- British Pharmacopoeia Volume I & II
- Monographs: Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Substances
Polyoxyl Castor Oil |
 |
(Macrogolglycerol Ricinoleate, Ph Eur monograph 1082)
Excipient.
Ph Eur
Contains mainly ricinoleyl glycerol ethoxylated with 30-50 molecules of ethylene oxide (nominal value), with small amounts of macrogol ricinoleate and of the corresponding free glycols. It results from the reaction of castor oil with ethylene oxide.
Clear, yellow viscous liquid or semi-solid.
Freely soluble in water, very soluble in methylene chloride, freely soluble in ethanol (96 per cent).
About 1.05.
500 mPa·s to 800 mPa·s at 25 °C.
A. Iodine value (see Tests).
B. Saponification value (see Tests).
C. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution To 1 g of the substance to be examined add 100 mL of a 100 g/L solution of potassium hydroxide R and boil under a reflux condenser for 30 min. Allow to cool. Acidify the solution with 20 mL of hydrochloric acid R. Shake the mixture with 50 mL of ether R and allow to stand until separation of the layers is obtained. Transfer the clear upper layer to a suitable tube, add 5 g of anhydrous sodium sulfate R, close the tube and allow to stand for 30 min. Filter and evaporate the filtrate to dryness on a water-bath. Dissolve 50 mg of the residue in 25 mL of ether R.
Reference solution Dissolve 50 mg of ricinoleic acid R in methylene chloride R and dilute to 25 mL with the same solvent.
Plate TLC octadecylsilyl silica gel plate R.
Mobile phase methylene chloride R, glacial acetic acid R, acetone R (10:40:50 V/V/V).
Application 2 µL.
Development Over a path of 8 cm.
Drying In a current of cold air.
Detection Spray with an 80 g/L solution of phosphomolybdic acid R in 2-propanol R and heat at 120 °C for 1-2 min.
Results The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in position and colour to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution.
D. Place about 2 g of the substance to be examined in a test-tube and add 0.2 mL of sulfuric acid R. Close the tube using a stopper fitted with a glass tube bent twice at right angles. Heat the tube until white fumes appear. Collect the fumes in 1 mL of mercuric chloride solution R. A white precipitate is formed and the fumes turn a filter paper impregnated with alkaline potassium tetraiodomercurate solution R black.
Dissolve 5.0 g in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 50 mL with the same solvent.
Solution S is not more opalescent than reference suspension III (2.2.1) and not more intensely coloured than reference solution BY5 (2.2.2, Method II). If intended for use in the manufacture of parenteral preparations, solution S is not more intensely coloured than reference solution BY6 (2.2.2, Method II).
Dissolve 2.0 g in a hot mixture of 10 mL of water R and 10 mL of ethanol (96 per cent) R. Add 0.1 mL of bromothymol blue solution R1. Not more than 0.5 mL of 0.1 M hydrochloric acid is required to change the colour of the indicator to yellow.
Maximum 2.0, determined on 5.0 g.
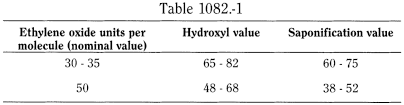
See Table 1082.-1.
25 to 35.
See Table 1082.-1.
Maximum 1 ppm of residual ethylene oxide and 10 ppm of residual dioxan.
Maximum 10 ppm.
12 mL of solution S, filtered if necessary, complies with test A. Prepare the reference solution using lead standard solution (1 ppm Pb) R.
Maximum 3.0 per cent, determined on 2.000 g.
Maximum 0.3 per cent, determined on 2.0 g.
Protected from light.
- — the amount of ethylene oxide reacted with castor oil (nominal value),
- — where applicable, that the substance is suitable for use in the manufacture of parenteral preparations.
Ph Eur