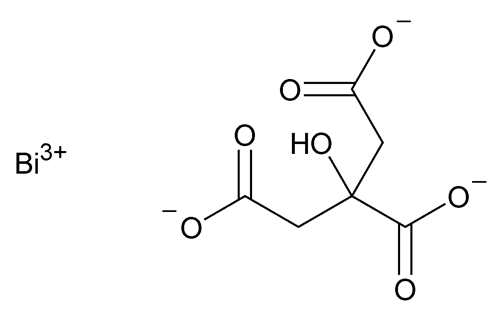
Bismuth Citrate
(biz' muth sit' rate).
» Bismuth Citrate contains not less than 49 percent and not more than 54 percent of bismuth (Bi).
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in tight, light-resistant containers, store at controlled room temperature, and prevent exposure to excessive heat.
Identification—
A:
Infrared Absorption  197K
197K : on the undried specimen.
: on the undried specimen.
B:
When strongly heated, the salt chars, and on ignition leaves a more or less blackened residue having a yellow surface. The residue is soluble in warm nitric acid, and this solution, when dropped into a large excess of water, produces a white turbidity.
C:
Dissolve 1 g in ammonia TS. When treated with hydrogen sulfide in excess, a black precipitate is obtained. Filter this mixture, drive off the excess hydrogen sulfide by heating, and allow to cool. To a portion of this cooled solution add an excess of calcium hydroxide TS, and boil: a white precipitate is formed. Reserve a second portion of the cooled solution for the test for Limit of nitrate.
Arsenic, Method I  211
211 —
Prepare the Test Preparation as follows. Triturate 300 mg with an equal weight of calcium hydroxide, and ignite. Dissolve the residue in 5 mL of 3 N hydrochloric acid: the limit is 10 µg per g.
—
Prepare the Test Preparation as follows. Triturate 300 mg with an equal weight of calcium hydroxide, and ignite. Dissolve the residue in 5 mL of 3 N hydrochloric acid: the limit is 10 µg per g.
Limit of nitrate—
To the second portion of cooled solution reserved from Identification test C, add an equal volume of sulfuric acid, mix, and allow to cool. Into the liquid, drop a crystal of ferrous sulfate, and allow to stand for 30 minutes: no brown or brownish black color appears around the crystal.
Limit of copper, lead, and silver—
Standard solution—
Prepare a solution containing 1000 µg of copper per mL, a solution containing 1000 µg of lead per mL, and a solution containing 1000 µg of silver per mL. Transfer 3.0 mL of each solution to a 2000-mL volumetric flask, dilute with 1 N nitric acid to volume, and mix. [note—The concentrations of copper, lead, and silver in this solution may be modified by using a different quantity or by further dilution to bring the absorption responses within the working range of the atomic absorption spectrophotometer. ]
Test solution—
Ignite about 3 g of Bismuth Citrate, accurately weighed, in a porcelain crucible, cool, and cautiously add 6 N nitric acid to dissolve the residue. Add 100 mL of water, and mix. A white precipitate forms. Filter this mixture, evaporate on a steam bath to obtain about 15 mL of solution, and filter again. Dilute the filtrate with water to 20.0 mL.
Procedure—
Concomitantly determine the absorbances of the Standard solution and the Test solution at the emission lines of 324.7 nm, 217 nm, and 328.1 nm for copper, lead, and silver, respectively, with an atomic absorption spectrophotometer (see Spectrophotometry and Light-Scattering  851
851 ) equipped with copper, lead, and silver hollow-cathode lamps and an oxidizing flame. The absorbances of the Test solution do not exceed those of the Standard solution for each element (10 µg per g).
) equipped with copper, lead, and silver hollow-cathode lamps and an oxidizing flame. The absorbances of the Test solution do not exceed those of the Standard solution for each element (10 µg per g).
Limit of soluble bismuth—
Standard solution—
Transfer 242.0 mg of bismuth nitrate pentahydrate to a 100-mL volumetric flask. Add 3 mL of 1.5 N nitric acid, swirl to dissolve, dilute with water to volume, and mix. Transfer 1.0 mL of this solution to a 500-mL volumetric flask, add 250 mL of 1.5 N nitric acid, dilute with water to volume, and mix. This solution contains 2.0 µg of bismuth (Bi) per mL. [note—The concentration of bismuth in this solution may be modified by using a different quantity or by further dilution to bring the absorption responses within the working range of the atomic absorption spectrophotometer. ]
Test solution—
Prepare a mixture of 5.0 g of Bismuth Citrate and 100 mL of water, and stir by mechanical means the suspension thus obtained for 2 hours. Pass through filter paper. Pass the filtrate thus obtained through a filter having a 0.1-µm or finer porosity. To 10.0 mL of the filtrate add 0.1 mL of nitric acid.
Procedure—
Concomitantly determine the absorbances of the Standard solution and the Test solution at the emission line of 223.06 nm for bismuth with an atomic absorption spectrophotometer (see Spectrophotometry and Light-Scattering  851
851 ) equipped with a bismuth hollow-cathode lamp and an oxidizing flame. The absorbances of the Test solution do not exceed those of the Standard solution (40 µg per g).
) equipped with a bismuth hollow-cathode lamp and an oxidizing flame. The absorbances of the Test solution do not exceed those of the Standard solution (40 µg per g).
Assay—
Transfer about 300 mg of Bismuth Citrate, accurately weighed, to a porcelain crucible, and ignite. Allow to cool, add 2 mL of nitric acid to the residue, dropwise, and warm until complete solution has been effected. Add about 60 mL of water and 0.3 mL of xylenol orange TS, and titrate with 0.05 N edetate disodium VS to a yellow endpoint. Each mL of 0.05 N edetate disodium is equivalent to 10.45 mg of bismuth (Bi).
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Elena Gonikberg, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8251 |
(SM32010) Monographs - Small Molecules 3 |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP35–NF30 Page 2367
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 27(2) Page 2118