Wheat Bran
» Wheat Bran is the outer fraction of the cereal grain, comprising the pericarp, seed coat (testa), nucellar tissue, and aleurone layer, and is derived from Triticum aestivum Linné, T. compactum Host, T. durum Desf., and other common einkorn and emmer wheat cultivars. It is obtained by the milling and processing of the whole wheat grain meeting U.S. Standards for Number 1 wheat (7 CFR 810.2201). It contains not less than 36.0 percent of dietary fiber.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in well-closed containers, secured against insect attack (see Preservation under Vegetable and Animal Substances in the General Notices).
Identification—
When examined microscopically, the following components of Wheat Bran are visible. Fragments of aleurone and nucellar layers (about 60% of the components) and fragments of seed coat and pericarp (about 40%). Aleurone and nucellar tissues composed of a usually single layer of thick-walled, isodiametric, translucent cells having conspicuous protoplasm and a single, inconspicuous layer of thick-walled, nearly transparent cells. Inconspicuous seed coat, consisting of two layers of thin-walled cells crossing at roughly right angles to each other. Pericarp composed of an inconspicuous endocarp layer of elongated, thick-walled tube cells; a cross layer with cells longer than wide, arranged side-by-side in rows, having thick, highly pitted side and end walls; and epicarp and hypoderm layers with cells longer than wide, arranged alternately in rows and having thick, highly pitted side and end walls. Epicarp and hypoderm cells larger than and crossing at right angles to the cells of the cross layer. A few trichomes also present, with lumens narrower than the thickness of their cell walls and originating from isodiametric-polygonal epicarp cells. If micronized, the original structures are mostly destroyed.
Microbial enumeration tests  61
61 and Tests for specified microorganisms
and Tests for specified microorganisms  62
62 —
The total aerobic microbial count does not exceed 10,000 cfu per g, and it meets the requirements of the test for the absence of Salmonella species and Escherichia coli.
—
The total aerobic microbial count does not exceed 10,000 cfu per g, and it meets the requirements of the test for the absence of Salmonella species and Escherichia coli.
Water, Method III, Procedure for Articles of Botanical Origin,  921
921 —
It loses not more than 12% of its weight.
—
It loses not more than 12% of its weight.
Total ash  561
561 :
not more than 8%.
:
not more than 8%.
Heavy metals, Method II  231
231 :
0.004%.
:
0.004%.
Absence of peroxidase activity—
Transfer about 1 g of Wheat Bran to a test tube, and add 50 mL of water. Add, in the order specified, 2 mL of 5.68 mM erythorbic acid, 3 mL of 0.69 mM dichloroindophenol, and 0.1 mL of 1.2% hydrogen peroxide, each freshly prepared. Stopper the test tube tightly, and shake until the sample is dissolved. Place into a water bath at 38 for 5 minutes: no color change is observed, indicating the absence of peroxidase activity.
for 5 minutes: no color change is observed, indicating the absence of peroxidase activity.
Limit of fat—
Transfer about 2 g of Wheat Bran, previously dried in a vacuum oven at 100 for 5 hours and accurately weighed, to an extraction thimble, and mix with an equivalent quantity of dry, clean sand. Place a fat-free cotton or glass wool plug on top of the thimble. Place the thimble in a continuous-extraction apparatus provided with a tared collection flask. Pour about 75 mL of solvent hexane through the sample into the collection flask. Extract at a condensation rate of 5 to 6 drops per second for 4 hours, then at a rate of 2 to 3 drops per second for the next 16 hours. Detach the collection flask, carefully evaporate the solvent, and dry the collection flask and its contents in a drying oven at 100
for 5 hours and accurately weighed, to an extraction thimble, and mix with an equivalent quantity of dry, clean sand. Place a fat-free cotton or glass wool plug on top of the thimble. Place the thimble in a continuous-extraction apparatus provided with a tared collection flask. Pour about 75 mL of solvent hexane through the sample into the collection flask. Extract at a condensation rate of 5 to 6 drops per second for 4 hours, then at a rate of 2 to 3 drops per second for the next 16 hours. Detach the collection flask, carefully evaporate the solvent, and dry the collection flask and its contents in a drying oven at 100 for 30 minutes to constant weight. Calculate the percentage of the extract (crude fat) in the portion of Wheat Bran taken: not more than 6% is found.
for 30 minutes to constant weight. Calculate the percentage of the extract (crude fat) in the portion of Wheat Bran taken: not more than 6% is found.
Limit of insect infestation—
Prepare a smooth slurry by transferring about 50 g of Wheat Bran to a 1 L beaker and adding 500 mL of 1.5 N hydrochloric acid. Add 50 mL of light mineral oil, and carefully heat to boiling on a hot plate. Boil for 10 minutes to digest, stirring occasionally to prevent scorching. Remove from the hot plate, and stir for 5 minutes with a magnetic stirrer, increasing the stirring speed until a vortex is formed without visible splashing. Quantitatively transfer the contents of the beaker to a separatory funnel with the aid of hot water. Allow to stand for 30 minutes, stirring gently with a glass rod several times during the first 10 minutes. Drain the lower layer to about 2.5 cm from the layer interface. Wash the funnel with hot water, and allow 5 minutes for the layers to separate. Drain the lower layer and wash with cold water several times until the lower phase is clear. Filter the contents of the funnel through ruled filter paper with the aid of a Büchner funnel and suction. Thoroughly rinse the separatory funnel with water and a detergent solution, filtering each rinse through the same paper. Examine the ruled filter paper under a microscope at 30× magnification: not more than 25 insect fragments are seen.
Limit of protein—
Place about 1 g of Wheat Bran, accurately weighed, in a 500-mL Kjeldahl flask, and proceed as directed for Method I under Nitrogen Determination  461
461 . Multiply the percent of nitrogen found by 6.31: not more than 18.5% is found.
. Multiply the percent of nitrogen found by 6.31: not more than 18.5% is found.
Content of total dietary fiber—
Phosphate buffer—
Prepare a pH 6.0 phosphate buffer (see Buffer Solutions under Solutions in the section Reagents, Indicators, and Solutions).
Protease solution—
Dissolve 5 mg of protease in 0.1 mL of Phosphate buffer.
Sample preparation—
Prepare two samples in parallel. In order to correct for any contribution from reagents, also perform examinations of blanks, which are treated similarly to the samples. Proceed as directed for Limit of fat. Mill to a coarse powder, and store in a desiccator.
Procedure—
Transfer about 1.0 g of each Sample preparation, accurately weighed, into separate 400-mL, tall-form beakers. Add 50 mL of Phosphate buffer, and adjust the pH, if necessary, to 6.0 ± 0.1. Add 0.2 mL of heat-stable 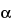 -amylase solution. Cover the beaker with aluminum foil, place in a boiling water bath for 15 minutes at 100
-amylase solution. Cover the beaker with aluminum foil, place in a boiling water bath for 15 minutes at 100 , shaking gently every 5 minutes, and cool to room temperature. Adjust with about 10 mL of 0.275 N sodium hydroxide solution to a pH of 7.5 ± 0.1. Add freshly prepared Protease solution, cover the beaker with aluminum foil, and incubate for 30 minutes at 60
, shaking gently every 5 minutes, and cool to room temperature. Adjust with about 10 mL of 0.275 N sodium hydroxide solution to a pH of 7.5 ± 0.1. Add freshly prepared Protease solution, cover the beaker with aluminum foil, and incubate for 30 minutes at 60 with continuous agitation. Cool, and add about 10 mL of 0.325 N hydrochloric acid and adjust to a pH of 4.5 ± 0.2. Add 0.3 mL of amyloglucosidase, cover with aluminum foil, and incubate for 20 minutes at 60
with continuous agitation. Cool, and add about 10 mL of 0.325 N hydrochloric acid and adjust to a pH of 4.5 ± 0.2. Add 0.3 mL of amyloglucosidase, cover with aluminum foil, and incubate for 20 minutes at 60 with continuous agitation. Heat 280 mL of alcohol to 60
with continuous agitation. Heat 280 mL of alcohol to 60 , add to the digest, and allow the precipitate to form at room temperature for 60 minutes. Place 0.5 g of chromatographic siliceous earth in a crucible with fritted disk, dry at 130
, add to the digest, and allow the precipitate to form at room temperature for 60 minutes. Place 0.5 g of chromatographic siliceous earth in a crucible with fritted disk, dry at 130 to constant weight, and weigh. Wet the chromatographic siliceous earth in the crucible by using a stream of 78% alcohol from a washing bottle, and apply suction to evenly distribute the chromatographic siliceous earth over the fritted disk. Maintain suction, and quantitatively transfer the enzyme digest precipitate to the crucible. Wash the residue successively with three 20-mL portions of 78% alcohol, two 10-mL portions of alcohol, and two 10-mL portions of acetone. In some cases, gums may form during filtration, trapping liquid in residue. If so, break the surface film with a spatula to improve filtration. Dry the crucible containing the residue at 105
to constant weight, and weigh. Wet the chromatographic siliceous earth in the crucible by using a stream of 78% alcohol from a washing bottle, and apply suction to evenly distribute the chromatographic siliceous earth over the fritted disk. Maintain suction, and quantitatively transfer the enzyme digest precipitate to the crucible. Wash the residue successively with three 20-mL portions of 78% alcohol, two 10-mL portions of alcohol, and two 10-mL portions of acetone. In some cases, gums may form during filtration, trapping liquid in residue. If so, break the surface film with a spatula to improve filtration. Dry the crucible containing the residue at 105 in an air oven for 16 hours, cool in a desiccator, and determine the weight of the residue. Determine the percentage of protein in the first Sample preparation as directed for Limit of protein. Incinerate the residue from the second Sample preparation as directed for Total Ash under Articles of Botanical Origin
in an air oven for 16 hours, cool in a desiccator, and determine the weight of the residue. Determine the percentage of protein in the first Sample preparation as directed for Limit of protein. Incinerate the residue from the second Sample preparation as directed for Total Ash under Articles of Botanical Origin  561
561 . Calculate the corrected weight, W, of the sample residue by the formula:
. Calculate the corrected weight, W, of the sample residue by the formula:
WU (1 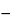 PU / 100
PU / 100 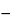 AU / 100)
AU / 100) 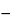 WB (1
WB (1 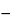 PB / 100
PB / 100 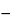 AB / 100)
AB / 100)
in which WU and WB are the average weights of the sample residues and the blank residues, respectively; PU and PB are percentages of protein present in the sample and in the blank, respectively; and AU and AB are percentages of ash found in the sample and in the blank, respectively. Then calculate the percentage of the total dietary fiber in the portion of Wheat Bran taken by the formula:
100W / WI
in which WI is the weight of the Sample preparation taken. Correct the final percentage of the total dietary fiber for fat and for water: not less than 36.0% is found.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
| Monograph | Maged H. Sharaf, Ph.D.
Senior Scientist 1-301-816-8318 |
(DSB05) Dietary Supplements - Botanicals |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Senior Scientist 1-301-816-8339 |
(MSA05) Microbiology and Sterility Assurance | |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Senior Scientist 1-301-816-8339 |
(MSA05) Microbiology and Sterility Assurance |
USP32–NF27 Page 3873