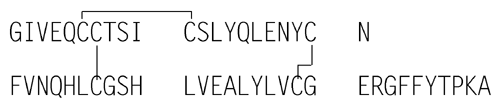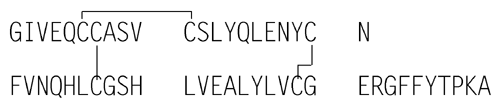Insulin
» Insulin is a protein that affects the metabolism of glucose. It is obtained from the pancreas of healthy bovine or porcine animals, or both, used for food by humans. Its potency, calculated on the dried basis, is not less than 26.5 USP Insulin Units in each mg; Insulin labeled as purified contains not less than 27.0 USP Insulin Units in each mg, calculated on the dried basis. The proinsulin content, determined by a validated method, is not more than 10 ppm.
note—One USP Insulin Unit is equivalent to 0.0342 mg of pure Insulin derived from beef or 0.0345 mg of pure Insulin derived from pork.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in tight containers. Store, protected from light, in a freezer.
Labeling—
Label it to indicate the one or more animal species to which it is related, as pork, as beef, or as a mixture of pork and beef. If the Insulin is purified, label it as such.
USP Reference standards  11
11 —
—
USP Endotoxin RS.
USP Insulin RS.
USP Insulin (Beef) RS .
.
USP Insulin (Pork) RS .
.
USP Endotoxin RS.
USP Insulin RS.
USP Insulin (Beef) RS
 .
.
USP Insulin (Pork) RS
 .
.
Identification—
A:
The retention time of the insulin peak in the chromatogram of the Assay preparation corresponds to the retention time of the appropriate species in the chromatogram of the Identification preparation, as obtained in the Assay. [note—It may be necessary to inject a mixture of Assay preparation and Identification preparation.]
B:
Proceed as directed for Identification test B under Insulin Human, except to use 1 mg of USP Insulin Reference Standard of the appropriate species to prepare the Standard digest solution, to use 1 mg of Insulin to prepare the Test digest solution, and to obtain a resolution, R, between digest fragments II and III of not less than 1.9: meets the requirements.
Microbial enumeration tests  61
61 and Tests for specified microorganisms
and Tests for specified microorganisms  62
62 —
The total bacterial count does not exceed 300 per g, the test being made on a portion of about 0.2 g, accurately weighed.
—
The total bacterial count does not exceed 300 per g, the test being made on a portion of about 0.2 g, accurately weighed.
Bacterial endotoxins  85
85 —
It contains not more than 10 USP Endotoxin Units in each mg.
—
It contains not more than 10 USP Endotoxin Units in each mg.
Loss on drying  731
731 —
Dry about 200 mg, accurately weighed, at 105
—
Dry about 200 mg, accurately weighed, at 105 for 16 hours: it loses not more than 10.0% of its weight.
for 16 hours: it loses not more than 10.0% of its weight.
Related compounds—
Solvent—
Dissolve 28.4 g of anhydrous sodium sulfate in 1000 mL of water. Pipet 2.7 mL of phosphoric acid into this solution, adjust, if necessary, with ethanolamine to a pH of 2.3, and mix.
Solution A—
Prepare a filtered and degassed mixture of Solvent and acetonitrile (82:18).
Solution B—
Prepare a filtered and degassed mixture of Solvent and acetonitrile (50:50).
Mobile phase—
Use variable mixtures of Solution A and Solution B as directed for Chromatographic system. Make adjustments if necessary (see System Suitability under Chromatography  621
621 ).
).
System suitability solution—
Proceed as directed in the Assay.
Standard solution A—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of USP Insulin RS of the appropriate species in 0.01 N hydrochloric acid to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 3.75 mg per mL.
Standard solution B—
Pipet 1 mL of Standard solution A into a 10-mL volumetric flask, dilute with 0.01 N hydrochloric acid to volume, and mix.
Standard solution C—
Pipet 1 mL of Standard solution B into a 10-mL volumetric flask, dilute with 0.01 N hydrochloric acid to volume, and mix.[note—These three Standard solutions may be stored at room temperature for up to 12 hours and in a refrigerator for up to 48 hours.]
Test solution—
Transfer about 7.5 mg of Insulin to a suitable capped vial, and add 2.0 mL of 0.01 N hydrochloric acid. Cap the vial, and shake gently to dissolve. Store this solution for not more than 2 hours at room temperature or for not more than 12 hours in a refrigerator.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 214-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 25-cm column that contains packing L1. The column temperature is maintained at 40
)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 214-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 25-cm column that contains packing L1. The column temperature is maintained at 40 , and the flow rate is about 1 mL per minute. The chromatograph is programmed as follows.
, and the flow rate is about 1 mL per minute. The chromatograph is programmed as follows.
Adjust the Mobile phase composition and the duration of the isocratic elution to obtain a retention time of about 31 minutes for insulin, with the A-21 desamido insulin eluting just prior to the start of the gradient elution phase. Chromatograph Standard solutions A, B, and C, record the chromatograms, and measure the peak responses as directed for Procedure: calculate the factor X1 by the formula:
| Time (minutes) |
Solution A
% |
Solution B
% |
Elution |
| 0 | 81 | 19 | equilibration |
| 0–60 | 81 | 19 | isocratic |
| 60–85 | 81®36 | 19®64 | linear gradient |
| 85–91 | 36 | 64 | isocratic |
| 91–92 | 36®81 | 64®19 | linear gradient |
10(rB / rA)
in which rB and rA are the areas of the peak responses obtained for Standard solution B and Standard solution A, respectively. The value of X1 is between 0.91 and 1.09. Calculate the factor X2 by the formula:
100(rC / rA)
in which rC and rA are the areas of the peak responses obtained for Standard solution C and Standard solution A, respectively. The value of X2 is between 0.7 and 1.3. Chromatograph the System suitability solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the resolution, R, between insulin and A-21 desamido insulin is not less than 2.0; and the tailing factor for the insulin peak is not more than 1.8.
Procedure—
Inject a volume (about 20 µL) of the Test solution into the chromatograph, record the chromatogram, and measure the areas of the responses for the main insulin peak, the A-21 desamido insulin peak, and the peaks from any other impurities. Calculate the percentage of insulin, %I, in the portion of Insulin taken by the formula:
100(rI / rs)
in which rI is the peak response for insulin, and rs is the sum of the responses for all of the peaks. Calculate the percentage of A-21 desamido insulin, %D, in the portion of Insulin taken by the formula:
100(rD / rs)
in which rD is the peak response for A-21 desamido insulin, and rs is the sum of the responses for all of the peaks. Calculate the percentage of other insulin related compounds in the portion of Insulin taken by the formula:
100 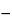 (%I + %D).
(%I + %D).
Not more than 10.0% of A-21 desamido insulin is found, and not more than 5.0% of other insulin related compounds is found. For Insulin derived from a single species, measure the responses of any peaks corresponding to beef or pork insulin, and calculate their concentration as a percentage of rs : the amount of cross-contamination is not more than 1.0%.
Limit of high molecular weight proteins—
Arginine solution—
Prepare a solution of l-arginine in water containing 1 mg per mL.
Mobile phase—
Prepare a filtered and degassed mixture of Arginine solution, acetonitrile, and glacial acetic acid (65:20:15). Make adjustments if necessary (see System Suitability under Chromatography  621
621 ).
).
Resolution solution—
Dissolve 4 mg of Insulin containing more than 0.4% high molecular weight proteins in 1 mL of 0.01 N hydrochloric acid. Store this solution in a refrigerator, and use within 7 days. [note—Insulin containing the indicated percentage of high molecular weight proteins may be prepared by allowing Insulin to stand at room temperature for about 5 days.]
Test solution—
Transfer about 4 mg of Insulin to a small vial, add 1 mL of 0.01 N hydrochloric acid, and mix to dissolve. Store in a refrigerator, and use within 7 days.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 276-nm detector and a 7.8-mm × 30-cm column that contains packing L20. The flow rate is about 0.5 mL per minute. Chromatograph the Resolution solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the retention times are between 13 and 17 minutes for the polymeric insulin complexes, about 17.5 minutes for the covalent insulin dimer, and between 18 and 22 minutes for the insulin monomer, with salts eluting after the insulin monomer; and the ratio of the height of the covalent insulin dimer peak to the height of the valley between the covalent insulin dimer peak and the insulin monomer peak is not less than 2.0.
)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 276-nm detector and a 7.8-mm × 30-cm column that contains packing L20. The flow rate is about 0.5 mL per minute. Chromatograph the Resolution solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the retention times are between 13 and 17 minutes for the polymeric insulin complexes, about 17.5 minutes for the covalent insulin dimer, and between 18 and 22 minutes for the insulin monomer, with salts eluting after the insulin monomer; and the ratio of the height of the covalent insulin dimer peak to the height of the valley between the covalent insulin dimer peak and the insulin monomer peak is not less than 2.0.
Procedure—
Inject a volume (about 100 µL) of the Test solution into the chromatograph, record the chromatogram, and measure the areas of the peak responses, disregarding any peaks having retention times greater than that of the insulin monomer. Calculate the percentage of high molecular weight proteins in the portion of Insulin taken by the formula:
100SrH / (SrH + rM)
in which SrH is the sum of the responses for all peaks having retention times less than that of the insulin monomer, and rM is the peak response of the insulin monomer: not more than 1.0% is found.
Zinc content  591
591 —
Determine the zinc content of about 10 mg of it, accurately weighed: not more than 1.0% is found, calculated on the dried basis.
—
Determine the zinc content of about 10 mg of it, accurately weighed: not more than 1.0% is found, calculated on the dried basis.
Assay—
Mobile phase—
Dissolve 28.4 g of anhydrous sodium sulfate in 1000 mL of water, pipet 2.7 mL of phosphoric acid into the solution, and adjust with ethanolamine to a pH of 2.3 if necessary. Prepare a filtered and degassed mixture of this solution and acetonitrile (74:26). The acetonitrile is warmed to a temperature equal to or higher than 20 to avoid precipitation. Make adjustments if necessary (see System Suitability under Chromatography
to avoid precipitation. Make adjustments if necessary (see System Suitability under Chromatography  621
621 ).
).
System suitability solution—
Dissolve about 1.5 mg of Insulin in 1.0 mL of 0.01 N hydrochloric acid. Allow to stand at room temperature for not less than 3 days to obtain a solution containing not less than 5% of A-21 desamido insulin.
note—The following Identification preparation, Standard preparation, and Assay preparation may be stored at room temperature for up to 12 hours or in a refrigerator for up to 48 hours.
Identification preparation—
Prepare a solution of USP Insulin (Pork) RS and USP Insulin (Beef) RS in 0.01 N hydrochloric acid containing about 0.6 mg of each per mL.
Standard preparation—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of USP Insulin RS of the appropriate species in 0.01 N hydrochloric acid to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 1.5 mg per mL.
Assay preparation—
Transfer about 15 mg of Insulin, accurately weighed, to a 10-mL volumetric flask, and dissolve in and dilute with 0.01 N hydrochloric acid to obtain a solution having a concentration of about 1.5 mg per mL.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 214-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 15-cm column that contains packing L1. The column temperature is maintained at 40
)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 214-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 15-cm column that contains packing L1. The column temperature is maintained at 40 , and the flow rate is about 1 mL per minute. Chromatograph the Standard preparation, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 1.6%. Chromatograph the System suitability solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the resolution, R, between insulin and A-21 desamido insulin is not less than 2.0; and the tailing factor for the insulin peak is not more than 1.8.
, and the flow rate is about 1 mL per minute. Chromatograph the Standard preparation, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 1.6%. Chromatograph the System suitability solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the resolution, R, between insulin and A-21 desamido insulin is not less than 2.0; and the tailing factor for the insulin peak is not more than 1.8.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 20 µL) of the Assay preparation, the Identification preparation, and the Standard preparation into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the peak responses for insulin and A-21 desamido insulin, using the chromatogram of the Identification preparation to identify the insulin peaks. For Insulin derived from a single species, calculate the potency on the undried basis, in USP Insulin Units per mg, of the Insulin in the Assay preparation by the formula:
(CS / CU)(SrU /SrS)
in which CS is the concentration, in USP Insulin Units per mL, of USP Insulin RS in the Standard preparation; CU is the concentration, in mg per mL, of Insulin in the Assay preparation; and SrU and SrS are the sums of the areas of the insulin and A-21 desamido insulin peaks obtained from the chromatograms of the Assay preparation and the Standard preparation, respectively. From the value obtained in the test for Loss on drying, calculate the potency on the dried basis. For Insulin derived from a mixture of beef and pork, calculate the total potency as the sum of the potencies of the beef- and pork-derived insulins, determined separately.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
Chromatographic Column—
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
| Monograph | Larry N. Callahan, Ph.D.
Senior Scientist 1-301-816-8385 |
(BBPP05) Biologics and Biotechnology - Proteins and Polysaccharides |
| Reference Standards | Lili Wang, Technical Services Scientist 1-301-816-8129 RSTech@usp.org |
|
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Senior Scientist 1-301-816-8339 |
(MSA05) Microbiology and Sterility Assurance | |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Senior Scientist 1-301-816-8339 |
(MSA05) Microbiology and Sterility Assurance | |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Senior Scientist 1-301-816-8339 |
(MSA05) Microbiology and Sterility Assurance |
USP32–NF27 Page 2639
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 31(5) Page 1375
Chromatographic columns text is not derived from, and not part of, USP 32 or NF 27.