Stinging Nettle
» Stinging Nettle consists of dried roots and rhizomes of Urtica dioica L. ssp dioica (Fam. Urticaceae), and may contain Urtica urens L., known in commerce as dwarf nettle, as a minor component. It contains not less than 0.8 percent of total amino acids, not less than 0.05 percent of 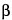 -sitosterol (C29H50O), and not less than 3 µg per g of scopoletin (C10H8O4), calculated on the dried basis.
-sitosterol (C29H50O), and not less than 3 µg per g of scopoletin (C10H8O4), calculated on the dried basis.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in tight containers, protected from light. Store at controlled room temperature.
Labeling—
The label states the Latin binomial and, following the official name, the parts of the plant contained in the article.
USP Reference standards  11
11 —
—
USP Aspartic Acid RS .
.
USP Glutamic Acid RS .
.
USP Scopoletin RS.
USP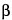 -Sitosterol RS.
-Sitosterol RS.
USP Aspartic Acid RS
 .
.
USP Glutamic Acid RS
 .
.
USP Scopoletin RS.
USP
Botanic characteristics—
Macroscopic—
The rhizome is irregularly bent, about 3 to 10 mm thick, and light gray-brown on the outside; thin roots spring from the knotty bulges of a lengthwise furrow. A transverse cut of the rhizome shows it is fibrous, light yellowish white, and usually has a small medulla cave. The roots are often very long, usually 0.5 to 2 mm thick, light yellow-brown on the outside, and contain some deep longitudinal furrows; a transverse cut shows a pale and almost pure-white color.
Histology—
The transverse section of the rhizome and root shows the following characteristics. The rhizome has a narrow cork composed of brown, thin-walled cells, a few rows of tangentially elongated cortical parenchyma, and a pericyclic region with numerous fibers occurring singly or, more frequently, in small groups. Fibers are much elongated with very thick and lignified walls. Some cells of the pericycle and outer part of secondary phloem contain large globular compound crystals of calcium oxalate. The vascular cambial region is distinct and continuous with narrow radial groups of vascular tissue separated by wide medullary rays. The secondary phloem is mainly parenchymatous with groups of thin-walled sieve tissue. The xylem is dense and completely lignified, containing scattered vessels, isolated or in small groups, associated with moderately thickened xylem parenchyma cells and numerous thicker-walled xylem fibers with slit-shaped pits. Individual vessels have fairly large, closely arranged, bordered pits, while the adjacent parenchyma has simple or bordered pits. Medullary rays indicate alternating areas of lignified and unlignified cells, appearing as tangential bands between the vascular bundles, each composed of five or six layers of cells; the lignified cells have moderately thickened walls with simple pits. The pith is composed of rounded, unlignified parenchyma, collapsed in the central part to form a cavity. Mature roots show a thin cork, narrow phelloderm, and secondary phloem and xylem with alternating areas of lignified and unlignified parenchyma in the wide medullary rays, similar to that found in the rhizome.
Identification, Thin-Layer Chromatographic Identification Test  201
201 —
—
Adsorbent:
0.50-mm layer of chromatographic silica gel mixture.
Test solution—
Extract 1 g of powder by refluxing with 10 mL of a solution containing toluene, ethyl acetate, and methanol (7:2:1) for 15 minutes, cool, and filter. Evaporate the filtrate to dryness under reduced pressure at less than 40 , and dissolve the residue in 2 mL of the toluene, ethyl acetate, methanol solution.
, and dissolve the residue in 2 mL of the toluene, ethyl acetate, methanol solution.
Standard solution—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of USP Scopoletin RS and USP 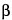 -Sitosterol RS in methanol to obtain a solution having a known concentration of 0.05 and 0.5 mg per mL, respectively.
-Sitosterol RS in methanol to obtain a solution having a known concentration of 0.05 and 0.5 mg per mL, respectively.
Application volume:
20 µL for the Test solution; 10 µL for the Standard solution.
Developing solvent system:
diethyl ether and methanol (9:1).
Procedure—
Proceed as directed in the chapter. Examine the plates under UV light at 365 nm. Spray the plate with about 10 mL of a mixture of water, 85% phosphoric acid, and 10% vanillin in 96% ethanol (4.5:4.5:1); heat between 100 and 105
and 105 for 10 minutes; and examine under daylight. The chromatogram of the Test solution exhibits a violet-red zone corresponding to the
for 10 minutes; and examine under daylight. The chromatogram of the Test solution exhibits a violet-red zone corresponding to the 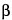 -sitosterol peak at the same RF value as the
-sitosterol peak at the same RF value as the 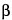 -sitosterol peak in the chromatogram of the Standard solution. Weakly violet-red zones above and below
-sitosterol peak in the chromatogram of the Standard solution. Weakly violet-red zones above and below 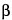 -sitosterol, corresponding to
-sitosterol, corresponding to 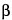 -sitosterol-glucoside, are visible.
-sitosterol-glucoside, are visible.
Microbial enumeration  2021
2021 —
The total aerobic microbial count does not exceed 106 cfu per g, the total combined molds and yeasts count does not exceed 104 cfu per g, and the bile-tolerant Gram-negative bacteria count does not exceed 103 cfu per g. It meets the requirements of the tests for absence of Salmonella species and Escherichia coli.
—
The total aerobic microbial count does not exceed 106 cfu per g, the total combined molds and yeasts count does not exceed 104 cfu per g, and the bile-tolerant Gram-negative bacteria count does not exceed 103 cfu per g. It meets the requirements of the tests for absence of Salmonella species and Escherichia coli.
Loss on drying  731
731 —
Dry 1.0 g of Stinging Nettle, finely powdered, at 105
—
Dry 1.0 g of Stinging Nettle, finely powdered, at 105 for 2 hours: it loses not more than 12.0% of its weight.
for 2 hours: it loses not more than 12.0% of its weight.
Foreign organic matter  561
561 :
not more than 2.0%.
:
not more than 2.0%.
Total ash  561
561 :
not more than 10%.
:
not more than 10%.
Pesticide residues  561
561 :
meets the requirements.
:
meets the requirements.
Content of total amino acids—
pH 5.5 Acetate buffer—
Mix 5.40 g of anhydrous sodium acetate, 0.3 mL of glacial acetic acid, and water to a final volume of 100 mL.
Reagent solution—
Prepare a solution containing about 1.00 g of ninhydrin, 1.50 g of hydrindantin, and 37.5 mL of propylene glycol, and adjust with pH 5.5 Acetate buffer to 50.0 mL. [note—Prepare the Reagent solution daily.]
Standard solution—
Dissolve accurately weighed quantities of USP Glutamic Acid RS and USP Aspartic Acid RS in water to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 0.1 mg of each per mL.
Test solution—
Finely powder an amount of Stinging Nettle, and transfer about 1.0 g, accurately weighed, to 80 mL of water. Place in an ultrasonic bath for 25 minutes, and centrifuge. Transfer the supernatant to a 100-mL volumetric flask, dilute with water to volume, and filter.
Procedure—
Transfer 5.0 mL of the Test solution and 1.0 mL of the Standard solution to two separate, appropriately labeled, 50-mL volumetric flasks. Add 4.0 mL of water to the Standard solution and 5.0 mL of Reagent solution to both the Test solution and the Standard solution. Heat in a boiling water bath for 30 minutes, cool, and adjust with a mixture of ethanol and water (1:1) to volume. Concomitantly determine the absorbances of the Standard solution and the Test solution in 1-cm cells at the wavelength of maximum absorbance at about 570 nm with a suitable spectrophotometer. Prepare a blank using 5.0 mL of water, and treat similarly to the Test solution. Calculate the percentage of total amino acids in the portion of Stinging Nettle taken by the formula:
2000(AU / AS)(WS / WU)
in which AU and AS are the absorbances of the Test solution and the Standard solution, respectively; WS is the sum of the weights, in mg, of USP Glutamic Acid RS and USP Aspartic Acid RS, calculated on the dried basis, in the Standard solution; and WU is the weight, in mg, of dried Stinging Nettle in the Test solution: not less than 0.8% of total amino acids is found.
Content of 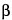 -sitosterol—
-sitosterol—
Derivatizing reagent—
Prepare a solution containing equal volumes (1:1:1) of BSTFA [N,O-bis(trimethylsilyl)trifluoroacetamide], anhydrous pyridine, and a mixture of BSA [N,O-(trimethylsilyl)acetamide], TMSI (N-trimethylsilyimidazole), and TMCS (trimethylchlorosilane) (3:3:2).
Internal standard solution—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of cholesterol in chloroform to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 10 mg per mL.
Standard solution—
Dissolve 50 mg of USP 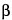 -Sitosterol RS, accurately weighed, in 2.0 mL of chloroform, add 1 mL of Internal standard solution, and dilute with chloroform to 5 mL. Transfer 0.5 mL of this solution to a 10-mL round-bottomed flask, dry the solvent under reduced pressure, add 1 mL of Derivatizing reagent, and mix.
-Sitosterol RS, accurately weighed, in 2.0 mL of chloroform, add 1 mL of Internal standard solution, and dilute with chloroform to 5 mL. Transfer 0.5 mL of this solution to a 10-mL round-bottomed flask, dry the solvent under reduced pressure, add 1 mL of Derivatizing reagent, and mix.
Test solution—
Finely powder an amount of Stinging Nettle, transfer 50.0 g to a Soxhlet apparatus, treat with chloroform, and extract for 6 hours. The volume of chloroform used is at least twice the volume of the thimble with an appropriate-size flask. Dry the solvent under reduced pressure, add 1.0 mL of Internal standard solution, and dilute with chloroform to 10 mL. Transfer 0.5 mL of this solution to a 10-mL round-bottomed flask, dry the solvent under reduced pressure, and add 0.5 mL of Derivatizing reagent.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
The gas chromatograph is equipped with a flame-ionization detector and a 0.20-mm × 25-m fused-silica capillary column coated with a 0.35-µm film of phase G2. The carrier gas is helium, flowing at a rate of about 0.5 mL per minute. The injection port and detector temperatures are maintained at 325
)—
The gas chromatograph is equipped with a flame-ionization detector and a 0.20-mm × 25-m fused-silica capillary column coated with a 0.35-µm film of phase G2. The carrier gas is helium, flowing at a rate of about 0.5 mL per minute. The injection port and detector temperatures are maintained at 325 . The column temperature is initially held at 300
. The column temperature is initially held at 300 and maintained at this temperature for 60 minutes. Chromatograph the Standard solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the tailing factor for each sterol peak is not more than 2.0; and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections determined from each sterol peak is not more than 5.0%.
and maintained at this temperature for 60 minutes. Chromatograph the Standard solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the tailing factor for each sterol peak is not more than 2.0; and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections determined from each sterol peak is not more than 5.0%.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 1 µL) of the Standard solution and the Test solution into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the peak responses of the sterols. Calculate the percentage of 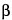 -sitosterol in the portion of Stinging Nettle taken by the formula:
-sitosterol in the portion of Stinging Nettle taken by the formula:
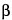 -sitosterol to the internal standard obtained from the Standard solution and the Test solution, respectively; CS is the concentration, in mg per mL, of USP
-sitosterol to the internal standard obtained from the Standard solution and the Test solution, respectively; CS is the concentration, in mg per mL, of USP 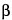 -Sitosterol RS in the Standard solution; and CU is the concentration, in mg per mL, of Stinging Nettle in the Test solution: not less than 0.05% of
-Sitosterol RS in the Standard solution; and CU is the concentration, in mg per mL, of Stinging Nettle in the Test solution: not less than 0.05% of 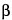 -sitosterol is found.
-sitosterol is found.
100(RU / RS)(CS / CU)
in which RU and RS are the peak response ratios of
Content of scopoletin—
Solution A—
Use water.
Solution B—
Use methanol.
Mobile phase—
Use variable mixtures of Solution A and Solution B as directed for Chromatographic system. Make adjustments if necessary (see System Suitability under Chromatography  621
621 ).
).
Standard solution—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of USP Scopoletin RS in methanol to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 0.02 µg per mL.
Test solution—
Finely powder an amount of Stinging Nettle, and mix 4.000 g, accurately weighed, with 25 mL of methanol. Place in an ultrasonic bath for 25 minutes, and centrifuge. Transfer 0.5 mL of the solution to a 10-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with methanol to volume.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a fluorescence detector set at an excitation wavelength of 366 nm and an emission wavelength of 420 nm and a 4.6-mm × 25-cm column that contains packing L1. The flow rate is about 1 mL per minute. The chromatograph is programmed as follows.
)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a fluorescence detector set at an excitation wavelength of 366 nm and an emission wavelength of 420 nm and a 4.6-mm × 25-cm column that contains packing L1. The flow rate is about 1 mL per minute. The chromatograph is programmed as follows.
Chromatograph about 10 µL of the Standard solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the capacity factor (k¢) determined from the scopoletin peak is not less than 5; the tailing factor for the scopoletin peak is not more than 2.0; and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 5.0%.
| Time (minutes) |
Solution A
(%) |
Solution B
(%) |
Elution |
| 0 | 75 | 25 | equilibration |
| 0–2 | 75®60 | 25®40 | linear gradient |
| 2–8 | 60 | 40 | isocratic |
| 8–10 | 60®0 | 40®100 | linear gradient |
| 10–15 | 0 | 100 | isocratic |
| 15–20 | 0®75 | 100®25 | linear gradient |
| 20–30 | 75 | 25 | isocratic |
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 10 µL) of the Standard solution and the Test solution into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the peak responses for scopoletin. Calculate the content of scopoletin (C10H8O4), in µg per g, in the portion of Stinging Nettle taken by the formula:
10,000(rU / rS)(CS / CU)
in which rU and rS are the peak responses of scopoletin in the Test solution and the Standard solution, respectively; CS is the concentration, in mg per mL, of USP Scopoletin RS in the Standard solution; and CU is the concentration, in mg per mL, of Stinging Nettle in the Test solution: not less than 3 µg per g of scopoletin is found.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
Chromatographic Column—
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
| Monograph | Maged H. Sharaf, Ph.D.
Senior Scientist 1-301-816-8318 |
(DSB05) Dietary Supplements - Botanicals |
| Reference Standards | Lili Wang, Technical Services Scientist 1-301-816-8129 RSTech@usp.org |
|
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Senior Scientist 1-301-816-8339 |
(MSA05) Microbiology and Sterility Assurance |
USP32–NF27 Page 1060
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 29(4) Page 1285
Chromatographic columns text is not derived from, and not part of, USP 32 or NF 27.