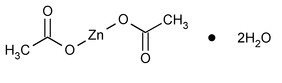
Zinc Acetate
C4H6O4Zn 183.48
Acetic acid, zinc salt, dihydrate;
Zinc acetate dihydrate

 [5970-45-6].
[5970-45-6].
Zinc acetate anhydrous

 [557-34-6].
[557-34-6].
(zink as' e tate).
C4H6O4Zn 183.48
Acetic acid, zinc salt, dihydrate;
Zinc acetate dihydrate
Zinc acetate anhydrous
DEFINITION
Zinc Acetate contains NLT 98.0% and NMT 102.0% of C4H6O4Zn·2H2O.
IDENTIFICATION
• A. Identification Tests—General, Zinc  191
191 :
A 50 mg/mL solution meets the requirements.
:
A 50 mg/mL solution meets the requirements.
• B. Identification Tests—General, Acetate  191
191 :
A 50 mg/mL solution meets the requirements.
:
A 50 mg/mL solution meets the requirements.
ASSAY
• Procedure
Sample solution:
To 400 mg of Zinc Acetate in 100 mL of water add 5 mL of ammonia–ammonium chloride buffer TS and 0.1 mL of eriochrome black TS.
Analysis:
Titrate the Sample solution with 0.05 M edetate disodium VS until the solution is deep blue in color. Each mL of 0.05 M edetate disodium is equivalent to 10.98 mg of zinc acetate dihydrate (C4H6O4Zn·2H2O).
Acceptance criteria:
98.0%–102.0%
IMPURITIES
• Chloride and Sulfate, Chloride  221
221 :
A 1.5-g portion shows no more chloride than corresponds to 0.10 mL of 0.020 N hydrochloric acid (0.005%).
:
A 1.5-g portion shows no more chloride than corresponds to 0.10 mL of 0.020 N hydrochloric acid (0.005%).
• Chloride and Sulfate, Sulfate  221
221 :
A 1.0-g portion shows no more sulfate than corresponds to 0.10 mL of 0.020 N sulfuric acid (0.010%).
:
A 1.0-g portion shows no more sulfate than corresponds to 0.10 mL of 0.020 N sulfuric acid (0.010%).
• Arsenic, Method I  211
211 :
NMT 3 ppm
:
NMT 3 ppm
• Lead  251
251
Standard solution:
To 20 mL of dilute nitric acid (1 in 100) add 0.01 mg of lead, 4 mL of Ammonia–cyanide solution, and 2 drops of Hydroxylamine hydrochloride solution, and shake for 30 s with 10.0 mL of Standard dithizone solution. Pass through acid-washed filter paper into a color-comparison tube.
Sample solution:
Dissolve 0.5 g of zinc acetate in 1 mL of a mixture of nitric acid and water (1:1) in a separator. Add 3 mL of Ammonium citrate solution and 0.5 mL of Hydroxylamine hydrochloride solution, and render alkaline with ammonium hydroxide to phenol red TS. Add 10 mL of Potassium cyanide solution, and immediately extract the solution with successive 5-mL portions of Dithizone extraction solution, draining off each extract into another separator, until the last portion of dithizone solution retains its green color. Shake the combined extracts for 30 s with 20 mL of dilute nitric acid (1 in 100), and discard the chloroform layer. Add to the acid solution 4.0 mL of Ammonia–cyanide solution and 2 drops of Hydroxylamine hydrochloride solution. Add 10.0 mL of Standard dithizone solution, and shake the mixture for 30 s. Filter the chloroform layer through acid-washed filter paper into a color-comparison tube.
Analysis:
Compare the color of the Sample solution with that of a Standard solution.
Acceptance criteria:
The color of the Sample solution does not exceed the color of the Standard solution (0.002%).
• Alkalies and Alkaline Earths
Sample solution:
Dissolve 2.0 g in 150 mL of water in a 200-mL volumetric flask. Add sufficient ammonium sulfide TS to precipitate the zinc completely, and dilute with water to volume. Pass through a dry filter, rejecting the first portion of the filtrate.
Analysis:
To 100 mL of the filtrate add 5 drops of sulfuric acid. Evaporate to dryness, and ignite.
Acceptance criteria:
The weight of the residue does not exceed 2 mg (0.2%).
SPECIFIC TESTS
• Insoluble Matter:
A 20-g portion, dissolved in 150 mL of water containing 1 mL of glacial acetic acid, shows NMT 1.0 mg of insoluble matter (0.005%).
• pH  791
791 :
6.0–8.0, in a solution (1 in 20)
:
6.0–8.0, in a solution (1 in 20)
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
• Packaging and Storage:
Preserve in tight containers.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Sujatha Ramakrishna, Ph.D.
Senior Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8349 |
(SM22010) Monographs - Small Molecules 2 |
USP35–NF30 Page 5068