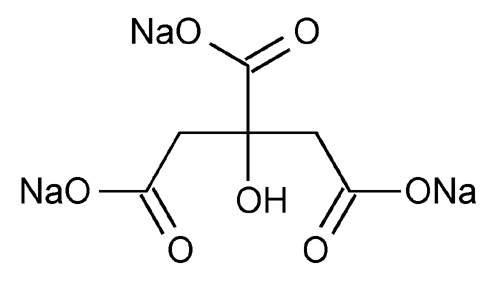
Sodium Citrate
1,2,3-Propanetricarboxylic acid, 2-hydroxy-, trisodium salt.
Trisodium citrate (anhydrous)
Trisodium citrate dihydrate 294.10
» Sodium Citrate is anhydrous or contains two molecules of water of hydration. It contains not less than 99.0 percent and not more than 100.5 percent of C6H5Na3O7, calculated on the anhydrous basis.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in tight containers.
Labeling—
Label it to indicate whether it is anhydrous or hydrous.
Identification—
B:
Upon ignition, it yields an alkaline residue which effervesces when treated with 3 N hydrochloric acid.
Alkalinity—
A solution of 1.0 g in 20 mL of water is alkaline to litmus paper, but after the addition of 0.20 mL of 0.10 N sulfuric acid no pink color is produced by 1 drop of phenolphthalein TS.
Water, Method III  921
921 —
Dry it at 180
—
Dry it at 180 for 18 hours: the anhydrous form loses not more than 1.0%, and the hydrous form between 10.0% and 13.0%, of its weight.
for 18 hours: the anhydrous form loses not more than 1.0%, and the hydrous form between 10.0% and 13.0%, of its weight.
Tartrate—
To a solution of 1 g in 2 mL of water add 1 mL of potassium acetate TS and 1 mL of 6 N acetic acid. Rub the wall of the tube with a glass rod: no crystalline precipitate is formed.
Heavy metals  231
231 —
Dissolve a portion equivalent to 4.4 g of anhydrous sodium citrate in enough water to make 50 mL of stock solution. Transfer 12 mL of this stock solution to a 50-mL color-comparison tube (Test Preparation). Transfer 11 mL of the stock solution to a second 50-mL color-comparison tube containing 1.0 mL of Standard Lead Solution (Monitor Preparation). Transfer 1.0 mL of Standard Lead Solution and 11 mL of water to a third 50-mL color-comparison tube (Standard Preparation). Proceed as directed for Procedure, omitting the dilution to 50 mL: the limit is 0.001%.
—
Dissolve a portion equivalent to 4.4 g of anhydrous sodium citrate in enough water to make 50 mL of stock solution. Transfer 12 mL of this stock solution to a 50-mL color-comparison tube (Test Preparation). Transfer 11 mL of the stock solution to a second 50-mL color-comparison tube containing 1.0 mL of Standard Lead Solution (Monitor Preparation). Transfer 1.0 mL of Standard Lead Solution and 11 mL of water to a third 50-mL color-comparison tube (Standard Preparation). Proceed as directed for Procedure, omitting the dilution to 50 mL: the limit is 0.001%.
Assay—
Transfer about 350 mg of Sodium Citrate, previously dried at 180 for 18 hours and accurately weighed, to a 250-mL beaker. Add 100 mL of glacial acetic acid, stir until completely dissolved, and titrate with 0.1 N perchloric acid VS, determining the endpoint potentiometrically. Perform a blank determination, and make any necessary correction. Each mL of 0.1 N perchloric acid is equivalent to 8.602 mg of C6H5Na3O7.
for 18 hours and accurately weighed, to a 250-mL beaker. Add 100 mL of glacial acetic acid, stir until completely dissolved, and titrate with 0.1 N perchloric acid VS, determining the endpoint potentiometrically. Perform a blank determination, and make any necessary correction. Each mL of 0.1 N perchloric acid is equivalent to 8.602 mg of C6H5Na3O7.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
| Monograph | Sujatha Ramakrishna, Ph.D.
Scientist 1-301-816-8349 |
(MDCV05) Monograph Development-Cardiovascular |
USP32–NF27 Page 3572