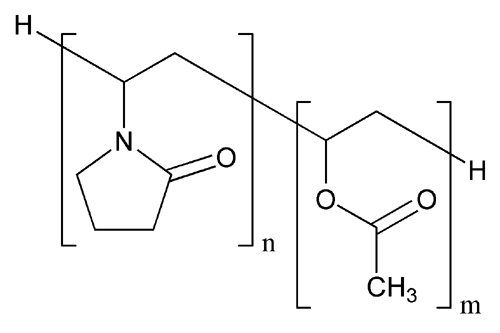
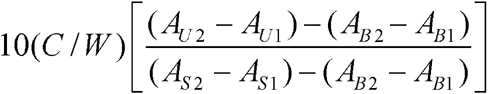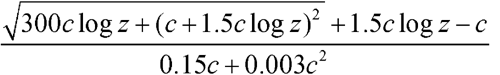Copovidone
» Copovidone is a copolymer of 1-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone and vinyl acetate in the mass proportion of 3:2. The nominal K-value of Copovidone as stated in the labeling is not less than 90.0 percent and not more than 110.0 percent.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in tight containers. No storage requirements specified.
Labeling—
Label it to indicate its nominal K-value.
Clarity and color of solution—
Dissolve 1.0 g in 10 mL of water: the solution is clear or slightly opalescent and colorless to pale yellow or pale red.
Identification—
B:
To 5 mL of a solution (1 in 50) add a few drops of iodine TS: a deep red color is produced.
Loss on drying  731
731 —
Dry it at 105
—
Dry it at 105 for 3 hours: it loses not more than 5.0% of its weight.
for 3 hours: it loses not more than 5.0% of its weight.
Residue on ignition  281
281 :
not more than 0.1%.
:
not more than 0.1%.
Limit of aldehydes—
Phosphate buffer—
Transfer 8.7 g of monobasic potassium phosphate to a 500-mL volumetric flask, and dissolve in 400 mL of water. Adjust, if necessary, with 1 N potassium hydroxide to a pH of 9.0, dilute with water to volume, and mix.
Aldehyde dehydrogenase solution—
Transfer a quantity of lyophilized aldehyde dehydrogenase equivalent to 70 units to a glass vial, dissolve in 10.0 mL of water, and mix. [note—This solution is stable for 8 hours at 4 .]
.]
NAD solution—
Transfer 40 mg of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide to a glass vial, dissolve in 10.0 mL of Phosphate buffer, and mix. [note—This solution is stable for 4 weeks at 4 .]
.]
Blank solution—
Use water.
Standard solution—
Transfer about 2 mL of water at 4 to a glass weighing bottle, and weigh accurately. Add about 100 mg of freshly distilled acetaldehyde, and weigh accurately. Transfer this solution to a 100-mL volumetric flask. Rinse the weighing bottle with several portions of water at 4
to a glass weighing bottle, and weigh accurately. Add about 100 mg of freshly distilled acetaldehyde, and weigh accurately. Transfer this solution to a 100-mL volumetric flask. Rinse the weighing bottle with several portions of water at 4 , and transfer each rinsing to the 100-mL volumetric flask. Dilute the solution in the 100-mL volumetric flask with water at 4
, and transfer each rinsing to the 100-mL volumetric flask. Dilute the solution in the 100-mL volumetric flask with water at 4 to volume. Store at 4
to volume. Store at 4 for about 20 hours. Pipet 1 mL of this solution into a 100-mL volumetric flask, dilute with Phosphate buffer to volume, and mix.
for about 20 hours. Pipet 1 mL of this solution into a 100-mL volumetric flask, dilute with Phosphate buffer to volume, and mix.
Test solution—
Transfer about 1 g of Copovidone, accurately weighed, to a 100-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in 50 mL of Phosphate buffer, dilute with Phosphate buffer to volume, and mix. Insert a stopper into the flask, heat at 60 for 1 hour, and cool to room temperature.
for 1 hour, and cool to room temperature.
Procedure—
Pipet 0.5 mL each of the Standard solution, the Test solution, and the Blank solution into separate 1-cm cells. Add 2.5 mL of Phosphate buffer and 0.2 mL of NAD solution to each cell. Cover the cells to exclude oxygen. Mix by inversion, and allow to stand for 2 to 3 minutes at 22 ± 2 . Determine the absorbances of the solutions at a wavelength of 340 nm. Add 0.05 mL of Aldehyde dehydrogenase solution to each cell. Cover the cells to exclude oxygen. Mix by inversion, and allow to stand for 5 minutes at 22 ± 2
. Determine the absorbances of the solutions at a wavelength of 340 nm. Add 0.05 mL of Aldehyde dehydrogenase solution to each cell. Cover the cells to exclude oxygen. Mix by inversion, and allow to stand for 5 minutes at 22 ± 2 . Determine the absorbances of the solutions at a wavelength of 340 nm. Calculate the percentage of aldehydes, expressed as acetaldehyde, in the portion of Copovidone taken by the formula:
in which C is the concentration, in mg per mL, of acetaldehyde in the Standard solution; W is the weight, in g, calculated on the dried basis, of Copovidone taken to prepare the Test solution; AU1, AS1, and AB1 are the absorbances of the solutions obtained from the Test solution, the Standard solution, and the Blank solution, respectively, before the addition of the Aldehyde dehydrogenase solution; and AU2, AS2, and AB2 are the absorbances of the solutions obtained from the Test solution, the Standard solution, and the Blank solution, respectively, after addition of the Aldehyde dehydrogenase solution: not more than 0.05% is found.
. Determine the absorbances of the solutions at a wavelength of 340 nm. Calculate the percentage of aldehydes, expressed as acetaldehyde, in the portion of Copovidone taken by the formula:
in which C is the concentration, in mg per mL, of acetaldehyde in the Standard solution; W is the weight, in g, calculated on the dried basis, of Copovidone taken to prepare the Test solution; AU1, AS1, and AB1 are the absorbances of the solutions obtained from the Test solution, the Standard solution, and the Blank solution, respectively, before the addition of the Aldehyde dehydrogenase solution; and AU2, AS2, and AB2 are the absorbances of the solutions obtained from the Test solution, the Standard solution, and the Blank solution, respectively, after addition of the Aldehyde dehydrogenase solution: not more than 0.05% is found.
Limit of hydrazine—
Standard solution—
Dissolve accurately weighed quantities of salicylaldazine and salicylaldehyde in toluene, and dilute quantitatively, and stepwise if necessary, with toluene to obtain a solution having known concentrations of 9 µg per mL and 10 mg per mL, respectively.
Test solution—
Transfer the equivalent of 2.5 g of dried Copovidone, accurately weighed, to a 50-mL centrifuge tube, add 25 mL of water, and mix to dissolve. Add 500 µL of a 1 in 20 solution of salicylaldehyde in methanol, adjust the solution with 0.25 N sulfuric acid to a pH of about 2, swirl, and heat in a water bath at 60 for 15 minutes. Allow to cool, add 2.0 mL of toluene, insert a stopper in the tube, shake vigorously for 2 minutes, and centrifuge. Use the clear upper toluene layer as the Test solution.
for 15 minutes. Allow to cool, add 2.0 mL of toluene, insert a stopper in the tube, shake vigorously for 2 minutes, and centrifuge. Use the clear upper toluene layer as the Test solution.
Procedure—
Separately apply 10 µL of the Test solution and the Standard solution to a suitable thin-layer chromatographic plate (see Chromatography  621
621 ) coated with a 0.25-mm layer of dimethylsilanized chromatographic silica gel mixture. Allow the spots to dry, and develop the chromatogram in a solvent system consisting of a mixture of acetonitrile and water (85:15) until the solvent front has moved about three-fourths of the length of the plate. Remove the plate from the developing chamber, mark the solvent front, and allow the solvent to evaporate. Locate the spots on the plate by examination under UV light at a wavelength of 365 nm: salicylaldazine appears as a fluorescent spot having an RF value of about 0.6 to 0.7, and the fluorescence of any salicylaldazine spot from the Test solution is not more intense than that produced by the spot obtained from the Standard solution: not more than 1 µg per g is found.
) coated with a 0.25-mm layer of dimethylsilanized chromatographic silica gel mixture. Allow the spots to dry, and develop the chromatogram in a solvent system consisting of a mixture of acetonitrile and water (85:15) until the solvent front has moved about three-fourths of the length of the plate. Remove the plate from the developing chamber, mark the solvent front, and allow the solvent to evaporate. Locate the spots on the plate by examination under UV light at a wavelength of 365 nm: salicylaldazine appears as a fluorescent spot having an RF value of about 0.6 to 0.7, and the fluorescence of any salicylaldazine spot from the Test solution is not more intense than that produced by the spot obtained from the Standard solution: not more than 1 µg per g is found.
Limit of peroxides—
Copovidone solution—
Transfer the equivalent of 2.0 g of dried Copovidone, accurately weighed, to a 50-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in and dilute with water to volume, and mix.
Test solution—
Transfer 25.0 mL of Copovidone solution to a 50-mL beaker, add 2 mL of titanium trichloride–sulfuric acid TS, and mix. Allow to stand for 30 minutes at room temperature.
Blank solution—
Transfer 25.0 mL of Copovidone solution to a 50-mL beaker, add 2 mL of 13% sulfuric acid, and mix.
Procedure—
Determine the absorbance of the Test solution in a 1-cm cell at the wavelength of maximum absorbance at about 405 nm, with a suitable spectrophotometer, using the Blank solution as the blank: the absorbance is not more than 0.35 (corresponding to not more than 0.04%, expressed as hydrogen peroxide).
Limit of monomers—
Dissolve the equivalent of 5.0 g of dried Copovidone in 20 mL of methanol, and slowly add 20.0 mL of iodobromide TS. Allow to stand for 30 minutes, protected from light, with repeated shaking. Add 5 mL of potassium iodide solution (1 in 10), and titrate the liberated iodine with 0.1 N sodium thiosulfate VS until the solution is yellow. Continue the titration dropwise until the solution is colorless, adding 3 mL of starch TS as the endpoint is approached. Perform a blank determination (see Residual Titrations under Titrimetry  541
541 ): the difference between the volumes of 0.1 N sodium thiosulfate consumed in the blank and the specimen titrations is not more than 0.9 mL, corresponding to not more than 0.1% of monomers calculated as vinylpyrrolidone.
): the difference between the volumes of 0.1 N sodium thiosulfate consumed in the blank and the specimen titrations is not more than 0.9 mL, corresponding to not more than 0.1% of monomers calculated as vinylpyrrolidone.
K-value—
Transfer an accurately weighed quantity of undried Copovidone, equivalent to about 1.0 g on the dried basis, to a 100-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in and dilute with water to volume, and mix. Allow to stand for 1 hour. Determine the viscosity, using a capillary-tube viscosimeter (see Viscosity  911
911 ), of this solution at 25 ± 0.2
), of this solution at 25 ± 0.2 . Calculate the K-value of Copovidone by the formula:
in which c is the weight, in g, on the dried basis, of the specimen tested in each 100.0 mL of solution; and z is the viscosity of the test solution relative to that of water: the K-value is not less than 90.0% and not more than 110.0% of the K-value stated on the label.
. Calculate the K-value of Copovidone by the formula:
in which c is the weight, in g, on the dried basis, of the specimen tested in each 100.0 mL of solution; and z is the viscosity of the test solution relative to that of water: the K-value is not less than 90.0% and not more than 110.0% of the K-value stated on the label.
Content of copolymerized vinyl acetate—
Determine the saponification value as directed for Saponification Value under Fats and Fixed Oils  401
401 . Calculate the percentage of copolymerized vinyl acetate in the Copovidone taken by the formula:
. Calculate the percentage of copolymerized vinyl acetate in the Copovidone taken by the formula:
0.1(86.09/56.11)(S)
in which 86.09 and 56.11 are the molecular weights of vinyl acetate and potassium hydroxide, respectively; and S is the saponification value: not less than 35.3% and not more than 41.4% of the copolymerized vinyl acetate component, calculated on the dried basis, is found.
Nitrogen, Method II  461
461 —
Proceed as directed using about 0.1 g of Copovidone, accurately weighed. In the procedure, use 5 g of a powdered mixture of potassium sulfate, cupric sulfate, and titanium dioxide (33:1:1) instead of potassium sulfate and cupric sulfate (10:1); omit the use of hydrogen peroxide; and heat until the solution has a clear, yellow-green color and the sides of the flask are free from carbonaceous material. Then heat for a further 45 minutes; add 20 mL of water, instead of 70 mL, after the second heating; and use bromocresol green–methyl red TS instead of methyl red–methylene blue TS. Titrate the distillate with 0.05 N sulfuric acid VS until the color of the solution changes from green through pale grayish blue to pale grayish red-purple: the nitrogen content, on the dried basis, is not less than 7.0% and not more than 8.0%.
—
Proceed as directed using about 0.1 g of Copovidone, accurately weighed. In the procedure, use 5 g of a powdered mixture of potassium sulfate, cupric sulfate, and titanium dioxide (33:1:1) instead of potassium sulfate and cupric sulfate (10:1); omit the use of hydrogen peroxide; and heat until the solution has a clear, yellow-green color and the sides of the flask are free from carbonaceous material. Then heat for a further 45 minutes; add 20 mL of water, instead of 70 mL, after the second heating; and use bromocresol green–methyl red TS instead of methyl red–methylene blue TS. Titrate the distillate with 0.05 N sulfuric acid VS until the color of the solution changes from green through pale grayish blue to pale grayish red-purple: the nitrogen content, on the dried basis, is not less than 7.0% and not more than 8.0%.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
| Monograph | Kevin T. Moore, Ph.D.
Scientist 1-301-816-8369 |
(EM205) Excipient Monographs 2 |
| Reference Standards | Lili Wang, Technical Services Scientist 1-301-816-8129 RSTech@usp.org |
USP32–NF27 Page 1209
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 32(6) Page 1843