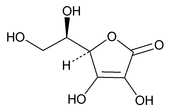
Erythorbic Acid
C6H8O6 176.12
o-Araboascorbic acid;
d-Erythro-hex-2-enoic acid delta-lactone;
Isoascorbic acid, d-isoascorbic acid

 [89-65-6].
[89-65-6].
(er'' i thor' bik as' id).
C6H8O6 176.12
o-Araboascorbic acid;
d-Erythro-hex-2-enoic acid delta-lactone;
Isoascorbic acid, d-isoascorbic acid
DEFINITION
Erythorbic Acid contains NLT 99.0% and NMT 100.5% of C6H8O6, calculated on the dried basis.
IDENTIFICATION
• B.
Sample solution:
20 mg/mL of Erythorbic Acid and water
Analysis:
To 2 mL of Sample solution add a few drops of sodium nitroferricyanide TS and then add 1 mL of 0.1 N sodium hydroxide.
Acceptance criteria:
A transient blue color immediately appears.
• C.
Analysis:
Dissolve about 15 mg of Erythorbic Acid in 15 mL of trichloroacetic acid (1:20). Add about 200 mg of activated charcoal, and shake the mixture vigorously for 1 min. Pass through a small fluted filter, refilter if necessary to obtain a clear filtrate, agitate the mixture until the pyrrole is dissolved, and heat in a water bath at 50 .
.
Acceptance criteria:
A blue color appears.
ASSAY
• Procedure
Sample:
400 mg
Titrimetric system
(See Titrimetry  541
541 .)
.)
Mode:
Direct titration
Titrant:
0.1 N iodine VS
Endpoint detection:
Colorimetric
Analysis:
Dissolve the Sample in a mixture of 100 mL of recently boiled and cooled water and 25 mL of 2 N sulfuric acid. Add 3 mL of starch TS, and titrate at once with 0.1 N iodine VS. Perform a blank determination.
Calculate the percentage of erythorbic acid (C6H8O6) in the Sample taken:
Result = [(V  B) × N × F × 100]/W
B) × N × F × 100]/W
| V | = | = Titrant volume consumed by the Sample (mL) |
| B | = | = Titrant volume consumed by the Blank (mL) |
| N | = | = Titrant actual normality (mEq/mL) |
| F | = | = equivalency factor, 88.06 mg/mEq |
| W | = | = weight of the Sample (mg) |
Acceptance criteria:
99.0%–100.5% on the dried basis
IMPURITIES
• Residue on Ignition  281
281 :
NMT 0.3%
:
NMT 0.3%
• Limit of Lead
[Note—Select reagents having as low a lead content as practicable, and store all solutions in borosilicate glass containers. Rinse all glassware thoroughly with warm 8 N nitric acid followed by deionized water. ]
Standard stock solution:
Dissolve 160 mg of lead nitrate in 100 mL of water containing 1 mL of nitric acid. Dilute with water to 1000 mL. On the day of use, transfer 10.0 mL of the above solution to a 100-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume. Each mL of this solution contains the equivalent of about 10 µg of lead.
[Note—Prepare the Standard solutions on the day of use. ]
Standard solution A:
1 µg/mL of lead from the Standard stock solution
Standard solution B:
2 µg/mL of lead from the Standard stock solution
Standard solution C:
5 µg/mL of lead from the Standard stock solution
Sample solution:
Transfer a weighed portion of about 10 g of Erythorbic Acid to an evaporating dish. Add 5 mL of 25% sulfuric acid, and distribute the sulfuric acid uniformly through the sample. Within a hood, place the dish on a steam bath to evaporate most of the water. Place the dish on a burner, and slowly pre-ash the sample by expelling most of the sulfuric acid. Place the dish in a muffle furnace at 525 , and ash the sample until the residue appears free from carbon. Cool, and cautiously wash down the inside of the evaporation dish with water. Add 5 mL of 1 N hydrochloric acid. Place the dish on a steam bath, and evaporate to dryness. Add 1.0 mL of 3 N hydrochloric acid and approximately 5 mL of water, and heat briefly on a steam bath to dissolve any residue. Transfer quantitatively to a 10-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume.
, and ash the sample until the residue appears free from carbon. Cool, and cautiously wash down the inside of the evaporation dish with water. Add 5 mL of 1 N hydrochloric acid. Place the dish on a steam bath, and evaporate to dryness. Add 1.0 mL of 3 N hydrochloric acid and approximately 5 mL of water, and heat briefly on a steam bath to dissolve any residue. Transfer quantitatively to a 10-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume.
Blank:
To an evaporating dish add 5 mL of 25% sulfuric acid, and distribute the sulfuric acid uniformly. Within a hood, place the dish on a steam bath to evaporate most of the water. Place the dish on a burner, and expel most of the sulfuric acid. Then place the dish in a muffle furnace at 525 for about the same amount of time as in the Sample solution preparation. Cool, and cautiously wash down the inside of the evaporation dish with water. Add 5 mL of 1 N hydrochloric acid. Place the dish on a steam bath, and evaporate to dryness. Add 1.0 mL of 3 N hydrochloric acid and approximately 5 mL of water, and heat briefly on a steam bath to dissolve any residue. Transfer quantitatively to a 10-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume.
for about the same amount of time as in the Sample solution preparation. Cool, and cautiously wash down the inside of the evaporation dish with water. Add 5 mL of 1 N hydrochloric acid. Place the dish on a steam bath, and evaporate to dryness. Add 1.0 mL of 3 N hydrochloric acid and approximately 5 mL of water, and heat briefly on a steam bath to dissolve any residue. Transfer quantitatively to a 10-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume.
Instrumental conditions
Mode:
Atomic absorption
Lamp:
Lead electrodeless discharge
Flame:
Air–acetylene
Analytical wavelength:
283.3 nm
Slit width:
0.7 nm
Standard curve
Samples:
Standard solution A, Standard solution B, Standard solution C, and Blank
Plot:
Corrected absorbance values versus their corresponding concentration (µg/mL). [Note—Determine the corrected absorbance values by subtracting the absorbance of the Blank from the absorbance of the Samples. ]
Analysis
Sample:
Sample solution
From the Standard curve, determine the lead concentration in the Sample solution. Calculate the lead content, in ppm, in the portion of Erythorbic Acid taken:
Result = V × CS/W
| V | = | = volume of the Sample solution (mL) |
| CS | = | = concentration of lead in the Sample solution (µg/mL) |
| W | = | = weight of Erythorbic Acid in the Sample solution (g) |
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 10 ppm
SPECIFIC TESTS
• Loss on Drying  731
731 :
Dry a sample in a vacuum over silica gel for 3 h: it loses NMT 0.4% of its weight.
:
Dry a sample in a vacuum over silica gel for 3 h: it loses NMT 0.4% of its weight.
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
• Packaging and Storage:
Preserve in tight, light-resistant containers.
• USP Reference Standards  11
11
USP Erythorbic Acid RS
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Robert H. Lafaver, M.S.
Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8335 |
(EXC2010) Monographs - Excipients |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP35–NF30 Page 1790
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 33(6) Page 1246