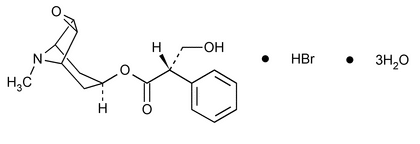Scopolamine Hydrobromide
(skoe pol' a meen hye'' droe broe' mide).
Benzeneacetic acid,
6
Anhydrous 384.27
» Scopolamine Hydrobromide contains not less than 98.5 percent and not more than 102.0 percent of C17H21NO4·HBr, calculated on the anhydrous basis.
[Caution—Handle Scopolamine Hydrobromide with exceptional care, since it is highly potent.
]
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in tight, light-resistant containers.
Identification—
A:
Infrared Absorption  197K
197K —
—
Test specimen—
Dissolve 3 mg in 1 mL of alcohol, and evaporate the solution on a steam bath to dryness. Dissolve the residue in 0.5 mL of chloroform, add 200 mg of potassium bromide, previously dried at 105 for 30 minutes, and stir frequently for 5 minutes. Allow the chloroform to evaporate to dryness, and stir frequently to obtain a flowing powder residue. Dry the residue on a steam bath for 5 minutes, then immediately compress the residue to a disk.
for 30 minutes, and stir frequently for 5 minutes. Allow the chloroform to evaporate to dryness, and stir frequently to obtain a flowing powder residue. Dry the residue on a steam bath for 5 minutes, then immediately compress the residue to a disk.
B:
To 1 mL of a solution (1 in 20) add a few drops of chlorine TS, and shake the mixture with 1 mL of chloroform: the latter assumes a brownish color.
Specific rotation  781S
781S :
between
:
between  24
24 and
and  26
26 .
.
Test solution:
an amount equivalent to 50 mg of anhydrous Scopolamine Hydrobromide per mL, in water.
pH  791
791 :
between 4.0 and 5.5, in a solution (1 in 20).
:
between 4.0 and 5.5, in a solution (1 in 20).
Water, Method III  921
921 —
Dry it in two stages (see Loss on drying
—
Dry it in two stages (see Loss on drying  731
731 ); first at 80
); first at 80 for 2 hours, and then at 105
for 2 hours, and then at 105 for an additional 3 hours: it loses not more than 13.0% of its weight.
for an additional 3 hours: it loses not more than 13.0% of its weight.
Residue on ignition  281
281 :
negligible, from 100 mg.
:
negligible, from 100 mg.
Limit of apoatropine—
To 15 mL of a solution (1 in 100) add 0.05 mL of 0.1 N potassium permanganate VS: the solution is not completely decolorized within 5 minutes.
Other foreign alkaloids—
To 1 mL of a solution (1 in 20) add a few drops of 6 N ammonium hydroxide: no turbidity is produced. Add 1 N potassium hydroxide to another 1-mL portion of the solution: only a transient whitish turbidity is produced.
Assay—
Dissolve about 750 mg of Scopolamine Hydrobromide, accurately weighed, in a mixture of 30 mL of glacial acetic acid and 10 mL of mercuric acetate TS, warming slightly to effect solution. Cool the solution to room temperature, add 2 drops of crystal violet TS, and titrate with 0.1 N perchloric acid VS. Perform a blank determination, and make any necessary correction. Each mL of 0.1 N perchloric acid is equivalent to 38.43 mg of C17H21NO4·HBr.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Feiwen Mao, M.S.
Senior Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8320 |
(SM32010) Monographs - Small Molecules 3 |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP35–NF30 Page 4615
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 31(1) Page 73