- British Pharmacopoeia Volume I & II
- Monographs: Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Substances
Nicotinamide |
 |
(Ph. Eur. monograph 0047)
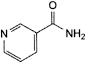
C6H6N2O 122.1 98-92-0
Component of vitamin B.
Ph Eur
Nicotinamide contains not less than 99.0 per cent and not more than the equivalent of 101.0 per cent of pyridine-3-carboxamide, calculated with reference to the dried substance.
A white or almost white, crystalline powder or colourless crystals, freely soluble in water and in ethanol.
First identification A, B.
Second identification A, C, D.
A. Melting point (2.2.14): 128 °C to 131 °C.
B. Examine by infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24), comparing with the spectrum obtained with nicotinamide CRS.
C. Boil 0.1 g with 1 mL of dilute sodium hydroxide solution R. Ammonia is evolved which is recognisable by its odour.
D. Dilute 2 mL of solution S (see Tests) to 100 mL with water R. To 2 mL of the solution, add 2 mL of cyanogen bromide solution R and 3 mL of a 25 g/L solution of aniline R and shake. A yellow colour develops.
Dissolve 2.5 g in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 50 mL with the same solvent.
Solution S is clear (2.2.1) and not more intensely coloured than reference solution BY7 (2.2.2, Method II).
The pH of solution S is 6.0 to 7.5.
Examine by thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27), using a TLC silica gel GF254 plate R.
Test solution Dissolve 0.4 g of the substance to be examined in a mixture of equal volumes of alcohol R and water R and dilute to 5.0 mL with the same mixture of solvents.
Reference solution Dilute 0.5 mL of the test solution to 200 mL with a mixture of equal volumes of alcohol R and water R.
Apply to the plate 5 µL of each solution. Develop over a path of 10 cm using a mixture of 4 volumes of water R, 45 volumes of ethanol R and 48 volumes of chloroform R. Allow the plate to dry and examine in ultraviolet light at 254 nm. Any spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution, apart from the principal spot, is not more intense than the spot in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution (0.25 per cent).
Dilute 12 mL of solution S to 18 mL with water R. 12 mL of the solution complies with limit test A for heavy metals (30 ppm). Prepare the standard using lead standard solution (1 ppm Pb) R.
Not more than 0.5 per cent, determined on 1.00 g by drying in vacuo for 18 h.
Not more than 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
Dissolve 0.250 g in 20 mL of anhydrous acetic acid R, heating slightly if necessary, and add 5 mL of acetic anhydride R. Titrate with 0.1 M perchloric acid, using crystal violet solution R as indicator until the colour changes to greenish-blue.
1 mL of 0.1 M perchloric acid is equivalent to 12.21 mg of C6H6N2O.
Ph Eur