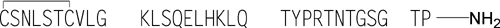Calcitonin Salmon
» Calcitonin Salmon is a polypeptide that has the same sequence as that of the hormone that regulates calcium metabolism and is secreted by the ultimobranchial gland of salmon. It is produced from either synthetic processes or microbial processes using recombinant DNA (rDNA) technology. The host cell-derived protein content and the host cell- or vector-derived DNA content of Calcitonin Salmon produced from an rDNA process are determined by validated methods. It contains not less than 90.0 percent and not more than 105.0 percent of calcitonin salmon, calculated on an acetic acid-free and dried basis.
note—One mg of acetic acid-free, anhydrous Calcitonin Salmon is equivalent to 6000 USP Calcitonin Salmon Units.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in tight containers. Store in a refrigerator or maintain in a frozen state, protected from light.
Labeling—
The labeling states that the material is synthetic or of recombinant DNA origin.
USP Reference standards  11
11 —
—
USP Calcitonin Salmon RS.
USP Calcitonin Salmon Related Compound A RS (N-acetyl-cys1-calcitonin).
(N-acetyl-cys1-calcitonin).
USP Calcitonin Salmon Related Compound B RS (calcitonin salmon-glycine).
USP Calcitonin Salmon RS.
USP Calcitonin Salmon Related Compound A RS
 (N-acetyl-cys1-calcitonin).
(N-acetyl-cys1-calcitonin).
USP Calcitonin Salmon Related Compound B RS (calcitonin salmon-glycine).
Identification—
The retention time of the major peak in the chromatogram of the Assay preparation corresponds to that of the Standard preparation, obtained as directed in the Assay.
Amino acid profile
(see Biotechnology-Derived Articles—Amino Acid Analysis  1052
1052 )—[note—This test needs to be performed only on material of synthetic origin. The concentration of amino acids in the Internal standard solution, the Standard amino acid solution, and the Standard solution and the amount of material used to prepare the Test solution can be adjusted depending on the method used for amino acid analysis. The concentrations given are based on analysis using Method 1.]
)—[note—This test needs to be performed only on material of synthetic origin. The concentration of amino acids in the Internal standard solution, the Standard amino acid solution, and the Standard solution and the amount of material used to prepare the Test solution can be adjusted depending on the method used for amino acid analysis. The concentrations given are based on analysis using Method 1.]
Internal standard solution—
Prepare a 1-mM solution of 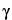 -aminobutyric acid.
-aminobutyric acid.
Standard amino acid solution—
Prepare a mixture containing equimolar amounts of ammonia and the l form of lysine, histidine, arginine, aspartic acid, threonine, serine, proline, valine, glutamic acid, glycine, leucine, and tyrosine, together with half the equimolar amount of l-cystine, in 0.1 M hydrochloric acid. The final concentration is about 2.5 mM for each amino acid.
Standard solution—
Transfer 5 mL of the Internal standard solution and 2 mL of the Standard amino acid solution into a 50-mL volumetric flask, dilute with 0.1 M hydrochloric acid to volume, and mix.
Test solution—
Place about 1.5 mg of an accurately weighed quantity of Calcitonin Salmon into a heavy-wall ignition tube, add 1.0 mL of 6 N hydrochloric acid, allow to cool, immerse the lower half of the tube in a freezing mixture until the contents are frozen, evacuate to approximately 10 µm of Hg, purge with nitrogen (repeat the evacuation and nitrogen purge three times), and seal the tube while it is under a 10 µm of Hg vacuum. Heat for 16 hours at 110 to 115
to 115 in an air oven. Cool, open the tube, dry in a vacuum desiccator, remove the contents, and allow to cool to room temperature. Dissolve in 0.1 M hydrochloric acid, transfer to a 10-mL volumetric flask, add 1 mL of Internal standard solution, dilute with 0.1 M hydrochloric acid to volume, and mix.
in an air oven. Cool, open the tube, dry in a vacuum desiccator, remove the contents, and allow to cool to room temperature. Dissolve in 0.1 M hydrochloric acid, transfer to a 10-mL volumetric flask, add 1 mL of Internal standard solution, dilute with 0.1 M hydrochloric acid to volume, and mix.
Procedure—
Standardize the amino acid analyzer, using the Standard solution. Inject the Test solution into the amino acid analyzer, and determine the relative proportion of amino acids.
Calculation of amino acid profile—
Express the content of each amino acid in moles, using an internal standard calibration technique. Calculate the relative proportions of the amino acids by taking as equivalent to 1 the sum of the number of moles of aspartic acid, glutamic acid, proline, glycine, valine, leucine, histidine, arginine, and lysine divided by 20. The requirements are met if the values fall within the following limits: aspartic acid, 1.8 to 2.2; glutamic acid, 2.7 to 3.3; proline, 1.7 to 2.3; glycine, 2.7 to 3.3; valine, 0.9 to 1.1; leucine, 4.5 to 5.3; histidine, 0.9 to 1.1; arginine, 0.9 to 1.1; lysine, 1.8 to 2.2; serine, 3.2 to 4.2; threonine, 4.2 to 5.2; tyrosine, 0.7 to 1.1; half cystine, 1.4 to 2.1.
Peptide mapping
(see Biotechnology-Derived Articles—Peptide Mapping  1055
1055 )—[note—This test needs to be performed only on material produced using rDNA technology.]
)—[note—This test needs to be performed only on material produced using rDNA technology.]
Solution A—
Prepare a filtered and degassed solution of water and trifluoroacetic acid (1000:1).
Solution B—
Prepare a filtered and degassed solution of acetonitrile, water, and trifluoroacetic acid (800:200:0.85).
Mobile phase—
Use variable mixtures of Solution A and Solution B as directed for Chromatographic system. Make adjustments to either solution as necessary (see System Suitability under Chromatography  621
621 ).
).
Trypsin solution—
Freshly prepare a solution containing 0.1 mg of trypsin (previously treated with l-1-tosylamido-2-phenylethyl chloromethyl ketone (TPCK) to remove chymotrypsin activity) per mL of water.
Tris buffer—
Prepare a solution containing 1 M tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane, 10 mM calcium chloride, and adjust with hydrochloric acid to a pH of 8.0.
Stopping solution—
Prepare a solution of water and trifluoroacetic acid (1:1).
Standard solution—
Prepare a solution containing 1.0 mg of USP Calcitonin Salmon RS per mL of water. Transfer 1 mL of this solution to a clean vial. Add 100 µL of Tris buffer and 50 µL of Trypsin solution, mix, and incubate at 2 to 8
to 8 for 16 to 20 hours. Quench the digestion by adding 10 µL of Stopping solution.
for 16 to 20 hours. Quench the digestion by adding 10 µL of Stopping solution.
Test solution—
Prepare a solution containing 1.0 mg of Calcitonin Salmon per mL of water. Proceed as directed for the Standard solution, beginning with “Transfer 1 mL of this solution”.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 214-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 25-cm column that contains packing L1. The flow rate is about 1.2 mL per minute. The chromatograph is programmed as follows.
)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 214-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 25-cm column that contains packing L1. The flow rate is about 1.2 mL per minute. The chromatograph is programmed as follows.
| Time (minutes) |
Solution A
(%) |
Solution B
(%) |
|
| 0–50 | 100®65 | 0®35 | linear gradient |
| 50–60 | 65®40 | 35®60 | linear gradient |
| 60–60.1 | 40®0 | 60®100 | linear gradient |
| 60.1–65.1 | 0 | 100 | isocratic |
| 65.1–65.2 | 0®100 | 100®0 | linear gradient |
| 65.2–80.2 | 100 | 0 | isocratic, re-equilibration |
Procedure—
[note—Condition the chromatographic system by running a blank gradient program prior to injecting the digests.] Separately inject equal volumes (about 20 µL) of the Standard solution and the Test solution, and record the chromatograms: the chromatographic profile of the Test solution is similar to that of the Standard solution.
Bioidentity—
RPMI 1640 with l-glutamine—
Prepare a mixture of the ingredients, in the quantities shown below, in sufficient water to obtain 1 L of RPMI 1640 with l-glutamine solution, and sterilize by filtration.
| Calcium Nitrate | 100.00 mg |
| Potassium Chloride | 400.00 mg |
| Magnesium Sulfate, Anhydrous | 48.84 mg |
| Potassium Chloride | 400 mg |
| Sodium Chloride | 6000 mg |
| Sodium Phosphate, Dibasic, Anhydrous | 800 mg |
| Sodium Bicarbonate | 2000 mg |
| Glucose | 2000 mg |
| Glycine | 10 mg |
| l-Arginine | 200 mg |
| l-Asparagine | 50 mg |
| l-Aspartic Acid | 20 mg |
| l-Cystine Dihydrochloride | 65 mg |
| l-Glutamic Acid | 20 mg |
| l-Glutamine | 300 mg |
| l-Histidine | 15 mg |
| l-Hydroxyproline | 20 mg |
| l-Isoleucine | 50 mg |
| l-Leucine | 50 mg |
| l-Lysine Hydrochloride | 40 mg |
| l-Methionine | 15 mg |
| l-Phenylalanine | 15 mg |
| l-Proline | 20 mg |
| l-Serine | 30 mg |
| l-Threonine | 20 mg |
| l-Tryptophan | 5 mg |
| l-Tyrosine Disodium Salt Dihydrate | 29 mg |
| l-Valine | 20 mg |
| Biotin | 0.2 mg |
| Choline Chloride | 3 mg |
| d-Calcium Pantothenate | 0.25 mg |
| Folic Acid | 1 mg |
| i-Inositol | 35 mg |
| Niacinamide | 1 mg |
| para-Aminobenzoic Acid | 1 mg |
| Pyridoxine Hydrochloride | 1 mg |
| Riboflavin | 0.2 mg |
| Thiamine Hydrochloride | 1 mg |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.005 mg |
Medium A (growth medium)—
Using aseptic technique, prepare the following tissue culture medium.
| RPMI 1640 with l-glutamine | 500 mL |
| Fetal bovine serum | 50 mL |
| 1 M HEPES | 5 mL |
| Penicillin/streptomycin solution (10,000 IU per mL/10 mg per mL) | 5 mL |
| Human insulin | 10 IU |
| Hydrocortisone | 0.5 mg |
Medium B (stimulation medium)—
Dissolve 5 g of albumin bovine serum (BSA) in 500 mL of 2 mM RPMI 1640 with l-glutamine.
2% BSA solution—
Dissolve 500 mg of albumin bovine serum in 25 mL of water. [note—Use within 1 day.]
Formic acid/BSA solution—
Add 25 mL of 0.1 M formic acid and 5 mL of 2% BSA solution to a 50-mL volumetric flask, dilute with water to volume, and mix. [note—Use within 2 days.]
Trypsin–EDTA solution (tetrasodium ethylenediaminetetraacetate)—
Prepare a sterile filtered solution containing 0.25% trypsin and 0.53 mM EDTA.
Dulbecco's phosphate buffered saline—
Dissolve 8 g of sodium chloride, 1.15 g of dibasic sodium phosphate, 0.2 g of monobasic potassium phosphate, 0.2 g of potassium chloride, 0.1 g of calcium chloride, and 0.1 g of magnesium chloride in 1 L of water.
Standard stock solution—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of USP Calcitonin Salmon RS in Formic acid/BSA solution to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 20 µg per mL.
Positive control solution—
Quantitatively dilute the Standard stock solution with Medium B to obtain a solution of USP Calcitonin Salmon RS having a known concentration of 1 ng per mL.
Negative control solution:
Medium B.
Standard solution A—
Quantitatively dilute the Standard stock solution with Medium B to obtain a solution of USP Calcitonin Salmon RS having a known concentration of 0.1 ng per mL.
Standard solution B—
Quantitatively dilute Standard solution A with Medium B to obtain a solution of USP Calcitonin Salmon RS having a known concentration of 0.033 ng per mL.
Standard solution C—
Quantitatively dilute Standard solution B with Medium B (1:2) to obtain a solution of USP Calcitonin Salmon RS having a known concentration of 0.011 ng per mL.
Standard solution D—
Quantitatively dilute Standard solution C with Medium B (1:2) to obtain a solution of USP Calcitonin Salmon RS having a known concentration of 0.0037 ng per mL.
Test stock solution—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of Calcitonin Salmon in Formic acid/BSA solution to obtain a solution having a concentration of about 20 µg per mL.
Test solution A—
Quantitatively dilute the Test stock solution with Medium B to obtain a solution of Calcitonin Salmon having a concentration of 0.1 ng per mL.
Test solution B—
Quantitatively dilute Test solution A with Medium B (1:2) to obtain a solution of Calcitonin Salmon having a concentration of 0.033 ng per mL.
Test solution C—
Quantitatively dilute Test solution B with Medium B (1:2) to obtain a solution of Calcitonin Salmon having a concentration of 0.011 ng per mL.
Test solution D—
Quantitatively dilute Test solution C with Medium B (1:2) to obtain a solution of Calcitonin Salmon having a concentration of 0.0037 ng per mL.
Cell culture preparation—
Prepare a cell culture of the human mammary tumor cell line T-47D. Cells are propagated using Medium A at 37 and 5% carbon dioxide. The medium is changed every 2 days, and cells are passaged every 5 to 9 days, using Trypsin–EDTA solution with a 1:4 subculture.
and 5% carbon dioxide. The medium is changed every 2 days, and cells are passaged every 5 to 9 days, using Trypsin–EDTA solution with a 1:4 subculture.
Cell suspension—
For the test, use a cell culture that is 5 to 9 days old. Remove the cell culture medium from the flask by aspiration, add 10 mL of Dulbecco's phosphate buffered saline, and rock the culture flask to rinse the entire monolayer. Remove the liquid by aspiration, add 2 mL of Trypsin–EDTA solution, spread over the entire monolayer, allow to stand for 3 to 5 minutes, and add 10 mL of Medium A. Homogenize the cell suspension using a pipet, transfer to a 15-mL polypropylene tube, centrifuge at about 220 × g for 5 minutes, pour off the supernatant, and resuspend the cell pellet in 10 mL of Medium A. Count the cells, and adjust the cell density through dilution, using Medium A, to 2.5 × 104 cells per mL.
Procedure—
Place 200 µL of the Cell suspension into each well of a 96-well culture plate (the tissue culture plate), and incubate for 18 to 24 hours at 37 and 5% carbon dioxide. Fill each well of an empty round-bottomed 96-well culture plate (the prepared plate) with 150 µL of one of the following solutions: Positive control solution, Negative control solution, Standard solutions A–D, and Test solutions A–D, so that each solution fills at least five wells on the prepared plate. After incubation, remove the culture medium from the tissue culture plate. Using an 8-channel or 12-channel pipet, rapidly transfer 100 µL of solution from each well of the prepared plate to each well of the tissue culture plate. Incubate for 15 minutes at ambient temperature, remove the solution from each well, stop stimulation by immediately adding an appropriate cell-lysis buffer, and quantitate cAMP produced within the cells, using a validated kit. Perform the test three times, using three different 96-well culture plates. [note—Some kits include a cell-lysis reagent and a sequestering agent for the cell-lysis reagent. The range of the test kit is between 0.05 ng and 10 ng per mL of cAMP. The number of cells used in the assay may vary depending on the validated kit used to quantitate cAMP.] Potency is determined by a 3-dose, 6-point parallel-line assay, using standard statistical methods. The calculation is carried out using both the lower three concentrations and the upper three concentrations. For the assay to be valid, the requirements for regression and parallelism must be met. If the requirements for validity are met to the same extent in both assessments (the lower and the higher assessments), the final result is determined from the concentration range that shows the higher value when the common slope is divided by the mean square error. The potency levels determined from all three performances of the test are homogeneous, and the confidence limits for all three determinations are between 64% and 156% of the calculated potency.
and 5% carbon dioxide. Fill each well of an empty round-bottomed 96-well culture plate (the prepared plate) with 150 µL of one of the following solutions: Positive control solution, Negative control solution, Standard solutions A–D, and Test solutions A–D, so that each solution fills at least five wells on the prepared plate. After incubation, remove the culture medium from the tissue culture plate. Using an 8-channel or 12-channel pipet, rapidly transfer 100 µL of solution from each well of the prepared plate to each well of the tissue culture plate. Incubate for 15 minutes at ambient temperature, remove the solution from each well, stop stimulation by immediately adding an appropriate cell-lysis buffer, and quantitate cAMP produced within the cells, using a validated kit. Perform the test three times, using three different 96-well culture plates. [note—Some kits include a cell-lysis reagent and a sequestering agent for the cell-lysis reagent. The range of the test kit is between 0.05 ng and 10 ng per mL of cAMP. The number of cells used in the assay may vary depending on the validated kit used to quantitate cAMP.] Potency is determined by a 3-dose, 6-point parallel-line assay, using standard statistical methods. The calculation is carried out using both the lower three concentrations and the upper three concentrations. For the assay to be valid, the requirements for regression and parallelism must be met. If the requirements for validity are met to the same extent in both assessments (the lower and the higher assessments), the final result is determined from the concentration range that shows the higher value when the common slope is divided by the mean square error. The potency levels determined from all three performances of the test are homogeneous, and the confidence limits for all three determinations are between 64% and 156% of the calculated potency.
Change to read:
Microbial enumeration tests
Water, Method Ic  921
921 :
not more than 10%.
:
not more than 10%.
Heavy metals, Method II  231
231 :
0.005%.
:
0.005%.
Acetic acid content  503
503 :
between 4% and 20%.
:
between 4% and 20%.
Test solution—
Transfer about 10 mg of Calcitonin Salmon, accurately weighed, to a 10-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in and dilute with Diluent to volume, and mix.
Related peptides and other related substances—
test 1—
[note—This test is performed on material produced by both chemical and recombinant DNA processes.]
Test solution—
Prepare as directed for the Assay preparation in the Assay.
Solution A, Solution B, Mobile phase, System suitability solution, and Chromatographic system—
Proceed as directed in the Assay.
Procedure—
Inject a volume (about 20 µL) of the Test solution into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the peak responses. Calculate the area percentage of each peak observed in the chromatogram. Disregard any peaks due to the solvent and any peaks whose area is less than 0.1% of the principal peak. No peak other than the principal peak constitutes more than 3.0% of the total area of all peaks. The sum of the areas of all the peaks apart from the principal peak is not greater than 5.0% of the sum of the areas of all the peaks including the principal peak.
test 2—
[note—This test needs to be performed only on material produced using rDNA technology.]
Phosphate buffer—
Dissolve 2.72 g of monobasic potassium phosphate in water, dilute with water to 1000 mL, and mix.
High salt phosphate buffer—
Dissolve 2.72 g of monobasic potassium phosphate and 29.2 g of sodium chloride in water, dilute with water to 1000 mL, and mix.
pH 3.0 Citrate buffer—
Dissolve 4.8 g of citric acid in 80 mL of water. Adjust with 1 M sodium hydroxide to a pH of 3.0, and dilute with water to 100.0 mL.
Solution A—
Prepare a filtered and degassed mixture of Phosphate buffer and acetonitrile (85:15). Adjust with 45% w/w potassium hydroxide to a pH of 5.0.
Solution B—
Prepare a filtered and degassed mixture of High salt phosphate buffer and acetonitrile (85:15). Adjust with 45% w/w potassium hydroxide to a pH of 4.6.
Mobile phase—
Use variable mixtures of Solution A and Solution B as directed for Chromatographic system. Make adjustments if necessary (see System Suitability under Chromatography  621
621 ).
).
Resolution solution—
Dissolve a suitable quantity of USP Calcitonin Salmon RS to obtain a solution containing 1 mg per mL of water. Combine equal volumes of this solution with USP Calcitonin Salmon Related Compound B RS. To 1 mL of this mixture add 100 µL of pH 3.0 Citrate buffer.
Test solution—
Dissolve a suitable quantity of Calcitonin Salmon in water to obtain a solution containing 0.5 mg per mL of water. To 1 mL of this solution add 100 µL of pH 3.0 Citrate buffer.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 214-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 20-cm column that contains packing L9. The flow rate is about 1.2 mL per minute. The chromatograph is programmed as follows.
)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 214-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 20-cm column that contains packing L9. The flow rate is about 1.2 mL per minute. The chromatograph is programmed as follows.
Chromatograph the Resolution solution, and measure the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the retention time for calcitonin salmon is about 9 minutes; the relative retention times are about 0.4 for [1,7-bis(3-sulfoalanine)]calcitonin salmon-glycine, 0.6 for [1,7-bis(3-sulfoalanine)]calcitonin salmon, and 0.9 for calcitonin salmon related compound B (calcitonin salmon-glycine); and the resolution, R, between calcitonin salmon and calcitonin salmon related compound B is not less than 3.0.
| Time (minutes) |
Solution A
(%) |
Solution B
(%) |
|
| 0–10 | 100®0 | 0®100 | linear gradient |
| 10–15 | 0 | 100 | isocratic |
| 15–15.1 | 0®100 | 100®0 | linear gradient |
| 15.1–22.1 | 100 | 0 | isocratic, re-equilibration |
Procedure—
Inject a volume (about 50 µL) of the Test solution into the chromatograph, and measure the peak responses. Calculate the percentage of each impurity in the portion of Calcitonin Salmon taken by the formula:
100 (ri / rs)
in which ri is the peak response for each impurity; and rs is the sum of the responses of all peaks: not more than 0.6% of calcitonin salmon related compound B is found; not more than 0.2% of [1,7-bis(3-sulfoalanine)]calcitonin salmon-glycine is found; not more than 0.2% of [1,7-bis(3-sulfoalanine)]calcitonin salmon is found; and not more than 0.1% of any other impurity is found.
Other requirements—
Where the label states that Calcitonin Salmon is sterile, it meets the requirements for Sterility  71
71 under Calcitonin Salmon Injection.
under Calcitonin Salmon Injection.
Assay—
Solution A—
Dissolve 3.26 g of tetramethylammonium hydroxide pentahydrate in 900 mL of water, add 100 mL of acetonitrile, and mix. Adjust with phosphoric acid to a pH of 2.5, pass through a filter having a 0.5-µm or finer porosity, and degas.
Solution B—
Dissolve 1.45 g of tetramethylammonium hydroxide pentahydrate in 400 mL of water, add 600 mL of acetonitrile, and mix. Adjust with phosphoric acid to a pH of 2.5, pass through a filter having a 0.5-µm or finer porosity, and degas.
Mobile phase—
Use variable mixtures of Solution A and Solution B as directed for Chromatographic system. Make adjustments if necessary (see System Suitability under Chromatography  621
621 ).
).
Standard preparation—
Transfer about 10.0 mg of USP Calcitonin Salmon RS, accurately weighed, into a 10-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in and dilute with Solution A to volume, and mix.
System suitability solution—
Dissolve the contents of a vial of USP Calcitonin Salmon Related Compound A RS in 0.4 mL of Solution A, add 0.1 mL of the Standard preparation, and mix.
Assay preparation—
Transfer about 10.0 mg of Calcitonin Salmon, accurately weighed, into a 10-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in and dilute with Solution A to volume, and mix.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 220-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 25-cm column that contains packing L1. The column temperature is maintained at about 65
)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 220-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 25-cm column that contains packing L1. The column temperature is maintained at about 65 . The flow rate is about 1 mL per minute. The chromatograph is programmed as follows.
. The flow rate is about 1 mL per minute. The chromatograph is programmed as follows.
Chromatograph the System suitability solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the relative retention times are about 1.15 for calcitonin salmon related compound A and 1.0 for calcitonin salmon; the resolution, R, between calcitonin salmon related compound A and calcitonin salmon is not less than 3; the tailing factor is not more than 2.5; and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 3%.
| Time (minutes) |
Solution A
(%) |
Solution B
(%) |
Elution |
| 0–30 | 72®48 | 28®52 | linear gradient |
| 30–32 | 48®72 | 52®28 | linear gradient |
| 32–55 | 72 | 28 | isocratic |
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 20 µL) of the Standard preparation and the Assay preparation into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the responses for the major peaks. Calculate the percentage of calcitonin salmon (C145H240N44O48S2) in the portion of Calcitonin Salmon taken by the formula:
P(WS / WU)(rU / rS)
in which P is the percentage of calcitonin salmon in USP Calcitonin Salmon RS; WS is the weight, in mg, of USP Calcitonin Salmon RS taken to prepare the Standard preparation; WU is the weight, in mg, of Calcitonin Salmon used to prepare the Assay preparation; and rU and rS are the main peak areas obtained from the Assay preparation and the Standard preparation, respectively.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
| Monograph | Larry N. Callahan, Ph.D.
Senior Scientist 1-301-816-8345 |
(BBPP05) Biologics and Biotechnology - Proteins and Polysaccharides |
| Reference Standards | Lili Wang, Technical Services Scientist 1-301-816-8129 RSTech@usp.org |
|
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Senior Scientist 1-301-816-8345 |
(MSA05) Microbiology and Sterility Assurance | |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Senior Scientist 1-301-816-8345 |
(MSA05) Microbiology and Sterility Assurance |
USP32–NF27 Page 1747
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 33(5) Page 878