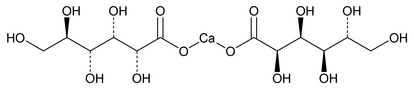
Calcium Gluconate
C12H22CaO14·H2O 448.39
d-Gluconic acid, calcium salt (2:1);
Calcium d-gluconate (1:2)

 [299-28-5].
[299-28-5].
Monohydrate

 [18016-24-5].
[18016-24-5].
(kal' see um gloo' koe nate).
C12H22CaO14·H2O 448.39
d-Gluconic acid, calcium salt (2:1);
Calcium d-gluconate (1:2)
Monohydrate
DEFINITION
Calcium Gluconate is anhydrous or contains one molecule of water of hydration. The anhydrous form contains NLT 98.0% and NMT 102.0% of calcium gluconate (C12H22CaO14), calculated on the dried basis. The monohydrate form contains NLT 99.0% and NMT 101.0% of calcium gluconate (C12H22CaO14·H2O) where labeled as intended for use in preparing injectable dosage forms, and NLT 98.5% and NMT 102.0% of calcium gluconate (C12H22CaO14·H2O) where labeled as not intended for use in preparing injectable dosage forms.
IDENTIFICATION
• A. Identification Tests—General, Calcium  191
191 :
A 20 mg/mL solution meets the requirements.
:
A 20 mg/mL solution meets the requirements.
• B. Thin-Layer Chromatography
Standard solution:
10 mg/mL of USP Potassium Gluconate RS
Sample solution:
10 mg/mL of Calcium Gluconate, heating in a water bath at 60 , if necessary, to dissolve
, if necessary, to dissolve
Chromatographic system
Mode:
TLC
Adsorbent:
0.25-mm layer of chromatographic silica gel
Application volume:
5 µL
Developing solvent system:
Alcohol, ethyl acetate, ammonium hydroxide, and water (50:10:10:30)
Spray reagent:
Dissolve 2.5 g of ammonium molybdate in 50 mL of 2 N sulfuric acid in a 100-mL volumetric flask. Add 1.0 g of ceric sulfate, swirl to dissolve, dilute with 2 N sulfuric acid to volume, and mix.
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Develop the chromatogram until the solvent front has moved about three-fourths of the length of the plate. Remove the plate from the chamber, and dry at 110 for 20 min. Allow to cool, and spray with the Spray reagent. Heat the plate at 110
for 20 min. Allow to cool, and spray with the Spray reagent. Heat the plate at 110 for about 10 min.
for about 10 min.
Acceptance criteria:
The principal spot of the Sample solution corresponds in color, size, and RF value to that of the Standard solution.
ASSAY
• Procedure
Sample:
800 mg of Calcium Gluconate
Blank:
150 mL of water containing 2 mL of 3 N hydrochloric acid
Titrimetric system
(See Titrimetry  541
541 .)
.)
Mode:
Direct titration
Titrant:
0.05 M edetate disodium VS
Endpoint detection:
Visual
Analysis:
Dissolve the Sample in 150 mL of water containing 2 mL of 3 N hydrochloric acid. While stirring, add 30 mL of Titrant from the titration buret. Add 15 mL of 1 N sodium hydroxide and 300 mg of hydroxy naphthol blue, and continue the titration to a blue endpoint. Perform the Blank determination.
Calculate the percentage of calcium gluconate (C12H22CaO14) in the Sample taken:
Result = {[(VS 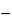 VB) × M × F]/W} × 100
VB) × M × F]/W} × 100
| VS | = | = Titrant volume consumed by the Sample (mL) |
| VB | = | = Titrant volume consumed by the Blank (mL) |
| M | = | = Titrant molarity (mM/mL) |
| F | = | = equivalency factor, 430.4 mg/mM |
| W | = | = Sample weight (mg) |
Acceptance criteria:
Anhydrous form, 98.0%–102.0%; monohydrate form, 99.0%–101.0% where labeled as intended for use in preparing injectable dosage forms; and monohydrate form, 98.5%–102.0% where labeled as not intended for use in preparing injectable dosage forms
IMPURITIES
• Arsenic, Method I  211
211
Test preparation:
Dissolve 1.0 g in a mixture of 10 mL of hydrochloric acid and 20 mL of water, and dilute with water to 55 mL.
Analysis:
Proceed as directed in the chapter, except to omit the addition of 20 mL of 7 N sulfuric acid.
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 3 ppm
• Chloride and Sulfate, Chloride  221
221 :
A 1.0-g portion shows no more chloride than corresponds to 0.07 mL of 0.020 N hydrochloric acid (0.005%). Where it is labeled as not intended for use in the preparation of injectable dosage forms, a 1.0-g portion shows no more chloride than corresponds to 1 mL of 0.020 N hydrochloric acid (0.07%).
:
A 1.0-g portion shows no more chloride than corresponds to 0.07 mL of 0.020 N hydrochloric acid (0.005%). Where it is labeled as not intended for use in the preparation of injectable dosage forms, a 1.0-g portion shows no more chloride than corresponds to 1 mL of 0.020 N hydrochloric acid (0.07%).
• Chloride and Sulfate, Sulfate  221
221 :
A 2.0-g portion dissolved in boiling water shows no more sulfate than corresponds to 0.1 mL of 0.020 N sulfuric acid (0.005%). Where it is labeled as not intended for use in the preparation of injectable dosage forms, a 2.0-g portion dissolved in boiling water shows no more sulfate than corresponds to 1 mL of 0.020 N sulfuric acid (0.05%).
:
A 2.0-g portion dissolved in boiling water shows no more sulfate than corresponds to 0.1 mL of 0.020 N sulfuric acid (0.005%). Where it is labeled as not intended for use in the preparation of injectable dosage forms, a 2.0-g portion dissolved in boiling water shows no more sulfate than corresponds to 1 mL of 0.020 N sulfuric acid (0.05%).
• Heavy Metals, Method II  231
231 :
NMT 10 ppm; NMT 20 ppm where Calcium Gluconate is labeled as not intended for use in the preparation of injectable dosage forms
:
NMT 10 ppm; NMT 20 ppm where Calcium Gluconate is labeled as not intended for use in the preparation of injectable dosage forms
• Limit of Iron
[Note—Calcium Gluconate labeled as not intended for use in the preparation of injectable dosage forms is exempt from this requirement. ]
Standard solutions:
0.2, 0.4, and 1.0 µg/mL of iron, prepared as follows. Separately transfer 2.0, 4.0, and 10.0 mL of Standard Iron Solution, prepared as directed under Iron  241
241 , to individual 100-mL volumetric flasks, each containing 1.37 g of calcium chloride, previously tested and shown to contain less than 5 ppm of iron, and dilute with 2 N hydrochloric acid to volume.
, to individual 100-mL volumetric flasks, each containing 1.37 g of calcium chloride, previously tested and shown to contain less than 5 ppm of iron, and dilute with 2 N hydrochloric acid to volume.
Sample solution:
Transfer 1.0 g of Calcium Gluconate to a 100-mL quartz glass flask. Add 20 mL of 12 N nitric acid, and heat to boiling until fumes are evolved. Add 0.5 mL of 30% hydrogen peroxide, and heat again until fumes are evolved. Repeat this process until the volume is reduced to about 5 mL. Cool, add 1.0 mL of perchloric acid, and heat to boiling. [Caution—Do not heat above 190 or evaporate to dryness because of danger of explosion.
] Transfer this solution to a 25-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with 2 N hydrochloric acid to volume.
or evaporate to dryness because of danger of explosion.
] Transfer this solution to a 25-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with 2 N hydrochloric acid to volume.
Blank solution:
Use 0.34 g of calcium chloride, previously tested and shown to contain less than 5 ppm of iron, instead of Calcium Gluconate, and prepare as directed under Sample solution.
Instrumental conditions
Mode:
Atomic absorption spectrophotometry
Analytical wavelength:
248.3 nm
Lamp:
Iron hollow-cathode
Flame:
Air–acetylene
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solutions, Sample solution, and Blank solution
Determine the absorbances of the Standard solutions and the Sample solution, using the Blank solution as the blank and making deuterium background corrections. Plot the absorbances of the Standard solutions versus concentration, in µg/mL, of iron, and draw the straight line best fitting the three plotted points. From the graph so obtained, determine the concentration, C, in µg/mL, of iron in the Sample solution.
Calculate the concentration of iron, in ppm, in the portion of Calcium Gluconate taken:
Result = (C × V)/W
| C | = | = concentration of iron in the Sample solution obtained from the regression equation (µg/mL) |
| V | = | = volume of Sample solution (mL) |
| W | = | = weight of Calcium Gluconate taken to prepare the Sample solution (g) |
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 5 ppm
• Limit of Magnesium and Alkali Metals
[Note—Calcium Gluconate labeled as not intended for use in preparing injectable dosage forms is exempt from this requirement. ]
Sample:
1.0 g
Analysis:
Dissolve completely the Sample in 100 mL of boiling water. Add 10 mL of ammonium chloride TS, 1 mL of ammonium hydroxide, and 50 mL of hot (maintained at 70 –80
–80 ) ammonium oxalate TS. Allow to stand for 4 h, dilute with water to 200 mL, and filter. Evaporate 100 mL of the filtrate to dryness, and ignite to constant weight.
) ammonium oxalate TS. Allow to stand for 4 h, dilute with water to 200 mL, and filter. Evaporate 100 mL of the filtrate to dryness, and ignite to constant weight.
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 0.4%: The weight of the residue does not exceed 2 mg.
• Limit of Phosphate
[Note—Calcium Gluconate labeled as not intended for use in the preparation of injectable dosage forms is exempt from this requirement. ]
Standard stock solution 1:
0.716 mg/mL of monobasic potassium phosphate
Standard stock solution 2:
Dilute 1.0 mL of Standard stock solution 1 with water to 100 mL.
Standard solution:
Dilute 2.0 mL of Standard stock solution 2 with water to 100 mL.
Sample stock solution:
To 10.0 g of Calcium Gluconate add 90 mL of hot water (70 –80
–80 ), and heat to boiling, with swirling, for 10 s to obtain a clear solution.
), and heat to boiling, with swirling, for 10 s to obtain a clear solution.
Sample solution:
Dilute 1 mL of the hot Sample stock solution with water to 100 mL.
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
To the Standard solution and Sample solution add 4 mL of sulfomolybdic acid TS, and mix. To both solutions add 0.1 mL of a freshly prepared mixture of 3 N hydrochloric acid and stronger acid stannous chloride TS (10:1), and mix.
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 0.01%: After 10 min any color in the Sample solution is not more intense than that in the Standard solution.
• Limit of Oxalate
[Note—Calcium Gluconate labeled as not intended for use in the preparation of injectable dosage forms is exempt from this requirement. ]
[Note—Use deionized water where water is indicated. ]
Mobile phase:
0.0017 M sodium bicarbonate and 0.0018 M sodium carbonate in water
Solution A:
0.0125 M sulfuric acid in water
Solution B:
Dilute 1 mL of hydrochloric acid with water to 1200 mL.
Standard solution:
1.5 µg/mL of sodium oxalate in Solution B
Sample solution:
20 mg/mL of Calcium Gluconate in Solution B. Sonicate if necessary.
Chromatographic system
Mode:
Ion chromatography
Detector:
Conductance
Columns
Analytical:
4-mm × 25-cm; 15-µm packing L12
Guard:
4-mm × 5-cm; 15-µm packing L12
Anion suppressor:
Micromembrane anion suppressor column connected in series with the guard and analytical columns. The anion suppressor column is equipped with a micromembrane that separates the Mobile phase from the Solution A flowing countercurrent to the Mobile phase at a rate of about 7 mL/min.
[Note—Condition the system for about 15 min with Mobile phase at a flow rate of 2 mL/min. ]
Flow rate:
2 mL/min
Injection size:
50 µL
System suitability
Sample:
Standard solution
Suitability requirements
Column efficiency:
NLT 2500 theoretical plates
Tailing factor:
NMT 1.2
Relative standard deviation:
NMT 2.0%
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of oxalate in the portion of Calcium Gluconate taken:
Result: (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × (Mr1/Mr2) × F × 100
| rU | = | = peak response for oxalate from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak response for oxalate from the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of sodium oxalate in the Standard solution (µg/mL) |
| CU | = | = concentration of Calcium Gluconate in the Sample solution (mg/mL) |
| Mr1 | = | = molecular weight of oxalate, 88.03 |
| Mr2 | = | = molecular weight of sodium oxalate, 134.00 |
| F | = | = conversion factor, 0.001 mg/µg |
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 0.01%
• Reducing Substances
Sample:
1.0 g of Calcium Gluconate
Blank:
20 mL of water
Titrimetric system
(See Titrimetry  541
541 .)
.)
Mode:
Residual titration
Titrant:
0.1 N iodine VS
Back titrant:
0.1 N sodium thiosulfate VS
Endpoint detection:
Visual
Analysis:
Transfer the Sample to a 250-mL conical flask, dissolve in 20 mL of hot water, cool, and add 25 mL of alkaline cupric citrate TS. Cover the flask, boil gently for 5 min, accurately timed, and cool rapidly to room temperature. Add 25 mL of 0.6 N acetic acid, 10.0 mL of Titrant, and 10 mL of 3 N hydrochloric acid, and titrate with the Back titrant, adding 3 mL of starch TS as the endpoint is approached. Perform the Blank determination.
Calculate the percentage of reducing substances (as dextrose) in the Sample taken:
Result = {[(VB 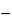 VS) × N × F]/W} × 100
VS) × N × F]/W} × 100
| VB | = | = Back titrant volume consumed by the Blank (mL) |
| VS | = | = Back titrant volume consumed by the Sample (mL) |
| N | = | = Back titrant normality (mEq/mL) |
| F | = | = equivalency factor, 27 mg/mEq |
| W | = | = Sample weight (mg) |
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 1.0%
SPECIFIC TESTS
• Loss on Drying  731
731 :
Dry a sample at 105
:
Dry a sample at 105 for 16 h: the anhydrous form loses NMT 3.0% of its weight; the monohydrate form, where labeled as intended for use in preparing injectable dosage forms, loses NMT 1.0% of its weight, and where labeled as not intended for use in preparing injectable dosage forms, loses NMT 2.0% of its weight.
for 16 h: the anhydrous form loses NMT 3.0% of its weight; the monohydrate form, where labeled as intended for use in preparing injectable dosage forms, loses NMT 1.0% of its weight, and where labeled as not intended for use in preparing injectable dosage forms, loses NMT 2.0% of its weight.
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
• Packaging and Storage:
Preserve in well-closed containers.
• Labeling:
Label it to indicate whether it is anhydrous or monohydrate. Where the quantity of calcium gluconate is indicated in the labeling of any solution containing Calcium Gluconate, this shall be understood to be in terms of anhydrous calcium gluconate (C12H22CaO14). Calcium Gluconate intended for use in preparing injectable dosage forms is so labeled. Calcium Gluconate not intended for use in preparing injectable dosage forms is so labeled; in addition, it may be labeled also as intended for use in preparing oral dosage forms.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Huy T. Dinh, M.S.
Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8594 |
(DS2010) Monographs - Dietary Supplements |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP35–NF30 Page 2453
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 27(6) Page 3258