolution, R, between the peaks in Standard solution 2 due to methyl oleate and methyl cis-vaccinate is not less than 1.3. The number of fatty acid methyl ester peaks exceeding 0.05% of the total area in the chromatogram of Standard solution 2 is at least 24, and the 24 largest peaks of the methyl esters account for more than 90% of the total area. (These correspond, in common elution order, to: 14:0, 15:0, 16:0, 16:1 n-7, 16:4 n-1, 18:0, 18:1 n-9, 18:1 n-7, 18:2 n-6, 18:3 n-3, 18:4 n-3, 20:1 n-11, 20:1 n-9, 20:1 n-7, 20:2 n-6, 20:4 n-6, 20:3 n-3, 20:4 n-3, 20:5 n-3, 22:1 n-11, 22:1 n-9, 21:5 n-3, 22:5 n-3, 22:6 n-3). Chromatograph Standard stock solution 1 and Standard solution 1, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the derivatization efficiency for the conversion of fatty acid ethyl ester to the fatty acid methyl ester is not less than 90.0% for each (DHA and EPA).
Procedure—
Separately inject duplicate equal volumes (about 1 µL) of Standard solution 1, Standard solution 2, Test solution 1, and Test solution 2 into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the peak responses. Identify the retention times of the relevant fatty acid methyl esters by comparison of the chromatogram of Standard solution 2 with the reference chromatogram supplied with the USP Fish Oil RS. Identify the retention time for the internal standard peak by comparing the chromatograms for Test solution 1 and Test solution 2. Calculate the percentage of EPA or DHA in the Fish Oil Containing Omega-3 Acids taken by the formula:
100FC / W(RU / RS)
in which F is the factor to express the content of DHA (F = 0.921) and EPA (F = 0.915) as free fatty acids; C is the concentration, in mg per mL, of either DHA or EPA in Standard solution 1; W is the weight, in mg, of the Fish Oil Containing Omega-3 Acids taken to prepare the Test stock solution; RS is the ratio of peak responses of either EPA or DHA relative to the internal standard in the chromatogram of Standard solution 1; and RU is the corrected peak response of either EPA or DHA relative to the internal standard in the chromatogram of Test solution 2 calculated as follows:
in which rU2 is the peak response of any peak at the locus of the internal standard in the chromatogram of Test solution 2; rU1 is the peak response of any peak at the locus of the internal standard in the chromatogram of Test solution 1; rT1 is the peak response of EPA or DHA in the chromatogram of Test solution 1; and rT2 is the peak response of EPA or DHA in the chromatogram of Test solution 2.
Content of total omega-3 acids—
Antioxidant solution, Internal standard solution, Standard stock solution 1, Standard stock solution 2, Standard solution 1, Standard solution 2, Test stock solution, Test solution 1, Test solution 2, and Chromatographic system—
Proceed as directed in the test for Content of EPA and DHA.
Procedure—
Proceed as directed in the test for Content of EPA and DHA, except to calculate the content of the total omega-3 acids by the formula:
in which EPA is the content of EPA, in mg per g, obtained from the test for Content of EPA and DHA;DHA is the content of DHA, in mg per g, obtained from test for Content of EPA and DHA; An-3 is the sum of the areas of the peaks corresponding to C18:3 n-3, C18:4 n-3, C20:4 n-3, C21:5 n-3, and C22:5 n-3 methyl esters in the chromatogram obtained with Test solution 2; AEPA is the area of the peak corresponding to the EPA methyl ester in the chromatogram obtained with Test solution 2; and ADHA is the area of the peak corresponding to the DHA methyl ester in the chromatogram obtained with Test solution 2.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
Chromatographic Column—
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
| Monograph | Curtis Phinney
1-301-816-8540 |
(DSN05) Dietary Supplements - Non-Botanicals |
| Reference Standards | Lili Wang, Technical Services Scientist 1-301-816-8129 RSTech@usp.org |
USP32–NF27 Page 1006
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 34(5) Page 1207
Chromatographic columns text is not derived from, and not part of, USP 32 or NF 27.