Chondroitin Sulfate Sodium
Chondroitin, hydrogen sulfate, sodium salt
» Chondroitin Sulfate Sodium is the sodium salt of the sulfated linear glycosaminoglycan obtained from bovine, porcine, or avian cartilages of healthy and domestic animals used for food by humans. Chondroitin Sulfate Sodium consists mostly of the sodium salt of the sulfate ester of N-acetylchondrosamine (2-acetamido-2-deoxy-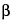 -d-galactopyranose) and d-glucuronic acid copolymer. These hexoses are alternately linked
-d-galactopyranose) and d-glucuronic acid copolymer. These hexoses are alternately linked 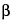 -1,4 and
-1,4 and 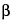 -1,3 in the polymer. Chondrosamine moieties in the prevalent glycosaminoglycan are monosulfated primarily on position 4 and less so on position 6. It contains not less than 90.0 percent and not more than 105.0 percent of chondroitin sulfate sodium, calculated on the dried basis.
-1,3 in the polymer. Chondrosamine moieties in the prevalent glycosaminoglycan are monosulfated primarily on position 4 and less so on position 6. It contains not less than 90.0 percent and not more than 105.0 percent of chondroitin sulfate sodium, calculated on the dried basis.
note—Chondroitin Sulfate Sodium is extremely hygroscopic once dried. Avoid exposure to the atmosphere, and weigh promptly.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in tight containers.
Labeling—
Label it to state the source(s) from which the article was derived, whether bovine, porcine, avian, or a mixture of any of them.
Clarity and color of solution—
Transfer 2.5 g of Chondroitin Sulfate Sodium to a 50-mL volumetric flask. Dissolve in and dilute with carbon dioxide-free water to volume, mix, and examine immediately. Measure the absorbance of this solution at 420 nm in a 1-cm cell, using carbon dioxide-free water as the blank: its absorbance is not greater than 0.35.
Identification—
B:
A solution containing 0.5 g in 10 mL of water meets the requirements of the test for Sodium  191
191 .
.
Microbial enumeration  2021
2021 —
The total bacterial count does not exceed 1000 cfu per g, and the total combined molds and yeasts count does not exceed cfu 100 cfu per g. It meets the requirements of the tests for absence of Salmonella species, and Escherichia coli.
—
The total bacterial count does not exceed 1000 cfu per g, and the total combined molds and yeasts count does not exceed cfu 100 cfu per g. It meets the requirements of the tests for absence of Salmonella species, and Escherichia coli.
pH  791
791 :
between 5.5 and 7.5, in a solution (1 in 100).
:
between 5.5 and 7.5, in a solution (1 in 100).
Loss on drying  731
731 —
Dry it at 105
—
Dry it at 105 for 4 hours: it loses not more than 10.0% of its weight. [note—Chondroitin Sulfate Sodium is extremely hygroscopic once dried. Avoid exposure to the atmosphere, and weigh promptly.]
for 4 hours: it loses not more than 10.0% of its weight. [note—Chondroitin Sulfate Sodium is extremely hygroscopic once dried. Avoid exposure to the atmosphere, and weigh promptly.]
Residue on ignition  281
281 :
between 20.0% and 30.0%, on the dried basis.
:
between 20.0% and 30.0%, on the dried basis.
Chloride  221
221 —
A 0.10-g portion shows no more chloride than corresponds to 0.7 mL of 0.020 N hydrochloric acid: not more than 0.50% is found.
—
A 0.10-g portion shows no more chloride than corresponds to 0.7 mL of 0.020 N hydrochloric acid: not more than 0.50% is found.
Sulfate  221
221 —
Dissolve 200 mg in 40 mL of water. Add 10 mL of a solution of cetylpyridinium chloride having a concentration of about 30 mg per mL, mix, and pass through a filter. A 25-mL portion of the filtrate shows no more sulfate than corresponds to 0.25 mL of 0.020 N sulfuric acid: not more than 0.24% is found.
—
Dissolve 200 mg in 40 mL of water. Add 10 mL of a solution of cetylpyridinium chloride having a concentration of about 30 mg per mL, mix, and pass through a filter. A 25-mL portion of the filtrate shows no more sulfate than corresponds to 0.25 mL of 0.020 N sulfuric acid: not more than 0.24% is found.
Heavy metals, Method II  231
231 :
0.002%.
:
0.002%.
Electrophoretic purity (see Electrophoresis  726
726 )—
)—
0.1 M Barium acetate buffer, pH 5.0—
Dissolve about 25.24 g of barium acetate in water, and dilute with water to 900 mL. Adjust with acetic acid to a pH of 5.0, dilute with water to 1 L, and mix.
Staining reagent:
0.1% toluidine blue in acetic acid; dissolve 1 g of toluidine blue in 1000 mL of 0.1 M acetic acid.
Standard solution 1—
Prepare a solution of USP Chondroitin Sulfate Sodium RS in water having a known concentration of about 30 mg per mL.
Standard solution 2—
Dilute 1 mL of Standard solution 1 with water to 50 mL, and mix.
Test solution—
Transfer 150 mg of Chondroitin Sulfate Sodium, accurately weighed, to a 5.0-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in and dilute with water to volume, and mix.
Procedure—
Fill the chambers of an electrophoresis apparatus suitable for separations on cellulose acetate membranes1 (a small submarine gel chamber or one dedicated to membrane media) with 0.1 M Barium acetate buffer, pH 5.0. Soak a cellulose acetate membrane about 5 to 6 cm × 12 to 14 cm in 0.1 M Barium acetate buffer, pH 5.0 for 10 minutes, or until evenly wetted, then blot dry between two sheets of absorbent paper. Using an applicator2 suitable for electrophoresis, apply equal volumes (about 0.5 µL) of the Test solution, Standard solution 1, and Standard solution 2 to the brighter side of the membrane held in position in an appropriate applicator stand or on a separating bridge in the chamber. Ensure that both ends of the membrane are dipped at least 0.5- to 1.0-cm deep into the buffer chambers. Apply a constant 60 volts (about 6 mA at the start) for 2 hours. [note—Perform the application of solutions and voltage within 5 minutes because further drying of the blotted paper reduces sensitivity.] Place the membrane in a plastic staining tray, and with the application side down, float or gently immerse in Staining reagent for 5 minutes. Then stir the solution gently for 1 minute. Remove the membrane, and destain in 5% acetic acid until the background clears. Compare the bands. The electropherogram obtained from the Test solution exhibits a major band that is identical in position to the band obtained from Standard solution 1. The band obtained from Standard solution 2 is clearly visible at a mobility similar to the band obtained from Standard solution 1. Any secondary band in the electropherogram of the Test solution is not more intense than the band obtained from Standard solution 2. Not more than 2% of any individual impurity is found. Document the results by taking a picture within 15 minutes of completion of destaining.
Limit of protein—
Alkaline cupric tartaric reagent—
Dissolve 200 mg of sodium tartrate dihydrate in 10 mL of water, and mark as Solution A. Dissolve 100 mg of cupric sulfate in 10 mL of water, and mark as Solution B. Dissolve 2.0 g of anhydrous sodium carbonate in 0.1 M sodium hydroxide, dilute with 0.1 M sodium hydroxide to 100 mL, and mark as Solution C. Mix well 1 mL of Solution A and 1 mL of Solution B, and to the mixture slowly add 100 mL of Solution C with stirring. Use within 24 hours, and discard afterwards.
Standard solution—
Transfer an accurately measured volume of 7 percent bovine serum albumin certified standard to a suitable container, and dilute quantitatively and stepwise with water to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 35 µg per mL.
Test solution—
Transfer an accurately weighed quantity of Chondroitin Sulfate Sodium, equivalent to 60 mg of the dried substance, to a 100-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in and dilute with water to volume, and mix.
Procedure—
Add 2.0 mL of freshly prepared Alkaline cupric tartaric reagent to test tubes containing 2.0 mL of water, 2.0 mL of the Test solution, or 2.0 mL of the Standard solution, and mix. After about 10 minutes, add 1.0 mL of Folin-Ciocalteu phenol TS, diluted with water (1:5) and prepared immediately before use, to each test tube, and mix immediately and vigorously. After 30 minutes, measure the absorbance of each solution at 750 nm against the blank. The absorbance of the Test solution is not greater than the absorbance of the Standard solution: not more than 6.0% of proteins is found, calculated on the dried basis.
Content of chondroitin sulfate sodium—
Cetylpyridinium chloride solution—
Prepare a solution of cetylpyridinium chloride in water having a concentration of about 1 mg per mL. Degas before use.
Diluent—
Weigh about 297 mg of monobasic potassium phosphate, 492 mg of dibasic potassium phosphate, and 250 mg of polysorbate 80, and transfer into a 1-L beaker. Dissolve in 1000 mL of water, and adjust with potassium hydroxide or phosphoric acid to a pH of 7.0 ± 0.2.
Standard solutions—
Prepare a solution having a known concentration of USP Chondroitin Sulfate Sodium RS in water, and dilute with water, quantitatively and stepwise if necessary, to obtain three Standard solutions having known concentrations of about 1.5 mg per mL, 1.0 mg per mL, and 0.5 mg per mL, respectively.
Test solution—
Transfer about 100 mg of dried Chondroitin Sulfate Sodium, accurately weighed, to a 100-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in 30 mL of water, dilute with water to volume, and mix.
Procedure—
Transfer 5.0 mL of each Standard solution and the Test solution to four separate titration vessels, and add about 25 mL of Diluent. Use a phototrode to determine the endpoint turbidimetrically, either at 420 nm, 550 nm, or 660 nm. Stir until a steady reading is obtained. Set the instrument to zero in absorbance mode. Titrate with Cetylpyridinium chloride solution. From a linear regression equation derived from the volumes of Cetylpyridinium chloride solution consumed, and the masses, in mg, of USP Chondroitin Sulfate Sodium RS in the aliquots of the respective Standard solutions, determine the mass of chondroitin sulfate sodium in the aliquot of the Test solution taken. Calculate the percentage of chondroitin sulfate sodium in the portion taken by the formula:
2000(M/W)
in which M is the mass of Chondroitin Sulfate Sodium found in the aliquot of the Test solution; and W is the weight, in mg, of Chondroitin Sulfate Sodium taken to prepare the Test solution.
1
Suitable cellulose acetate membranes for electrophoresis are available from Malta Chemetron SRL, Milano, Italy (www.maltachemetron.com); Fluka Chemical Corp., Milwaukee, WI; and DiaSys Corp., Waterbury, CT (www.diasys.com).
2
Suitable applications are available from DiaSys Corp., Waterbury, CT (www.diasys.com); and Helena Laboratories, Beaumont, TX (www.helena.com).
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
| Monograph | Larry N. Callahan, Ph.D.
Senior Scientist 1-301-816-8385 |
(BBPP05) Biologics and Biotechnology - Proteins and Polysaccharides |
| Reference Standards | Lili Wang, Technical Services Scientist 1-301-816-8129 RSTech@usp.org |
|
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Senior Scientist 1-301-816-8339 |
(MSA05) Microbiology and Sterility Assurance |
USP32–NF27 Page 980
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 30(6) Page 2068