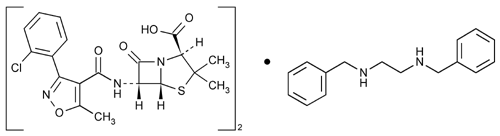
Cloxacillin Benzathine
4-Thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid, 6-[[[3-(2-chlorophenyl)-5-methyl-4-isoxazolyl]carbonyl]amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-, [2S-(2
(2S,5R,6R)-6-[3-(o-Chlorophenyl)-5-methyl-4-isoxazolecarboxamido]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid compound with N,N¢-dibenzylethylenediamine (2:1)
» Cloxacillin Benzathine has a potency equivalent to not less than 704 µg and not more than 821 µg of cloxacillin (C19H18ClN3O5S) per mg, calculated on the anhydrous basis.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in tight containers.
Labeling—
Label it to indicate that it is for veterinary use only. Where it is intended for use in preparing sterile dosage forms, the label states that it is sterile or must be subjected to further processing during the preparation of sterile dosage forms.
Identification—
Solutions:
Obtain the test solution as follows. To about 20 mg in a 50-mL conical flask, add 5 mL of 5 N sodium hydroxide, and heat on a steam bath for 20 minutes. Cool, transfer 1 mL of this solution to a separator containing 10 mL of 1.2 N sulfuric acid, and extract with 50 mL of ether. Wash the ether extract with 30 mL of water, and extract the ether layer with 50 mL of 0.1 N sodium hydroxide. Similarly prepare the Standard solution from about 15 mg of USP Cloxacillin Sodium RS.
Crystallinity  695
695 :
meets the requirements.
:
meets the requirements.
pH  791
791 :
between 3.0 and 6.5, in a suspension containing 10 mg per mL.
:
between 3.0 and 6.5, in a suspension containing 10 mg per mL.
Sterility  71
71 —
Where the label states that Cloxacillin Benzathine is sterile, it meets the requirements when tested as directed for Direct Inoculation of the Culture Medium under Test for Sterility of the Product to be Examined, except to use Fluid Thioglycollate Medium containing polysorbate 80 solution (1 in 200) and an amount of sterile penicillinase sufficient to inactivate the cloxacillin in each tube, to use Soybean–Casein Digest Medium containing polysorbate 80 solution (1 in 200) and an amount of sterile penicillinase sufficient to inactivate the cloxacillin in each tube, and to shake the tubes once daily.
—
Where the label states that Cloxacillin Benzathine is sterile, it meets the requirements when tested as directed for Direct Inoculation of the Culture Medium under Test for Sterility of the Product to be Examined, except to use Fluid Thioglycollate Medium containing polysorbate 80 solution (1 in 200) and an amount of sterile penicillinase sufficient to inactivate the cloxacillin in each tube, to use Soybean–Casein Digest Medium containing polysorbate 80 solution (1 in 200) and an amount of sterile penicillinase sufficient to inactivate the cloxacillin in each tube, and to shake the tubes once daily.
Water, Method I  921
921 :
not more than 5.0%.
:
not more than 5.0%.
Assay—
0.1 M Phosphate buffer—
Dissolve 55.2 g of monobasic sodium phosphate in water, and dilute with water to 4 L.
Mobile phase—
Combine 1000 mL of acetonitrile and 3000 mL of 0.1 M Phosphate buffer. Adjust with phosphoric acid or 1 N sodium hydroxide to a pH of 4.6 ± 0.2. Pass through a 0.45-µm nylon filter, and degas. [note—The retention time of cloxacillin is very sensitive to the acetonitrile content of the Mobile phase.]
Diluent—
Transfer 13.8 g of monobasic sodium phosphate to a 2-L volumetric flask, mix, and dilute with water to volume. Combine 1800 mL of the resulting solution with 1200 mL of acetonitrile. Adjust with phosphoric acid or 1 N sodium hydroxide to a pH of 6.4.
Standard preparations—
In duplicate, dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of USP Cloxacillin Sodium RS in Diluent to obtain solutions having known concentrations of about 112 µg per mL.
Assay preparations—
In duplicate, dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of Cloxacillin Benzathine in Diluent to obtain solutions having concentrations of about 128 µg per mL.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 220-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 25-cm column that contains 10-µm packing L1. The flow rate is about 1.5 mL per minute and the column temperature is 40
)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 220-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 25-cm column that contains 10-µm packing L1. The flow rate is about 1.5 mL per minute and the column temperature is 40 . Chromatograph the Standard preparations, and record the peak areas as directed for Procedure: the tailing factor is less than 2.0; the peak areas of the two Standard preparations agree within 98% to 102%; and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 2%.
. Chromatograph the Standard preparations, and record the peak areas as directed for Procedure: the tailing factor is less than 2.0; the peak areas of the two Standard preparations agree within 98% to 102%; and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 2%.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 10 µL) of the Standard preparations and the Assay preparations into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the areas for the major peaks. Calculate the quantity, in µg, of C19H18ClN3O5S in each mg of Cloxacillin Benzathine taken by the formula:
P(CS / CU)(rU / rS)
in which P is the assigned potency, in µg of cloxacillin per mg, of USP Cloxacillin Sodium RS; CS and CU are the concentrations, in µg per mL, of cloxacillin sodium and cloxacillin benzathine in the Standard preparations and the Assay preparations, respectively; and rU and rS are the average peak areas of the cloxacillin peaks obtained from the Assay preparations and the Standard preparations, respectively.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
Chromatographic Column—
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
| Monograph | Ian DeVeau, Ph.D.
Director, Veterinary Drugs and Radiopharmaceuticals 1-301-816-8178 |
(VET05) Veterinary Drugs 05 |
| Reference Standards | Lili Wang, Technical Services Scientist 1-301-816-8129 RSTech@usp.org |
|
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Senior Scientist 1-301-816-8339 |
(MSA05) Microbiology and Sterility Assurance |
USP32–NF27 Page 2002
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 31(4) Page 1050
Chromatographic columns text is not derived from, and not part of, USP 32 or NF 27.