| 参考文献No. | 486225 |
| 标题: | Synthesis and antiplatelet, antiinflammatory, and antiallergic activities of substituted 3-chloro-5,8-dimethoxy-1,4-naphthoquinone and related compounds |
| 作者: | Huang, L.-J.; Chang, F.C.; Lee, K.H.; Wang, J.P.; Teng, C.M.; Kuo, S.C. |
| 来源: | Bioorg Med Chem 1998,6(12),2261 |
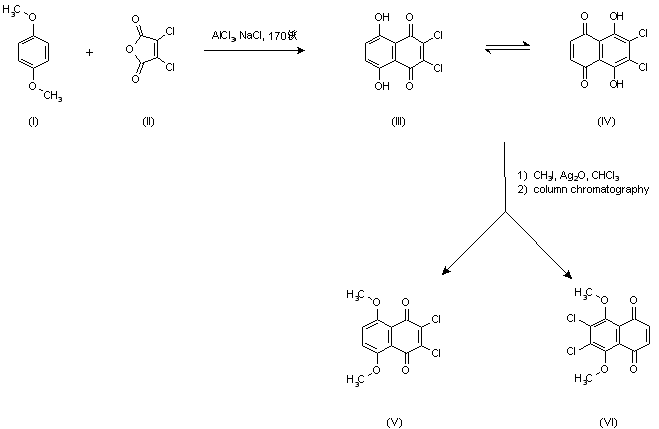 |
| 合成路线图解说明: Friedel Crafts condensation of p-dimethoxybenzene (I) with dichloromaleic anhydride (II) in a molten mixture of AlCl3 and NaCl yielded a dihydroxynaphthoquinone, assumed to exist as an equilibrium mixture between posicional isomers (III) and (IV). Subsequent methylation with CH3I in the presence of Ag2O yielded a mixture of dimethoxy quinones (V) and (VI) from which the target compound (V) was isolated by column chromatography. |
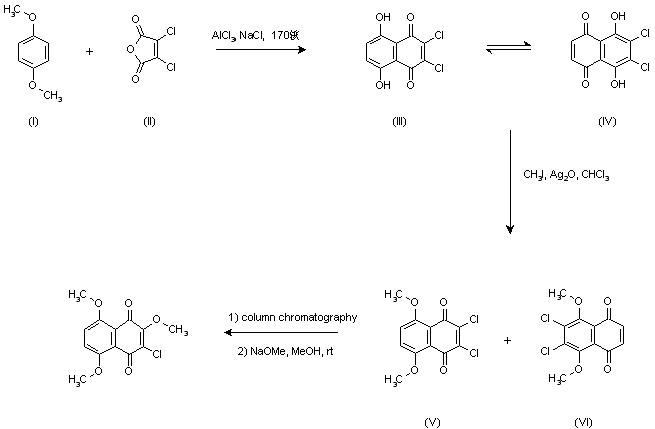 |
| 合成路线图解说明: Friedel Crafts condensation of p-dimethoxybenzene (I) with dichloromaleic anhydride (II) in a molten mixture of AlCl3 and NaCl yielded a dihydroxynaphthoquinone, assumed to exist as an equilibrium mixture between posicional isomers (III) and (IV). Subsequent methylation with CH3I in the presence of Ag2O yielded a mixture of dimethoxy quinones (V) and (VI), which were separated by column chromatography. Treatment of isomer (V) with NaOMe in MeOH then produced the target trimethoxy quinone. |
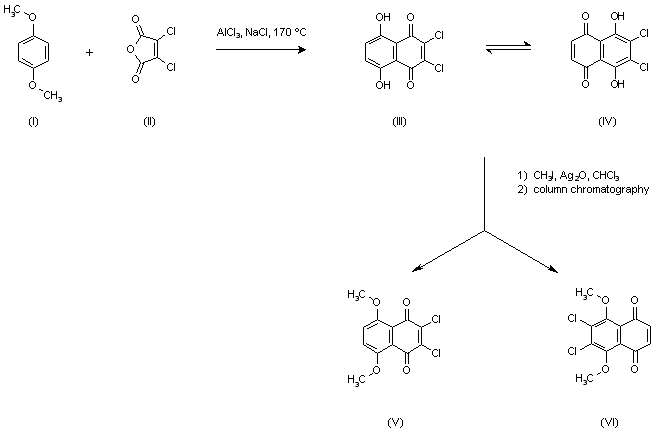 |
| 合成路线图解说明: Friedel Crafts condensation of p-dimethoxybenzene (I) with dichloromaleic anhydride (II) in a molten mixture of AlCl3 and NaCl yielded a dihydroxynaphthoquinone, assumed to exist as an equilibrium mixture between posicional isomers (III) and (IV). Subsequent methylation with CH3I in the presence of Ag2O yielded a mixture of dimethoxy quinones (V) and (VI) from which the target compound (VI) was isolated by column chromatography. |
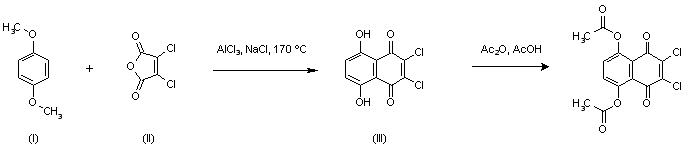 |
| 合成路线图解说明: Friedel Crafts condensation of p-dimethoxybenzene (I) with dichloromaleic anhydride (II) in a molten mixture of AlCl3 and NaCl yielded dihydroxynaphthoquinone (III). Subsequent acetylation with Ac2O and AcOH furnished the target diacetate. |
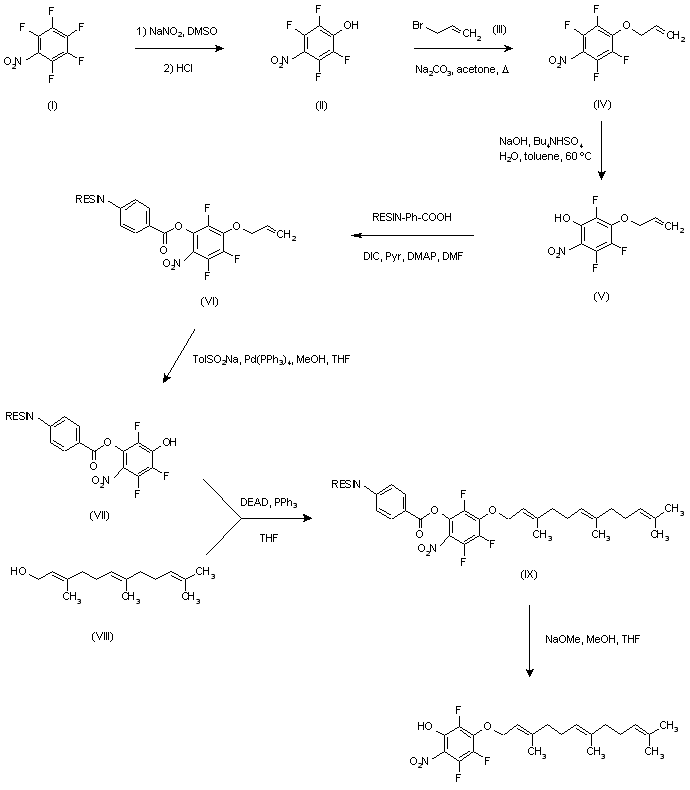 |
| 合成路线图解说明: Pentafluoronitrobenzene (I) was reacted with NaNO2 in DMSO to give phenol (II), which was then protected as the allyl ether (IV) upon treatment with allyl bromide (III) and Na2CO3 in refluxing acetone. Further displacement of one fluorine atom of (III) with NaOH under phase transfer conditions afforded phenol (V). This was then attached to a solid phase carboxypolystyrene resin using diisopropyl carbodiimide (DIC) in the presence of pyridine and DMAP. Deprotection of the allyl ether from the resulting resin ester (VI) was accomplished with sodium p-toluenesulfinate and palladium catalyst to yield phenol (VII). The Mitsunobu etherification of phenol (VII) with farnesol (VIII) furnished farnesyl ether (IX). The final product was then cleaved from the resin by treatment with NaOMe in MeOH-THF. |