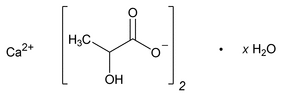
Calcium Lactate
C6H10CaO6·5H2O308.30
C6H10CaO6218.22
Propanoic acid, 2-hydroxy-, calcium salt (2:1), hydrate;
Calcium lactate (1:2) hydrate

 [41372-22-9].
[41372-22-9].
Calcium lactate (1:2) pentahydrate

 [5743-47-5].
[5743-47-5].
Anhydrous

 [814-80-2].
[814-80-2].
(kal' see um lak' tate).
C6H10CaO6·5H2O308.30
C6H10CaO6218.22
Propanoic acid, 2-hydroxy-, calcium salt (2:1), hydrate;
Calcium lactate (1:2) hydrate
Calcium lactate (1:2) pentahydrate
Anhydrous
DEFINITION
Calcium Lactate contains NLT 98.0% and NMT 101.0% of calcium lactate (C6H10CaO6), calculated on the dried basis.
IDENTIFICATION
• A. Identification Tests—General, Calcium  191
191 : Meets the requirements
: Meets the requirements
ASSAY
• Procedure
Sample: Weighed portion of Calcium Lactate equivalent to 350 mg of C6H10CaO6
Blank: 150 mL of water and 2 mL of 3 N hydrochloric acid
Titrimetric system
(See Titrimetry  541
541 .)
.)
Mode: Direct titration
Titrant: 0.05 M edetate disodium VS
Endpoint detection: Visual
Analysis: Dissolve the Sample in a mixture of water and 3 N hydrochloric acid (150:2). While stirring with a magnetic stirrer, add 30 mL of Titrant from the titration buret. Add 15 mL of 1 N sodium hydroxide and 300 mg of hydroxy naphthol blue, and continue the titration to a blue endpoint. Perform the Blank determination.
Calculate the percentage of calcium lactate (C6H10CaO6) in the Sample taken:
Result = {[(VS  VB) × M × F]/W} × 100
VB) × M × F]/W} × 100
| VS | = | = Titrant volume consumed by the Sample (mL) |
| VB | = | = Titrant volume consumed by the Blank (mL) |
| M | = | = Titrant molarity (mM/mL) |
| F | = | = equivalency factor, 218.2 mg/mM |
| W | = | = Sample weight (mg) |
Acceptance criteria: 98.0%–101.0% on the dried basis
IMPURITIES
• Heavy Metals  231
231
Test preparation: Dissolve 1 g in 2.5 mL of 1 N acetic acid, and dilute with water to 25 mL.
Acceptance criteria: NMT 20 ppm
• Limit of Magnesium and Alkali Salts
Sample: 1.0 g Calcium Lactate
Analysis: Mix the Sample with 40 mL of water, carefully add 1 mL of hydrochloric acid, and heat the solution to boiling. Rapidly add 40 mL of oxalic acid TS, and stir vigorously until precipitation is well established. Add immediately to the warm mixture 2 drops of methyl red TS and then 6 N ammonium hydroxide, dropwise, until the mixture is just alkaline. Cool to room temperature, transfer to a 100-mL graduated cylinder, dilute with water to 100 mL, mix, and allow to stand for 4 h or overnight. Filter, and to 50 mL of the clear filtrate in a platinum dish add 0.5 mL of sulfuric acid. Evaporate the mixture on a steam bath to a small volume. Carefully heat over a free flame to dryness, and continue heating to complete decomposition and volatilization of ammonium salts. Finally, ignite the residue to constant weight.
Acceptance criteria: NMT 1.0%: The weight of the residue does not exceed 5.0 mg.
• Volatile Fatty Acid
Sample solution: Stir 500 mg of Calcium Lactate with 1 mL of sulfuric acid, and warm.
Acceptance criteria: The mixture does not emit an odor of volatile fatty acid.
SPECIFIC TESTS
• Acidity
Sample solution: 50 mg/mL
Analysis: Titrate 20 mL of Sample solution with 0.10 N sodium hydroxide, using phenolphthalein TS as the indicator.
Acceptance criteria: NMT 0.50 mL is required for neutralization, equivalent to NMT 0.45% as lactic acid.
• Loss on Drying  731
731
Sample: 1–2 g
Analysis: Distribute the Sample evenly in a suitable weighing dish to a depth of NMT 3 mm, and dry at 120 for 4 h.
for 4 h.
Acceptance criteria: See Table 1.
Table 1
| Form | Loss on Drying (%) |
|---|---|
| Pentahydrate | 22.0–27.0 |
| Trihydrate | 15.0–20.0 |
| Monohydrate | 5.0–8.0 |
| Anhydrous | NMT 3.0 |
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
• Packaging and Storage: Preserve in tight containers.
• Labeling: The label indicates whether it is the dried form or is hydrous; if the latter, the label indicates the degree of hydration. Where the quantity of Calcium Lactate is indicated in the labeling of any solution containing Calcium Lactate, this shall be understood to be in terms of calcium lactate pentahydrate (C6H10CaO6·5H2O).
Auxiliary Information— Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Huy T. Dinh, M.S. Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8594 | (DS2010) Monographs - Dietary Supplements |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP35–NF30 Page 2457
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 31(6) Page 1608Chromatographic Column—
Chromatographic columns text is not derived from, and not part of, USP 35 or NF 30.