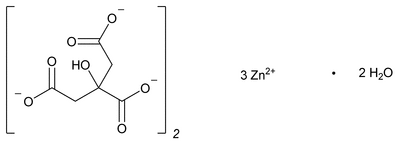Zinc Citrate
C12H10O14Zn3·2H2O 610.36
2-Hydroxy-1,2,3-propanetricarboxylic acid zinc salt, dihydrate

 [5990-32-9].
[5990-32-9].
Anhydrous

 [546-46-3].
[546-46-3].
C12H10O14Zn3·2H2O 610.36
2-Hydroxy-1,2,3-propanetricarboxylic acid zinc salt, dihydrate
Anhydrous
DEFINITION
Zinc Citrate contains NLT 31.3% of zinc (Zn), calculated on the dried basis.
IDENTIFICATION
• A. Identification Tests—General, Zinc  191
191 :
A solution (1 in 10) meets the requirements.
:
A solution (1 in 10) meets the requirements.
• B. Identification Tests—General, Citrate  191
191 :
A solution (1 in 10) meets the requirements.
:
A solution (1 in 10) meets the requirements.
ASSAY
• Procedure
Sample:
350 mg of Zinc Citrate, previously dried at 105 for 2 h
for 2 h
Blank:
60 mL of water
Titrimetric system
(See Titrimetry  541
541 .)
.)
Mode:
Direct titration
Titrant:
0.05 M edetate disodium VS
Endpoint detection:
Visual
Analysis:
Dissolve the Sample in 60 mL of water. Add 10 mL of ammonia–ammonium chloride buffer TS and 0.1 mL of eriochrome black TS. Titrate with the Titrant to a blue endpoint. Perform a blank determination.
Calculate the percentage of zinc (Zn) in the portion of Zinc Citrate taken:
Result = [(V  B) × M × F × 100]/W
B) × M × F × 100]/W
| V | = | = sample titrant volume (mL) |
| B | = | = blank titrant volume (mL) |
| M | = | = titrant molarity (mM/mL) |
| F | = | = equivalency factor, 65.4 mg/mM |
| W | = | = sample weight (mg) |
Acceptance criteria:
NLT 31.3% on the dried basis
IMPURITIES
• Chloride and Sulfate, Chloride  221
221 :
A 1.0-g portion shows no more chloride than corresponds to 0.7 mL of 0.020 N hydrochloric acid (NMT 0.05%).
:
A 1.0-g portion shows no more chloride than corresponds to 0.7 mL of 0.020 N hydrochloric acid (NMT 0.05%).
• Chloride and Sulfate, Sulfate  221
221 :
A 1.8-g portion shows no more sulfate than corresponds to 0.5 mL of 0.020 N sulfuric acid (NMT 0.05%).
:
A 1.8-g portion shows no more sulfate than corresponds to 0.5 mL of 0.020 N sulfuric acid (NMT 0.05%).
• Limit of Arsenic, Cadmium, and Lead
Arsenic standard solution:
1.0 µg/mL in 1% nitric acid, prepared from an arsenic standard solution (10 mg/L)
Cadmium standard solution:
1.0 µg/mL in 1% nitric acid, prepared from a cadmium standard solution (10 mg/L)
Lead standard solution:
1.0 µg/mL in 1% nitric acid, prepared from a lead standard solution (10 mg/L)
Multi-element standard solution:
10 µg/L of lead, 5 µg/L of cadmium, and 3 µg/L of arsenic in 1% nitric acid, prepared from the Lead standard solution, Cadmium standard solution, and Arsenic standard solution, respectively
Sample solution:
2 mg/mL of Zinc Citrate in 1% nitric acid
Instrumental conditions
(See Plasma Spectrochemistry  730
730 .)
.)
Mode:
ICP-MS
Radio frequency:
1350 Watts
Nebulizer flow rate:
0.9 L/min
[Note—The radio frequency and nebulizer flow rate settings may be developed and optimized based on the manufacturer's recommendation. ]
Detection atomic masses:
As, Cd, and Pb
Blank:
1% nitric acid solution
Analysis
Samples:
Multi-element standard solution, Sample solution, and Blank
Determine the responses of the Multi-element standard solution, Sample solution, and Blank at the masses indicated above.
Calculate the content of each element, in µg/g, in the portion of Zinc Citrate taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU)
| rU | = | = peak response of the corresponding element from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak response of the corresponding element from the Multi-element standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of the corresponding element in the Multi-element standard solution (µg/L) |
| CU | = | = concentration of Zinc Citrate in the Sample solution (g/L) |
Acceptance criteria
Arsenic:
NMT 3 µg/g
Cadmium:
NMT 5 µg/g
Lead:
NMT 10 µg/g
SPECIFIC TESTS
• Loss on Drying  731
731 :
Dry a sample at 105
:
Dry a sample at 105 for 2 h: it loses NMT 1.0% of its weight.
for 2 h: it loses NMT 1.0% of its weight.
• Microbial Enumeration Tests  2021
2021 :
The total aerobic microbial count does not exceed 103 cfu/g. The total combined yeasts and molds count does not exceed 102 cfu/g.
:
The total aerobic microbial count does not exceed 103 cfu/g. The total combined yeasts and molds count does not exceed 102 cfu/g.
• Microbiological Procedures for Absence of Specified Microorganisms  2022
2022 :
It meets the requirements of the test for absence of Escherichia coli.
:
It meets the requirements of the test for absence of Escherichia coli.
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
• Packaging and Storage:
Preserve in well-closed containers.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Huy T. Dinh, M.S.
Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8594 |
(DS2010) Monographs - Dietary Supplements |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8339 |
(GCM2010) General Chapters - Microbiology | |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8339 |
(GCM2010) General Chapters - Microbiology |
USP35–NF30 Page 1662
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 34(2) Page 315