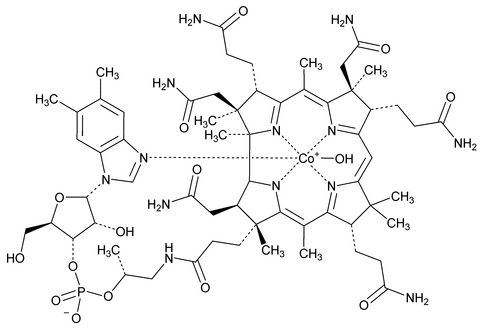
Hydroxocobalamin
C62H89CoN13O15P1346.36
Cobinamide, dihydroxide, dihydrogen phosphate (ester), mono(inner salt), 3¢-ester with 5,6-dimethyl-1- -d-ribofuranosyl-1H-benzimidazole;
-d-ribofuranosyl-1H-benzimidazole;
Cobinamide dihydroxide dihydrogen phosphate (ester), mono(inner salt), 3¢-ester with 5,6-dimethyl-1- -d-ribofuranosylbenzimidazole
-d-ribofuranosylbenzimidazole 

 [13422-51-0].
[13422-51-0].
(hye drox'' oh koe bal' a min).
C62H89CoN13O15P1346.36
Cobinamide, dihydroxide, dihydrogen phosphate (ester), mono(inner salt), 3¢-ester with 5,6-dimethyl-1-
Cobinamide dihydroxide dihydrogen phosphate (ester), mono(inner salt), 3¢-ester with 5,6-dimethyl-1-
DEFINITION
Hydroxocobalamin contains NLT 95.0% and NMT 102.0% of hydroxocobalamin (C62H89CoN13O15P), calculated on the dried basis.
IDENTIFICATION
• A. Ultraviolet Absorption  197U
197U
Wavelength range: 400–700 nm
Sample solution: Use the Sample solution as directed in pH-dependent Cobalamins.
Acceptance criteria: Meets the requirements in the chapter. The visible absorption spectrum of the Sample solution exhibits maxima at 426 ± 2, 516 ± 2, and 550 ± 2 nm.
• B. Cobalt
Sample: 1 mg of Hydroxocobalamin
Analysis: Fuse the Sample with 50 mg of potassium pyrosulfate in a porcelain crucible. Cool, break up the mass with a glass rod, add 3 mL of water, and boil until dissolved. Add 1 drop of phenolphthalein TS, and add 2 N sodium hydroxide dropwise until a pink color appears. Add 0.5 g of sodium acetate, 0.5 mL of 1 N acetic acid, and 0.5 mL of a 10-mg/mL solution of nitroso R salt. Add 0.5 mL of hydrochloric acid, and boil for 1 min.
Acceptance criteria: A red or orange-red color appears immediately after the addition of nitroso R salt. The red or orange-red color persists after boiling with the addition of hydrochloric acid.
ASSAY
• Procedure
Cyanocobalamin tracer reagent, Cresol–carbon tetrachloride solution, Phosphate–cyanide solution, Butanol–benzalkonium chloride solution, and Alumina–resin column: Prepare as directed in Cobalamin Radiotracer Assay  371
371 .
.
Standard solution: Use Standardization as directed in Cobalamin Radiotracer Assay  371
371 .
.
Sample solution: Transfer 40 mg of Hydroxocobalamin to a 2000-mL volumetric flask. Dissolve in and dilute with water to volume. Transfer 25.0 mL of this solution to a beaker. Add 5.0 mL of Cyanocobalamin tracer reagent, and proceed as directed for Assay preparation in Cobalamin Radiotracer Assay  371
371 , beginning with “Add, while working under a hood, 5 mg of sodium nitrite…”.
, beginning with “Add, while working under a hood, 5 mg of sodium nitrite…”.
Analysis
Samples: Standard solution and Sample solution
Proceed as directed for Procedure in Cobalamin Radiotracer Assay  371
371 .
.
Calculate the percentage of hydroxocobalmin (C62H89CoN13O15P) in the portion of Hydroxocobalamin taken:
Result = (AU/AS) × (CS/CU) × (RS/RU) × (Mr1/Mr2) × 100
| AU | = | = absorbance of the Sample solution at 361 nm |
| AS | = | = absorbance of the Standard solution at 361 nm |
| CS | = | = concentration of USP Cyanocobalamin RS in the Standard solution (µg/mL) |
| CU | = | = concentration of Hydroxocobalamin in the Sample solution (µg/mL) |
| RS | = | = corrected average radioactivity values of the Standard solution (counts/min/mL) |
| RU | = | = corrected average radioactivity values of the Sample solution (counts/min/mL) |
| Mr1 | = | = molecular weight of hydroxocobalamin, 1346.36 |
| Mr2 | = | = molecular weight of cyanocobalamin, 1355.37 |
Acceptance criteria: 95.0%–102.0% on the dried basis
IMPURITIES
• Limit of Cyanocobalamin
Cyanocobalamin tracer reagent, Cresol–carbon tetrachloride solution, Butanol–benzalkonium chloride solution, and Alumina–resin column: Prepare as directed in Cobalamin Radiotracer Assay  371
371 .
.
Standard solution: Use Standardization as directed in Cobalamin Radiotracer Assay  371
371 .
.
Sample solution: 50 mg of Hydroxocobalamin in 25 mL of water
Analysis: Transfer 5.0 mL of the Sample solution to a glass-stoppered, 50-mL centrifuge tube, and add 5.0 mL of Cyanocobalamin tracer reagent and 15 mL of Cresol–carbon tetrachloride solution. Insert the stopper, shake gently, centrifuge, carefully remove the upper, aqueous layer by aspiration, and discard the aspirated liquid. Add 25 mL of 5 N sulfuric acid, insert the stopper, shake gently, centrifuge, and remove and discard the upper, aqueous layer. Repeat the washing with additional 25-mL portions of the 5 N sulfuric acid until the acid wash is colorless (6–8 washings), and discard the acid washings. Add Cresol–carbon tetrachloride solution as necessary during the acid washings to maintain the volume of this phase at NLT 10 mL. Wash this solution successively with two 10-mL portions of saturated dibasic sodium phosphate solution and one 10-mL portion of water, and discard all of the aqueous washings. Proceed as directed for Procedure in Cobalamin Radiotracer Assay  371
371 , beginning with “To the washed extract add 30 mL of a mixture of 2 volumes of Butanol–benzalkonium chloride solution and 1 volume of carbon tetrachloride”.
, beginning with “To the washed extract add 30 mL of a mixture of 2 volumes of Butanol–benzalkonium chloride solution and 1 volume of carbon tetrachloride”.
Repeat the same procedure for the Standard solution.
Calculate the percentage of cyanocobalamin in the portion of Hydroxocobalamin taken:
Result = (AU/AS) × (CS/CU) × (RS/RU) × 100
| AU | = | = absorbance of the Sample solution at 361 nm |
| AS | = | = absorbance of the Standard solution at 361 nm |
| CS | = | = concentration of USP Cyanocobalamin RS in the Standard solution (µg/mL) |
| CU | = | = concentration of Hydroxocobalamin in the Sample solution (µg/mL) |
| RS | = | = corrected average radioactivity values of the Standard solution (counts/min/mL) |
| RU | = | = corrected average radioactivity values of the Sample solution (counts/min/mL) |
Acceptance criteria: NMT 5.0% on the dried basis
SPECIFIC TESTS
• Loss on Drying  731
731 : Dry a sample at a pressure below 5 mm of mercury at 100
: Dry a sample at a pressure below 5 mm of mercury at 100 for 2 h: it loses 14.0%–18.0% of its weight.
for 2 h: it loses 14.0%–18.0% of its weight.
• pH-Dependent Cobalamins
[Note—Perform the test in subdued light. ]
Buffer A: Dissolve 23.8 g of sodium borate and 402 mg of boric acid in 1500 mL of water. The pH is 9.3.
Buffer B: Dissolve 2.61 g of sodium acetate and 20.5 g of sodium chloride in 5.25 mL of glacial acetic acid, and dilute with water to 1500 mL. The pH is 4.0.
Sample stock solution: Transfer 40 mg of Hydroxocobalamin into a 25-mL volumetric flask. Dissolve and dilute with carbon dioxide-free water to volume.
Sample solution A: Transfer 1.0-mL aliquot of the Sample stock solution to a glass-stoppered test tube. Add 3.0 mL of Buffer A and mix.
Sample solution B: Transfer 1.0-mL aliquot of the Sample stock solution to a glass-stoppered test tube. Add 3.0 mL of Buffer B and mix.
Instrumental conditions
Mode: Visible
Analytical wavelength: 550 nm
Cell: 1 cm
Analysis
Samples: Sample solution A and Sample solution B
Determine the absorbance of Sample solution A against that of Sample solution B. Calculate the percentage of pH-dependent cobalamins, as hydroxocobalamin, in the portion of Hydroxocobalamin taken:
Result = A/(F × C)
| A | = | = pH corrected absorbance of Sample solution A |
| F | = | = coefficent of extinction (E1%) of pure hydroxocobalamin in pH 9.3 buffer (100 mL · g |
| C | = | = concentration of Hydroxocobalamin in Sample solution A (g/mL) |
Acceptance criteria: 95.0%–102.0% on the dried basis
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
• Packaging and Storage: Preserve in tight, light-resistant containers, and store in a cool place.
Auxiliary Information— Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Huy T. Dinh, M.S. Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8594 | (DS2010) Monographs - Dietary Supplements |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP35–NF30 Page 3452
Chromatographic Column—
Chromatographic columns text is not derived from, and not part of, USP 35 or NF 30.