Forskohlii
DEFINITION
Forskohlii consists of the dried roots of Plectranthus barbatus Andrews, also known as Coleus barbatus (Andrews) Benth. and Coleus forskohlii Briq. (Fam. Lamiaceae). It contains NLT 0.4% of forskolin, calculated on the dried basis.
IDENTIFICATION
• A. Thin-Layer Chromatographic Identification Test  201
201
Standard solution A:
50 µg/mL of USP Forskolin RS in acetonitrile. Sonicate for about 10 min.
Standard solution B:
5 mg/mL of USP Powdered Forskohlii Extract RS in acetonitrile. Sonicate for about 15 min, centrifuge, and use the supernatant.
Sample stock solution:
Use the Sample solution, prepared as directed in the test for Content of Forskolin.
Sample solution:
Dilute 10 mL of the Sample stock solution with acetonitrile to 25 mL.
Adsorbent:
Chromatographic silica gel with an average particle size of 10–15 µm (TLC plates)
Application volume:
10 µL as 4-mm bands
Developing solvent system:
Toluene and ethyl acetate (85:15)
Spray reagent:
5% vanillin in glacial acetic acid and 10% sulfuric acid in water (1:1)
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution A, Standard solution B, and Sample solution
Apply the Samples as bands to a suitable thin-layer chromatographic plate (see Chromatography  621
621 ). Use a saturated chamber. Develop the chromatograms until the solvent front has moved up about 90% of the plate. Remove the plate from the chamber, dry, spray with the Spray reagent, heat for 5–10 min at 105
). Use a saturated chamber. Develop the chromatograms until the solvent front has moved up about 90% of the plate. Remove the plate from the chamber, dry, spray with the Spray reagent, heat for 5–10 min at 105 , and examine under visible light.
, and examine under visible light.
Acceptance criteria:
The chromatogram of the Sample solution exhibits the following: a violet zone due to forskolin at an RF value of approximately 0.3, corresponding in color and RF to that in the chromatogram of Standard solution A; and a minor violet zone, a pink zone, and a brick red zone at RF values of approximately 0.1, 0.62, and 0.69, due to isoforskolin, 1,9-dideoxyforskolin and crocetindialdehyde, respectively. Zones detected in the Sample solution chromatogram correspond in position and color to zones in the chromatogram of Standard solution B. Other minor zones may be observed in the Sample solution and Standard solution B chromatograms.
• B.
The chromatogram of the Sample solution obtained in the test for Content of Forskolin shows a main peak at a retention time corresponding to that of forskolin in the chromatogram of Standard solution A. Identify other diterpene peaks in the Sample solution chromatogram by comparison with the chromatogram of Standard solution B and the reference chromatogram provided with the lot of USP Powdered Forskohlii Extract RS. The Sample solution chromatogram shows an additional peak corresponding to isoforskolin.
COMPOSITION
• Content of Forskolin
Solution A:
Use filtered and degassed acetonitrile.
Solution B:
Use filtered and degassed water.
Standard solution A:
Sonicate a quantity of USP Forskolin RS in acetonitrile to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 1.0 mg/mL.
Standard solution B:
5 mg/mL of USP Powdered Forskohlii Extract RS in acetonitrile, sonicate for about 15 min, centrifuge, and use the supernatant. Before injection, pass through a membrane filter of 0.45-µm or finer pore size.
Sample solution:
Transfer about 3.0 g of Forskohlii, finely powdered, to a 100-mL round-bottom flask fitted with a reflux condenser. Add 50 mL of acetonitrile, reflux on a water bath for 20 min, cool to room temperature, and decant the supernatant. Repeat until the last extract is colorless. Combine the extracts, filter, concentrate under vacuum, and adjust the volume with acetonitrile to 100 mL. Before injection, pass through a membrane filter of 0.45-µm or finer pore size, discarding the first 5 mL of the filtrate.
System suitability solution:
Standard solution A and 0.01% toluene in acetonitrile (1:1)
Mobile phase:
See the gradient table below.
| Time (min) |
Solution A (%) |
Solution B (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 45 | 55 |
| 25 | 45 | 55 |
| 28 | 95 | 5 |
| 35 | 95 | 5 |
| 36 | 45 | 55 |
| 45 | 45 | 55 |
Chromatographic system
Mode:
LC
Detector:
UV 220 nm
Column:
4.6-mm × 25-cm; 5-µm, 100 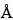
Column temperature:
30 ± 2
Flow rate:
1.8 mL/min
Injection size:
20 µL
System suitability
Samples:
Standard solution A, Standard solution B, and System suitability solution
[Note—The approximate relative retention times for isoforskolin and forskolin are 0.51 and 1.00, respectively. ]
Suitability requirements:
The chromatogram from Standard solution B is similar to the reference chromatogram provided with the lot of USP Powdered Forskohlii Extract RS being used.
Resolution:
NLT 1.5 between the forskolin and toluene peaks, System suitability solution
Relative standard deviation:
NMT 2% determined from the forskolin peak for replicate injections, Standard solution A
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution A, Standard solution B, and Sample solution
Using the chromatogram of Standard solution A, Standard solution B, and the reference chromatogram provided with the lot of USP Powdered Forskohlii Extract RS, identify the retention times of the peaks corresponding to isoforskolin and forskolin.
Calculate the percentage of forskolin in the portion of Forskohlii taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × 100
| rU | = | = peak response of forskolin from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak response of forskolin from Standard solution A |
| CS | = | = concentration of USP Forskolin RS in Standard solution A (mg/mL) |
| CU | = | = concentration of Forskohlii in the Sample solution (mg/mL) |
Acceptance criteria:
NLT 0.4% on the dried basis
IMPURITIES
Inorganic Impurities
• Heavy Metals, Method III  231
231 :
NMT 20 ppm
:
NMT 20 ppm
Organic Impurities
• Procedure 1: Articles of Botanical Origin, Foreign Organic Matters  561
561 :
NMT 2.0%
:
NMT 2.0%
• Procedure 2: Articles of Botanical Origin, General Method for Pesticide Residues Analysis  561
561 :
Meets the requirements
:
Meets the requirements
SPECIFIC TESTS
• Botanic Characteristics
Macroscopic:
Fresh root, pale pinkish yellow, cylindrical to subcylindrical, with tapering ends, 5–12 in length, 1–2 cm in diameter; surface rough, shows lateral rootlets or scars of rootlets and transversely running lenticels. Pharmacopeial article, dark brown; surface rough, irregularly cylindrical, longitudinally wrinkled, showing irregular grooves and prominent ridges; fracture short; cut surface is yellowish white; characteristic and pleasant aromatic odor, and slightly bitter to pungent taste.
Histology
Transverse section of roots:
Irregular circular in outline; showing narrow cork, 10–15 rows of tangentially elongated radially arranged cork cells; cortex composed of 10–15 rows of thin-wall parenchyma cells showing sclereids and crystals of calcium oxalate; vascular cambium in the form of a continuous ring; xylem showing narrow rays of vessels, few lignified fibers are present in older roots, 3–8 cell-wide medullary rays, and parenchyma showing few sclereids, oleoresin canals and simple starch grains; pith composed of parenchyma cells in young roots and is replaced by compactly arranged vessels, fibers, and tracheids in mature roots.
• Loss on Drying  731
731 :
Dry 1.0 g of finely powdered Forskohlii at 105
:
Dry 1.0 g of finely powdered Forskohlii at 105 for 3 h: it loses NMT 12.0% of its weight.
for 3 h: it loses NMT 12.0% of its weight.
• Articles of Botanical Origin, Total Ash  561
561 :
NMT 6%, determined on 1.0 g of finely powdered Forskohlii
:
NMT 6%, determined on 1.0 g of finely powdered Forskohlii
• Microbial Enumeration Tests  2021
2021 :
The total aerobic bacterial count does not exceed 105 cfu/g, the total combined molds and yeasts count does not exceed 103 cfu/g, and the bile-tolerant Gram-negative bacteria does not exceed 103 cfu/g.
:
The total aerobic bacterial count does not exceed 105 cfu/g, the total combined molds and yeasts count does not exceed 103 cfu/g, and the bile-tolerant Gram-negative bacteria does not exceed 103 cfu/g.
• Microbiological Procedures for Absence of Specified Microorganisms  2022
2022 :
Meets the requirements of the tests for absence of Salmonella species and Escherichia coli
:
Meets the requirements of the tests for absence of Salmonella species and Escherichia coli
• Articles of Botanical Origin, Test for Aflatoxins  561
561 :
Meets the requirements
:
Meets the requirements
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
• Packaging and Storage:
Preserve in well-closed containers, protected from light and moisture, and store at room temperature.
• Labeling:
The label states the Latin binomial and, following the official name, the parts of the plant contained in the article.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Maged H. Sharaf, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8318 |
(DS2010) Monographs - Dietary Supplements |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8339 |
(GCM2010) General Chapters - Microbiology | |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8339 |
(GCM2010) General Chapters - Microbiology | |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP35–NF30 Page 1298
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 36(3) Page 695