- British Pharmacopoeia Volume I & II
- Monographs: Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Substances
Aspirin |
 |
(Acetylsalicylic Acid, Ph Eur monograph 0309)
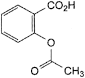
C9H8O4 180.2 50-78-2
Salicylate; non-selective cyclo-oxygenase inhibitor;antipyretic; analgesic; anti-inflammatory.
Effervescent Soluble Aspirin Tablets
Gastro-resistant Aspirin Tablets
Dispersible Co-codaprin Tablets
Ph Eur
2-(Acetyloxy)benzoic acid.
99.5 per cent to 101.0 per cent (dried substance).
White or almost white, crystalline powder or colourless crystals.
Slightly soluble in water, freely soluble in ethanol (96 per cent).
About 143 °C (instantaneous method).
First identification A, B.
Second identification B, C, D.
A. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison acetylsalicylic acid CRS.
B. To 0.2 g add 4 mL of dilute sodium hydroxide solution R and boil for 3 min. Cool and add 5 mL of dilute sulfuric acid R. A crystalline precipitate is formed. Filter, wash the precipitate and dry at 100-105 °C. The melting point (2.2.14) is 156 °C to 161 °C.
C. In a test tube mix 0.1 g with 0.5 g of calcium hydroxide R. Heat the mixture and expose to the fumes produced a piece of filter paper impregnated with 0.05 mL of nitrobenzaldehyde solution R. A greenish-blue or greenish-yellow colour develops on the paper. Moisten the paper with dilute hydrochloric acid R. The colour becomes blue.
D. Dissolve with heating about 20 mg of the precipitate obtained in identification test B in 10 mL of water R and cool. The solution gives reaction (a) of salicylates (2.3.1).
The solution is clear (2.2.1) and colourless (2.2.2, Method II).
Dissolve 1.0 g in 9 mL of ethanol (96 per cent) R.
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Prepare the solutions immediately before use.
Test solution Dissolve 0.100 g of the substance to be examined in acetonitrile for chromatography R and dilute to 10.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (a) Dissolve 50.0 mg of salicylic acid R (impurity C) in the mobile phase and dilute to 50.0 mL with the mobile phase. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 100.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (b) Dissolve 10 mg of salicylic acid R (impurity C) in the mobile phase and dilute to 10.0 mL with the mobile phase. To 1.0 mL of this solution add 0.2 mL of the test solution and dilute to 100.0 mL with the mobile phase.
- — size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
- — stationary phase: octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 µm).
Mobile phase phosphoric acid R, acetonitrile for chromatography R, water R (2:400:600 V/V/V).
Flow rate 1 mL/min.
Detection Spectrophotometer at 237 nm.
Injection 10 µL.
Run time 7 times the retention time of acetylsalicylic acid.
Identification of impurities Use the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) to identify the peak due to impurity C.
Relative retention With reference to acetylsalicylic acid (retention time = about 5 min): impurity A = about 0.7; impurity B = about 0.8; impurity C = about 1.3; impurity D = about 2.3; impurity E = about 3.2; impurity F = about 6.0.
System suitability Reference solution (b):
- — resolution: minimum 6.0 between the peaks due to acetylsalicylic acid and impurity C.
- — impurities A, B, C, D, E, F: for each impurity, not more than 1.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.15 per cent);
- — unspecified impurities: for each impurity, not more than 0.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.05 per cent);
- — total: not more than 2.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.25 per cent);
- — disregard limit: 0.3 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.03 per cent).
Maximum 20 ppm.
Dissolve 1.0 g in 12 mL of acetone R and dilute to 20 mL with water R. 12 mL of the solution complies with test B. Prepare the reference solution using lead standard solution (1 ppm Pb) obtained by diluting lead standard solution (100 ppm Pb) R with a mixture of 6 volumes of water R and 9 volumes of acetone R.
Maximum 0.5 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in vacuo.
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
In a flask with a ground-glass stopper, dissolve 1.000 g in 10 mL of ethanol (96 per cent) R. Add 50.0 mL of 0.5 M sodium hydroxide. Close the flask and allow to stand for 1 h. Using 0.2 mL of phenolphthalein solution R as indicator, titrate with 0.5 M hydrochloric acid. Carry out a blank titration.
1 mL of 0.5 M sodium hydroxide is equivalent to 45.04 mg of C9H8O4.
In an airtight container.
Specified impurities A, B, C, D, E, F.
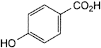
A. 4-hydroxybenzoic acid,
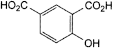
B. 4-hydroxybenzene-1,3-dicarboxylic acid (4-hydroxyisophthalic acid),
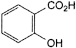
C. 2-hydroxybenzenecarboxylic acid (salicylic acid),
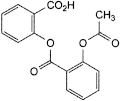
D. 2-[[2-(acetyloxy)benzoyl]oxy]benzoic acid (acetylsalicylsalicylic acid),
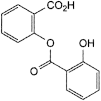
E. 2-[(2-hydroxybenzoyl)oxy]benzoic acid (salicylsalicylic acid),
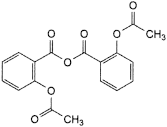
F. 2-(acetyloxy)benzoic anhydride (acetylsalicylic anhydride).
Ph Eur