Echinacea pallida
» Echinacea pallida consists of the dried rhizome and roots of Echinacea pallida (Nutt.) Nutt. (Fam. Asteraceae). It is harvested in the fall after 3 or more years of growth. It contains not less than 0.5 percent of total phenols, calculated on the dried basis as the sum of caftaric acid (C13H12O9), chicoric acid (C22H18O12), chlorogenic acid (C16H18O9), and echinacoside (C35H46O20).
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in well-closed, light-resistant containers.
Labeling—
The label states the Latin binomial and, following the official name, the parts of the plant contained in the article.
Botanic characteristics—
Macroscopic—
The outer surface of the rhizome is pale to yellowish-brown, crowned with the remains of the aerial stem, and sometimes shows surface annulations up to 15 mm in diameter. The roots are pale to yellowish-brown, cylindrical or slightly tapering, sometimes spirally twisted, longitudinally wrinkled and deeply furrowed, up to 4 to 10 mm in diameter, and pass imperceptibly into rhizome. The short fracture, when dry, becomes tough and pliable on exposure to air.
Microscopic—
The rhizomes and roots in transverse section show a thin outer bark separated from a wide xylem by a distinct cambial line. The cork is composed of several rows of thin-walled cells containing yellowish-brown pigment. The rhizome has a small circular pith, occasional small groups of thick-walled, lignified fibers in the pericycle, and a parenchymatous cortex. The phloem and xylem are composed of narrow strands of vascular tissue separated by wide, nonlignified medullary rays. Xylem vessels are lignified, 25 to 75 µm in diameter, usually with reticulate thickening but occasionally with spiral or annular thickening. Sclereids occur singly or in small groups, varying considerably in size and shape from rounded to rectangular to elongated and fiber-like, are up to 300 µm long and 20 to 40 µm wide, with intercellular spaces forming schizogenous oleoresin canals that are 80 to 150 µm in diameter and contain a dense black deposit present both inside and outside of the central cylinder (unlike Echinacea angustifolia, where the canals are present only outside of the central cylinder). Spherocrystalline masses of inulin occur throughout the parenchymatous tissues. Lignified fibers, present in the periphery of the cortex, are 100 to 300 µm long and occur singly with phytomelanin often absent (unlike Echinacea angustifolia, where the fibers occur scattered in groups, are 300 to 800 µm long, and are usually surrounded by phytomelanin).
Identification—
A:
Thin-Layer Chromatographic Identification Test  201
201 —
—
presence of echinacoside and absence of dicaffeoylquinic acids (cynarin[e])—
Test solution—
Proceed as directed for Identification test A under Echinacea angustifolia, except to use Echinacea pallida instead of Echinacea angustifolia.
Standard solution 1—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of USP Powdered Echinacea pallida Extract RS in methanol to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 10 mg per mL.
Standard solution 2, Developing solvent system, Spray reagent 1, and Spray reagent 2—
Proceed as directed for Identification test A under Echinacea angustifolia.
Procedure—
Proceed as directed in the chapter. Develop the chromatograms in Developing solvent system until the solvent front has moved not less than 12 cm, and dry the plate in a current of air. Spray the plate with Spray reagent 1 followed by Spray reagent 2, and examine the plate under UV light at 365 nm: the chromatogram obtained from the Test solution shows a yellowish zone at an RF value of 0.14, characteristic of echinacoside (absent or traces in Echinacea purpurea), corresponding in color and RF value to that in the chromatogram of Standard solution 1, and does not show a zone characteristic of 1,3-dicaffeoylquinic acid (present in Echinacea angustifolia) corresponding in color and RF value to that in the chromatogram of Standard solution 2. Other colored zones of varying intensities may be observed in the chromatogram of the Test solution.
B:
Thin-Layer Chromatographic Identification Test  201
201 —
—
presence of ketoalkenynes—
Test solution—
Evaporate to dryness the chloroform extract retained from preparation of the Test solution in Identification test A at 40 in vacuum. To the residue add 1 mL of alcohol, and pass through a nylon membrane filter having a porosity of 0.45 µm.
in vacuum. To the residue add 1 mL of alcohol, and pass through a nylon membrane filter having a porosity of 0.45 µm.
Standard solution 1—
Transfer an accurately weighed quantity of USP Powdered Echinacea pallida Extract RS to a centrifuge tube, and add chloroform to obtain a solution having a concentration of about 10 mg per mL. Shake for 1 minute, and centrifuge. Use the supernatant.
Standard solution 2—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of 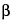 -sitosterol in methanol to obtain a solution having a concentration of about 1 mg per mL.
-sitosterol in methanol to obtain a solution having a concentration of about 1 mg per mL.
Developing solvent system—
Prepare a mixture of toluene and ethyl acetate (7:3).
Spray reagent 1—
Prepare a 1% solution of vanillin in alcohol.
Spray reagent 2—
Prepare a 10% solution of sulfuric acid in alcohol.
Procedure—
Proceed as directed for Identification test A. Spray the plate with Spray reagent 1 followed by Spray reagent 2, and heat the plate at 120 for 3 minutes. The chromatogram obtained from the Test solution shows green, brown, and violet zones above the spot for
for 3 minutes. The chromatogram obtained from the Test solution shows green, brown, and violet zones above the spot for 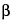 -sitosterol (RF range 0.6 to 0.8). These zones (unlike those in Echinacea angustifolia and Echinacea purpurea) are characteristic of ketoalkenynes, and correspond in RF value to the zones in the chromatogram obtained from Standard solution 1.
-sitosterol (RF range 0.6 to 0.8). These zones (unlike those in Echinacea angustifolia and Echinacea purpurea) are characteristic of ketoalkenynes, and correspond in RF value to the zones in the chromatogram obtained from Standard solution 1.
C:
The retention time of the major peak in the chromatogram of the Test solution corresponds to that of the echinacoside peak in the chromatogram of Standard solution 1, as obtained in the test for Content of total phenols. The peak area of any peak detected at the locus of 1,3-dicaffeoylquinic acid is not more than 1% of the peak area for the echinacoside peak.
Volatile oil content  561
561 :
between 1.0 and 2.0 mL per 100 g.
:
between 1.0 and 2.0 mL per 100 g.
Content of total phenols—
Solvent, Solution A, Solution B, Mobile phase, and Standard solution 2—
Prepare as directed for Content of total phenols under Echinacea angustifolia.
Standard solution 1—
Proceed as directed for Content of total phenols under Echinacea angustifolia, except to use USP Powdered Echinacea pallida Extract RS instead of USP Powdered Echinacea angustifolia Extract RS.
Test solution—
Proceed as directed for Content of total phenols under Echinacea angustifolia, except to use finely powdered Echinacea pallida instead of Echinacea angustifolia.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
Prepare as directed for Content of total phenols under Echinacea angustifolia. Chromatograph Standard solution 1, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the chromatogram obtained is similar to the Reference Chromatogram for total phenols provided with USP Powdered Echinacea pallida Extract RS. Chromatograph Standard solution 2, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the capacity factor, k¢, is not less than 3.0; the tailing factor is not more than 2.0; and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 2.5%.
)—
Prepare as directed for Content of total phenols under Echinacea angustifolia. Chromatograph Standard solution 1, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the chromatogram obtained is similar to the Reference Chromatogram for total phenols provided with USP Powdered Echinacea pallida Extract RS. Chromatograph Standard solution 2, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the capacity factor, k¢, is not less than 3.0; the tailing factor is not more than 2.0; and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 2.5%.
Procedure—
Proceed as directed for Content of total phenols under Echinacea angustifolia. Separately calculate the percentages of caftaric acid (C13H12O9), chicoric acid (C22H18O12), chlorogenic acid (C16H18O9), and echinacoside (C35H46O20) in the portion of Echinacea pallida taken by the formula:
2500F(C/W)(ri / rS)
in which F is the response factor and is equal to 0.695 for chicoric acid, 0.881 for caftaric acid, 1.000 for chlorogenic acid, and 2.220 for echinacoside; C is the concentration, in mg per mL, of USP Chlorogenic Acid RS in Standard solution 2; W is the weight, in mg, of Echinacea pallida taken; and ri and rS are the peak responses for the relevant analyte obtained from the Test solution and Standard solution 2, respectively. Calculate the percentage of total phenols in the portion of Echinacea pallida taken by adding the individual percentages calculated.
Other requirements—
It meets the requirements of the tests for Loss on drying, Foreign organic matter, Total ash, Acid-insoluble ash, Pesticide residues, and Heavy metals under Echinacea angustifolia.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
Chromatographic Column—
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
| Monograph | Maged H. Sharaf, Ph.D.
Senior Scientist 1-301-816-8318 |
(DSB05) Dietary Supplements - Botanicals |
| Reference Standards | Lili Wang, Technical Services Scientist 1-301-816-8129 RSTech@usp.org |
USP32–NF27 Page 996
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 30(2) Page 555
Chromatographic columns text is not derived from, and not part of, USP 32 or NF 27.