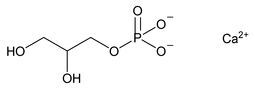Calcium Glycerophosphate
C3H7CaO6P 210.14
1,2,3-Propanetriol, mono(dihydrogen phosphate) calcium salt (1:1);
Calcium glycerophosphate

 [27214-00-2].
[27214-00-2].
C3H7CaO6P 210.14
1,2,3-Propanetriol, mono(dihydrogen phosphate) calcium salt (1:1);
Calcium glycerophosphate
DEFINITION
Calcium Glycerophosphate is a mixture, in variable proportions, of calcium (RS)-2,3-dihydroxypropyl phosphate and calcium 2-hydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)ethyl phosphate, which may be hydrated. Calcium Glycerophosphate contains NLT 18.6% and NMT 19.4% of calcium (Ca), calculated on the dried basis.
IDENTIFICATION
• A.
Analysis:
Ignite 0.1 g in a crucible. Take up the residue with 5 mL of nitric acid, heat on a water bath for 1 min, and filter. Mix 1 mL of the filtrate with 2 mL of ammonium molybdate TS.
Acceptance criteria:
A yellow color develops.
• B.
Analysis:
Dissolve 20 mg of the substance being examined in 5 mL of 5 M acetic acid, and add 0.5 mL of potassium ferrocyanide solution (53 mg/mL). The resulting solution remains clear. To the clear solution, add 50 mg of ammonium chloride.
Acceptance criteria:
A white crystalline precipitate is produced.
ASSAY
• Procedure
Sample:
200 mg
Titrimetric system
(See Titrimetry  541
541 .)
.)
Mode:
Direct titration
Titrant:
0.1 M edetate disodium VS
Endpoint detection:
Colorimetric
Blank:
300 mL of water. Add 6 mL of 10 M sodium hydroxide and 15 mg of calconcarboxylic acid triturate.
Analysis:
Dissolve the Sample in 300 mL of water, add 6 mL of 10 M sodium hydroxide and 15 mg of calconcarboxylic acid triturate. Titrate with Titrant until the solution is a distinct blue color.
Calculate the percentage of calcium (Ca) in the portion of Calcium Glycerophosphate taken:
Result = [(V  B) × M × F × 100]/W
B) × M × F × 100]/W
| V | = | = Sample titrant volume (mL) |
| B | = | = Blank titrant volume (mL) |
| M | = | = titrant molarity (mM/mL) |
| F | = | = equivalency factor, 40.08 mg/mM |
| W | = | = weight of the Sample (mg) |
Acceptance criteria:
18.6%–19.4% on the dried basis
IMPURITIES
• Lead  251
251 :
NMT 4 ppm
:
NMT 4 ppm
• Iron  241
241
Standard solution:
Dilute 1 volume of Standard Iron Solution, prepared as directed in the chapter, with water to 10 volumes (1 µg/mL).
Analysis:
Dissolve 0.20 g in 10 mL of water. Add 2 mL of a 20% (w/v) solution of citric acid, 0.1 mL of thioglycolic acid, and mix. Make alkaline with 10 M ammonia, dilute with water to 20 mL, and allow to stand for 5 min. Any pink color produced is not more intense than that obtained by treating 4 mL of the Standard solution in the same manner.
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 20 ppm
• Heavy Metals, Method I  231
231 :
NMT 20 ppm
:
NMT 20 ppm
• Limit of Chloride
Standard solution:
8.24 µg/mL of sodium chloride in water
Sample solution:
Dissolve 125 mg in a 10-mL mixture of 5 M acetic acid and water (2:8), and dilute with water to 15 mL.
Analysis:
To the Sample solution add 1 mL of 2 M nitric acid, then add 1 mL of a silver nitrate solution (17 mg/mL), and allow to stand for 5 min protected from light. To 10 mL of the Standard solution add 5 mL of water, 1 mL of 2 M nitric acid, and 1 mL of silver nitrate solution (17 mg/mL), and allow to stand for 5 min protected from light. When viewed against a dark background, the Sample solution is not more turbid than the Standard solution.
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 0.04%
• Limit of Sulfate
Standard solution:
36.2 µg/mL of potassium sulfate in water
Sample solution:
Use the Sample solution prepared as directed in the test for Appearance of Solution.
Analysis:
To 15 mL of the Standard solution add 0.5 mL of 5 M acetic acid and 1 mL of barium chloride solution (250 mg/mL). Repeat, using 15 mL of the Sample solution. Allow the solutions to stand for 5 min protected from light. When viewed against a dark background, the Sample solution is not more turbid than the Standard solution.
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 0.2%
• Limit of Arsenic
Standard stock solution:
In a 250-mL volumetric flask dissolve 330 mg of arsenic trioxide in 5 mL of 2 N sodium hydroxide, and dilute with water to volume. Transfer 1 mL of this solution to a 100-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume.
Standard solution:
Transfer 1 mL of Standard stock solution into a 10-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water volume.
Tin(II) chloride solution:
Heat 20 g of tin with 85 mL of hydrochloric acid until no more hydrogen is released. Allow to cool. Dilute 1 volume of this solution with 10 volumes of dilute hydrochloric acid (200 mg/mL of hydrochloric acid in water).
Sample solution:
Transfer 330 mg of Calcium Glycerophosphate to a 25.0-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume.
Apparatus:
Prepare a 100-mL side-arm conical flask containing a magnetic stirring bar. Attach to the conical flask a ground-glass stopper through which passes a glass tube 20-cm long, with an internal diameter of 5 mm. The lower end of the tube is inside the conical flask and has been drawn to a tip with an internal diameter of 1 mm. An orifice 3 mm in diameter is 15 mm from the tip and at least 3 mm below the lower surface of the stopper. The upper end of the tube has a flat ground surface at a right angle to the axis of the tube. A second glass tube of the same internal diameter and 30 mm long, with a similar flat ground surface, is placed in contact with the ground surface of the first tube and is held in position by a clamp and springs. Into the lower tube, insert 55 mg of loosely packed lead acetate cotton. Place a disk of mercuric bromide paper between the flat surfaces of the tubes.
Analysis:
Before placing the tube assembly into the flask, transfer the Sample solution to the flask, and add 15.0 mL of hydrochloric acid, 0.1 mL of Tin(II) chloride solution, and 5 mL of potassium iodide TS. Allow to stand for 15 min, and add 5 g of activated zinc. Assemble the apparatus immediately, and immerse the flask in a water bath at a temperature such that a uniform evolution of gas is maintained. After not less than 2 h, examine the stain produced on the mercuric bromide paper. Perform the same procedure using 1.0 mL of the Standard solution. The stain produced on the mercuric bromide paper by the Sample solution is not more intense than that produced by the Standard solution.
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 3 ppm
• Limit of Phosphates
Sulfomolybdic solution:
Dissolve with heating 2.5 g of ammonium molybdate in 20 mL of water. Dilute 28 mL of sulfuric acid with 50 mL of water, and cool. Mix the two solutions, and dilute with water to 100 mL.
Tin(II) chloride solution:
Prepare as directed in the test for Limit of Arsenic.
Standard stock solution:
14.3 µg/mL of monobasic potassium phosphate in water.
Standard solution:
Transfer 1.0 mL of Standard stock solution to a 100-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume.
Sample solution:
Transfer 2.5 mL of the Sample solution from the test for Appearance of Solution to a 100-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume.
Analysis:
To 100 mL of the Sample solution add 4 mL of Sulfomolybdic solution, mix, and add 0.1 mL of Tin(II) chloride solution. To 100 mL of the Standard solution, add 4 mL of Sulfomolybdic solution, mix, and add 0.1 mL of Tin(II) chloride solution. Allow the preparations to stand for 10 min, then examine 20 mL of each preparation. Any color produced by the Sample solution is not more intense than that produced by the Standard solution.
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 0.04%
• Citric Acid
Mercury(II) sulfate solution:
1 g of mercuric oxide in 20 mL of water and 4 mL of sulfuric acid
Analysis:
Mix 5 g of Calcium Glycerophosphate with 20 mL of carbon dioxide-free water, and filter. To the filtrate add 0.15 mL of sulfuric acid, and filter. To the filtrate add 5 mL of Mercury(II) sulfate solution, and heat to boiling. Add 0.5 mL of 0.2 M potassium permanganate, and heat to boiling.
Acceptance criteria:
No precipitate is formed.
• Glycerol and Alcohol-soluble Substances
Analysis:
Mix 1 g with 25 mL of alcohol, and shake for 1 min. Filter, evaporate the filtrate to dryness on a water bath, and dry the residue at 70 for 1 h.
for 1 h.
Acceptance criteria:
The residue weighs NMT 5 mg (0.5%).
SPECIFIC TESTS
• Appearance of Solution
Opalescent suspension:
Dissolve 1g of hydrazine sulfate in 100 mL of water and allow to stand for 4–6 h. Add 25 mL of this solution to 25 mL of a solution containing 100mg/mL of methenamine in water, and allow to stand for 24 h.
Primary reference suspension:
Dilute 15.0 mL of the Opalescent suspension with water to 1000 mL. [Note—This suspension is freshly prepared and may be stored for NMT 24 h. ]
Reference suspension:
Primary reference suspension and water (30:70). [Note—Shake before using. ]
Sample solution:
Dissolve 1.5 g at room temperature in 150 mL of carbon dioxide-free water.
Analysis:
Compare the opalescence of equal volumes of the Sample solution and the Reference suspension.
Acceptance criteria:
The Sample solution is not more opalescent than the Reference suspension.
• Acidity or Alkalinity
Analysis:
Dissolve 1 g of Calcium Glycerophosphate in 100 mL of water. Add 0.1 mL of 1.0% (w/v) phenolphthalein solution.
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 0.5 mL of 0.1 M sodium hydroxide or 0.1 M hydrochloric acid is required to change the color of the indicator.
• Loss on Drying  731
731 :
Dry a sample at 150
:
Dry a sample at 150 for 4 h: it loses NMT 12.0% of its weight.
for 4 h: it loses NMT 12.0% of its weight.
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
• Packaging and Storage:
Preserve in well-closed containers, and store at controlled room temperature.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Huy T. Dinh, M.S.
Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8594 |
(DS2010) Monographs - Dietary Supplements |
USP35–NF30 Page 1218
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 32(6) Page 1765