Dextran 1
» Dextran 1 is a low molecular weight fraction of dextran, consisting of a mixture of isomaltooligosaccharides. It is obtained by controlled hydrolysis and fractionation of dextrans produced by fermentation of Leuconostoc mesenteroides (strain NRRL B-512; CIP 78.59, or its sub-strains, for example L. mesenteroides B-512F; NCTC, 10817), in the presence of sucrose. It is a glucose polymer in which the linkages between glucose units are almost exclusively 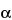 -1,6. Its weight-average molecular weight is about 1000.
-1,6. Its weight-average molecular weight is about 1000.
Packaging and storage—
Store in well-closed containers at a temperature between 4 and 30
and 30 .
.
Labeling—
Where it is intended for use in preparing injectable dosage forms, the label states that it is sterile or must be subjected to further processing during the preparation of injectable dosage forms.
Identification—
A:
Infrared Absorption  197K
197K —To 1 to 2 mg each of USP Dextran 1 RS and the sample add one to two drops of water, grind in an agate mortar for 1 to 2 minutes, add about 300 mg of potassium bromide, and mix to a slurry. [note—Do not grind.] Dry under vacuum at 40
—To 1 to 2 mg each of USP Dextran 1 RS and the sample add one to two drops of water, grind in an agate mortar for 1 to 2 minutes, add about 300 mg of potassium bromide, and mix to a slurry. [note—Do not grind.] Dry under vacuum at 40 for 15 minutes, and if it is not dry, continue drying for another 15 minutes. Crush the residue, prepare a disk, and run the IR spectrum with a blank potassium bromide disk in the reference beam.
for 15 minutes, and if it is not dry, continue drying for another 15 minutes. Crush the residue, prepare a disk, and run the IR spectrum with a blank potassium bromide disk in the reference beam.
B:
It meets the requirements of the test for Molecular weight distribution and average molecular weight.
Absorbance  851
851 —
The absorbance of a 15% solution in water at 375 nm is not more than 0.12, water being used as the blank.
—
The absorbance of a 15% solution in water at 375 nm is not more than 0.12, water being used as the blank.
Specific rotation  781S
781S :
between +148
:
between +148 and +164
and +164 at 20
at 20 , for a solution in water, on the dried basis (dry at 70
, for a solution in water, on the dried basis (dry at 70 under vacuum to constant weight), and corrected for the content of sodium chloride.
under vacuum to constant weight), and corrected for the content of sodium chloride.
Microbial enumeration tests  61
61 and Tests for specified microorganisms
and Tests for specified microorganisms  62
62 —
The total aerobic microbial count does not exceed 102 cfu per g, determined by plate-count; and the total combined molds and yeasts count does not exceed 10 cfu per g.
—
The total aerobic microbial count does not exceed 102 cfu per g, determined by plate-count; and the total combined molds and yeasts count does not exceed 10 cfu per g.
Bacterial endotoxins  85
85 (where it is labeled as intended for use in the preparation of injectables):
not more than 25.0 USP Endotoxin Units per g.
(where it is labeled as intended for use in the preparation of injectables):
not more than 25.0 USP Endotoxin Units per g.
pH  791
791 :
between 4.5 and 7.0, in a 15% solution in water.
:
between 4.5 and 7.0, in a 15% solution in water.
Heavy metals, Method II  231
231 :
not more than 5 µg per g.
:
not more than 5 µg per g.
Limit of alcohol and related impurities—
Test solution—
Proceed as directed for Test solution in the test for Limit of alcohol and related impurities under Dextran 40, except to use 5.0 g of Dextran 1.
Standard solution, Chromatographic system, and Procedure—
Proceed as directed in the test for Limit of alcohol and related impurities under Dextran 40. The total area of peaks from impurities in the Test solution does not exceed the area of the n-propyl alcohol solution peak.
Limit of sodium chloride—
Dissolve 5 g of Dextran 1, accurately weighed, in 100 mL of water. Add 0.2 mL of potassium chromate TS, and titrate with 0.1 N silver nitrate VS (see Titrimetry  541
541 ). Each mL of 0.1 N silver nitrate is equivalent to 5.844 mg of sodium chloride: not more than 1.5% of sodium chloride is found.
). Each mL of 0.1 N silver nitrate is equivalent to 5.844 mg of sodium chloride: not more than 1.5% of sodium chloride is found.
Limit of nitrogenous impurities  461
461 (where it is labeled as intended for use in the preparation of injectables)—
(where it is labeled as intended for use in the preparation of injectables)—
Sulfate solution—
To 1000 mL sulfuric acid add 5 g of anhydrous cupric sulfate and 500 g of potassium sulfate. Dissolve by heating, and store at 60 .
[note—If storage at 60
.
[note—If storage at 60 is not possible, prepare a smaller quantity of Sulfate solution on the day of use, adjusting proportions accordingly.]
is not possible, prepare a smaller quantity of Sulfate solution on the day of use, adjusting proportions accordingly.]
Indicator—
Dilute a mixture of 20 mL of a 0.1% solution of bromocresol green in alcohol and 4 mL of methyl red TS with water to 100 mL.
Procedure—
Transfer 0.2 g Dextran 1, accurately weighed, to a micro-Kjeldahl flask. Add 4 mL of Sulfate solution. Heat until the solution exhibits a clear green color and the sides of the flask are free from carbonaceous material. Cool, cautiously add 30 mL of water, mix, and transfer the solution to a steam distillation unit. Rinse the Kjeldahl flask with three 5-mL portions of water, adding the washings to the solution. Add 15 mL of 45% sodium hydroxide solution, immediately close the distillation apparatus, and start steam distillation immediately. Receive the distillate in 1 mL of Indicator and sufficient water to cover the end of the condensing tube. Upon completion of the distillation, remove the receiving flask, and rinse the end of the condensing tube with a small quantity of water, adding the rinse to the distillate. Titrate the distillate with 0.010 N hydrochloric acid until the color changes from blue to reddish violet. Perform a blank determination, and make any necessary correction. The corrected volume of 0.010 N hydrochloric acid required to change the color does not exceed 0.15 mL (110 ppm of nitrogen).
Molecular weight distribution and average molecular weight—
Mobile phase—
Prepare a filtered and degassed solution of sodium chloride containing 2.9 g per L.
Calibration solution—
Prepare a solution containing about 0.45 mg of isomaltotriose (3 glucose units) and 0.60 mg of sodium chloride per mL.
Reference solution—
Prepare a solution of USP Dextran 1 RS in Mobile phase containing 6.0 to 6.5 mg per mL.
Test solution—
Prepare a solution of Dextran 1 in Mobile phase containing 6.0 to 6.5 mg per mL.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a differential refractive index detector and two 10-mm × 30-cm columns in series that contain packing L54 and are maintained at 20–25
)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a differential refractive index detector and two 10-mm × 30-cm columns in series that contain packing L54 and are maintained at 20–25 . The flow rate is 0.07 to 0.08 mL per minute, maintained constant to ±1%.
. The flow rate is 0.07 to 0.08 mL per minute, maintained constant to ±1%.
Procedure—
Inject about 100 µL of the Calibration solution, record the chromatogram, and note the retention times of the peaks. Separately inject equal volumes (about 100 µL) of the Reference solution and Test solution, and record the chromatograms. Using the retention times in the chromatogram of Calibration solution, identify the peaks due to isomaltotriose and sodium chloride in the chromatograms of Reference solution and Test solution. Disregard the peak due to sodium chloride in Reference solution and Test solution. Calculate the weight-average molecular weight, MW, by the formula:
Calculate the amounts of the fractions with fewer than 3 and with more than 9 glucose units for the Reference solution and the Test solution: the Mw and amounts of the fractions obtained for the Reference solution are within the values stated in the data sheet that accompanies USP Dextran 1 RS. The Mw of Dextran 1 is between 850 and 1150. The fraction with fewer than 3 units of glucose is less than 15%, and the fraction with more than 9 units of glucose is less than 20%.
SWi Mi
in which Wi is the weight proportion of oligosaccharide i; and Mi is the molecular weight of oligosaccharide i. Use the following molecular weight values for calculation:
| Glucose | 180 |
| Isomaltose | 342 |
| Isomaltotriose | 504 |
| Isomaltotetraose | 666 |
| Isomaltopentaose | 828 |
| Isomaltohexaose | 990 |
| Isomaltoheptaose | 1152 |
| Isomaltooctaose | 1314 |
| Isomaltononaose | 1476 |
| Isomaltodecaose | 1638 |
| Isomaltoundecaose | 1800 |
| Isomaltododecaose | 1962 |
| Isomaltotridecaose | 2124 |
| Isomaltotetradecaose | 2286 |
| Isomaltopentadecaose | 2448 |
| Isomaltohexadecaose | 2610 |
| Isomaltoheptadecaose | 2772 |
| Isomaltooctadecaose | 2934 |
| Isomaltononadecaose | 3096 |
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
Chromatographic Column—
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
| Monograph | Anita Y. Szajek, Ph.D.
Senior Scientist 1-301-816-8325 |
(BBBBP05) Biologics and Biotechnology - Blood and Blood Products |
| Reference Standards | Lili Wang, Technical Services Scientist 1-301-816-8129 RSTech@usp.org |
|
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Senior Scientist 1-301-816-8339 |
(MSA05) Microbiology and Sterility Assurance | |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Senior Scientist 1-301-816-8339 |
(MSA05) Microbiology and Sterility Assurance | |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Senior Scientist 1-301-816-8339 |
(MSA05) Microbiology and Sterility Assurance |
USP32–NF27 Page 2097
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 29(6) Page 1866
Chromatographic columns text is not derived from, and not part of, USP 32 or NF 27.