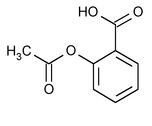
Aspirin
(as' pir in).
» Aspirin contains not less than 99.5 percent and not more than 100.5 percent of C9H8O4, calculated on the dried basis.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in tight containers.
Identification—
A:
Heat it with water for several minutes, cool, and add 1 or 2 drops of ferric chloride TS: a violet-red color is produced.
Loss on drying  731
731 —
Dry it over silica gel for 5 hours: it loses not more than 0.5% of its weight.
—
Dry it over silica gel for 5 hours: it loses not more than 0.5% of its weight.
Readily carbonizable substances  271
271 —
Dissolve 500 mg in 5 mL of sulfuric acid : the solution has no more color than Matching Fluid Q.
—
Dissolve 500 mg in 5 mL of sulfuric acid : the solution has no more color than Matching Fluid Q.
Residue on ignition  281
281 :
not more than 0.05%.
:
not more than 0.05%.
Substances insoluble in sodium carbonate TS—
A solution of 500 mg in 10 mL of warm sodium carbonate TS is clear.
Chloride  221
221 —
Boil 1.5 g with 75 mL of water for 5 minutes, cool, add sufficient water to restore the original volume, and filter. A 25-mL portion of the filtrate shows no more chloride than corresponds to 0.10 mL of 0.020 N hydrochloric acid (0.014%).
—
Boil 1.5 g with 75 mL of water for 5 minutes, cool, add sufficient water to restore the original volume, and filter. A 25-mL portion of the filtrate shows no more chloride than corresponds to 0.10 mL of 0.020 N hydrochloric acid (0.014%).
Sulfate —
Dissolve 6.0 g in 37 mL of acetone, and add 3 mL of water. Titrate potentiometrically with 0.02 M lead perchlorate, prepared by dissolving 9.20 g of lead perchlorate in water to make 1000 mL of solution, using a pH meter capable of a minimum reproducibility of ±0.1 mV (see pH  791
791 ) and equipped with an electrode system consisting of a lead-specific electrode and a silver–silver chloride reference glass-sleeved electrode containing a solution of tetraethylammonium perchlorate in glacial acetic acid (1 in 44) (see Titrimetry
) and equipped with an electrode system consisting of a lead-specific electrode and a silver–silver chloride reference glass-sleeved electrode containing a solution of tetraethylammonium perchlorate in glacial acetic acid (1 in 44) (see Titrimetry  541
541 ): not more than 1.25 mL of 0.02 M lead perchlorate is consumed (0.04%). [note—After use, rinse the lead-specific electrode with water, drain the reference electrode, flush with water, rinse with methanol, and allow to dry. ]
): not more than 1.25 mL of 0.02 M lead perchlorate is consumed (0.04%). [note—After use, rinse the lead-specific electrode with water, drain the reference electrode, flush with water, rinse with methanol, and allow to dry. ]
Heavy metals—
Dissolve 2 g in 25 mL of acetone, and add 1 mL of water. Add 1.2 mL of thioacetamide–glycerin base TS and 2 mL of pH 3.5 Acetate Buffer (see Heavy Metals  231
231 ), and allow to stand for 5 minutes: any color produced is not darker than that of a control made with 25 mL of acetone and 2 mL of Standard Lead Solution (see Heavy Metals
), and allow to stand for 5 minutes: any color produced is not darker than that of a control made with 25 mL of acetone and 2 mL of Standard Lead Solution (see Heavy Metals  231
231 ), treated in the same manner. The limit is 10 µg per g.
), treated in the same manner. The limit is 10 µg per g.
Limit of free salicylic acid—
Dissolve 2.5 g in sufficient alcohol to make 25.0 mL. To each of two matched color-comparison tubes add 48 mL of water and 1 mL of a freshly prepared, diluted ferric ammonium sulfate solution (prepared by adding 1 mL of 1 N hydrochloric acid to 2 mL of ferric ammonium sulfate TS and diluting with water to 100 mL). Into one tube pipet 1 mL of a standard solution of salicylic acid in water, containing 0.10 mg of salicylic acid per mL. Into the second tube pipet 1 mL of the 1 in 10 solution of Aspirin. Mix the contents of each tube: after 30 seconds, the color in the second tube is not more intense than that in the tube containing the salicylic acid (0.1%).
Assay—
Place about 1.5 g of Aspirin, accurately weighed, in a flask, add 50.0 mL of 0.5 N sodium hydroxide VS, and boil the mixture gently for 10 minutes. Add phenolphthalein TS, and titrate the excess sodium hydroxide with 0.5 N sulfuric acid VS. Perform a blank determination (see Residual Titrations under Titrimetry  541
541 ). Each mL of 0.5 N sodium hydroxide is equivalent to 45.04 mg of C9H8O4.
). Each mL of 0.5 N sodium hydroxide is equivalent to 45.04 mg of C9H8O4.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Clydewyn M. Anthony, Ph.D.
Senior Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8139 |
(SM22010) Monographs - Small Molecules 2 |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP35–NF30 Page 2245
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 34(5) Page 1143