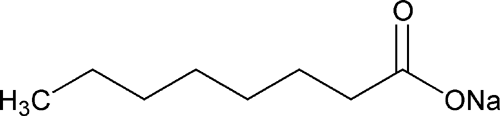
Sodium Caprylate
» Sodium Caprylate contains not less than 99.0 percent and not more than 101.0 percent of C8H15NaO2, calculated on the anhydrous basis.
Appearance of solution—
Dissolve 2.5 g of Sodium Caprylate in 25.0 mL of freshly boiled and cooled water: the resulting solution is clear and colorless, and if not, not more intensely colored than a reference solution prepared as follows:
Reference stock solution—
Pipet 30.0 mL of ferric chloride CS, 30.0 mL of cobaltous chloride CS, and 24.0 mL of cupric sulfate CS into a 100-mL volumetric flask. Dilute with 1% (w/v) hydrochloric acid to volume, and mix.
Reference solution—
Pipet 1.0 mL of the Reference stock solution into a 100-mL volumetric flask. Dilute with 1% (w/v) hydrochloric acid to volume, and mix.
Identification—
A:
The retention time of the major peak in the chromatogram of Test solution 1 corresponds to that in the chromatogram of the Reference solution, as obtained in the test for Chromatographic purity.
B:
Proceed as directed below.
Methoxyphenylacetic reagent—
Dissolve 2.7 g of methoxyphenylacetic acid in 6 mL of 10% tetramethylammonium hydroxide solution in methanol, and add 20 mL of alcohol. Store in a polyethylene container.
Procedure—
Dissolve about 20 mg of Sodium Caprylate in 0.5 mL of water, add 1.5 mL of Methoxyphenylacetic reagent, and cool in ice water for 30 minutes. A voluminous, white, crystalline precipitate is formed. Place in water at 20 , and stir for 5 minutes. The precipitate does not disappear. Add 1 mL of ammonia TS. The precipitate dissolves completely. Add 1 mL of ammonium carbonate solution (16 in 100): no precipitate is formed.
, and stir for 5 minutes. The precipitate does not disappear. Add 1 mL of ammonia TS. The precipitate dissolves completely. Add 1 mL of ammonium carbonate solution (16 in 100): no precipitate is formed.
pH  791
791 :
between 8.0 and 10.5, in a solution obtained in the test for Appearance of solution.
:
between 8.0 and 10.5, in a solution obtained in the test for Appearance of solution.
Water, Method I  921
921 :
not more than 3.0%.
:
not more than 3.0%.
Heavy metals, Method II  231
231 —
Dissolve 2.0 g of Sodium Caprylate in 10 mL of glacial acetic acid, add 10 mL of alcohol, and use 12 mL of the solution obtained as the Test Preparation. Prepare the Standard Preparation using 1 mL of Standard Lead Solution and 9 mL of a mixture of glacial acetic acid and alcohol (1:1). The limit is 5 µg per g.
—
Dissolve 2.0 g of Sodium Caprylate in 10 mL of glacial acetic acid, add 10 mL of alcohol, and use 12 mL of the solution obtained as the Test Preparation. Prepare the Standard Preparation using 1 mL of Standard Lead Solution and 9 mL of a mixture of glacial acetic acid and alcohol (1:1). The limit is 5 µg per g.
Chromatographic purity—
Reference solution—
Transfer 10 mg of USP Caprylic Acid RS to a 10-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with ethyl acetate to volume.
Test solution 1—
Dissolve 116 mg of Sodium Caprylate in 5 mL of water, add 1 mL of dilute sulfuric acid (1 in 35), and extract with 10 mL of ethyl acetate. Separate the organic layer, and dry it over anhydrous sodium sulfate.
Test solution 2—
Dilute 1.0 mL of Test solution 1 with ethyl acetate to 100 mL, transfer 5.0 mL of the solution obtained, and dilute with ethyl acetate to 50 mL.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
The gas chromatograph is equipped with a flame-ionization detector, a split injection system with a split ratio of about 1:100, and a 0.25-mm × 30-m fused silica column coated with a 0.25-µm layer of phase G25. The carrier gas is helium, flowing at a rate of 1.5 mL per minute. The chromatograph is programmed as follows. Initially the temperature of the column is equilibrated at 100
)—
The gas chromatograph is equipped with a flame-ionization detector, a split injection system with a split ratio of about 1:100, and a 0.25-mm × 30-m fused silica column coated with a 0.25-µm layer of phase G25. The carrier gas is helium, flowing at a rate of 1.5 mL per minute. The chromatograph is programmed as follows. Initially the temperature of the column is equilibrated at 100 , then 1 minute after the injection, the temperature is increased at a rate of 5
, then 1 minute after the injection, the temperature is increased at a rate of 5 per minute to 220
per minute to 220 , and maintained at 220
, and maintained at 220 for another 10 minutes. The injection port temperature and the detector temperature are maintained at 250
for another 10 minutes. The injection port temperature and the detector temperature are maintained at 250 . Chromatograph Test solution 2, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the signal-to-noise ratio of the principal peak is not less than 5.
. Chromatograph Test solution 2, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the signal-to-noise ratio of the principal peak is not less than 5.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 1 µL) of the Reference solution, Test solution 2, and Test solution 1 into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the responses for the major peaks. Disregard any peaks with an area less than half of the area of the principal peak from Test solution 2, and any peak due to the solvent. Calculate the percentage of each impurity in the portion of Sodium Caprylate taken by the formula:
100(ri / rs)
in which ri is the peak response of the individual impurity, and rs is the sum of the responses of all the peaks: not more than 0.3% of any impurity is found, and the sum of all the impurities found is not greater than 0.5%.
Assay—
Transfer an accurately weighed quantity of about 150 mg of Sodium Caprylate to a 125-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in 50 mL of glacial acetic acid, and titrate with 0.1 N perchloric acid VS, determining the endpoint potentiometrically. Perform a blank determination, and make any necessary correction. Each mL of 0.1 N perchloric acid is equivalent to 16.62 mg of C8H15NaO2.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
| Monograph | Robert H. Lafaver, B.A.
Scientist 1-301-816-8335 |
(EM105) Excipient Monographs 1 |
| Reference Standards | Lili Wang, Technical Services Scientist 1-301-816-8129 RSTech@usp.org |
USP32–NF27 Page 1340
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 33(3) Page 493