Powdered Cellulose
DEFINITION
Powdered Cellulose is purified, mechanically disintegrated cellulose prepared by processing alpha cellulose obtained as a pulp from fibrous plant materials.
IDENTIFICATION
• A. Procedure
Iodinated zinc chloride solution:
Dissolve 20 g of zinc chloride and 6.5 g of potassium iodide in 10.5 mL of water. Add 0.5 g of iodine, and shake for 15 min.
Sample:
10 mg
Analysis:
Place the Sample on a watch glass, and disperse in 2 mL of Iodinated zinc chloride solution.
Acceptance criteria:
The substance takes on a violet-blue color.
• B. Procedure
Sample:
0.25 g of Powdered Cellulose, accurately weighed to 0.1 mg
Analysis:
Transfer the Sample to a 125-mL conical flask. Add 25.0 mL of water and 25.0 mL of 1.0 M cupriethylenediamine hydroxide solution. Immediately purge the solution with nitrogen, insert the stopper, and shake on a wrist action shaker, or other suitable mechanical shaker, until completely dissolved. Transfer an appropriate volume of the solution to a calibrated number 150 Cannon-Fenske, or equivalent, viscometer. Allow the solution to equilibrate at 25 ± 0.1 for NLT 5 min. Time the flow between the two marks on the viscometer, and record the flow time, t1, in s.
for NLT 5 min. Time the flow between the two marks on the viscometer, and record the flow time, t1, in s.
Calculate the kinematic viscosity, (KV)1, of the Powdered Cellulose taken:
Result = t1 × k1
| k1 | = | = viscometer constant (see Viscosity |
Obtain the flow time, t2, for a 0.5 M cupriethylenediamine hydroxide solution using a number 100 Cannon-Fenske, or equivalent, viscometer.
Calculate the kinematic viscosity, (KV)2, of the solvent:
Result = t2 × k2
| k2 | = | = viscometer constant |
Determine the relative viscosity, 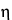 rel, of the Powdered Cellulose specimen taken:
rel, of the Powdered Cellulose specimen taken:
Result = (KV)1/(KV)2
| (KV)1 | = | = kinematic viscosity of the Powdered Cellulose |
| (KV)2 | = | = kinematic viscosity of the solvent |
Determine the intrinsic viscosity, [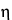 ]c, by interpolation, using the Intrinsic Viscosity Table in the Reference Tables section.
]c, by interpolation, using the Intrinsic Viscosity Table in the Reference Tables section.
Calculate the degree of polymerization, P:
Result = 95 × [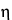 ]c/WS × [(100
]c/WS × [(100  %LOD)/100]
%LOD)/100]
| WS | = | = weight of the Powdered Cellulose taken (g) |
| %LOD | = | = value obtained from the test for Loss on Drying |
Acceptance criteria:
The degree of polymerization is greater than 440.
IMPURITIES
Inorganic Impurities
• Residue on Ignition  281
281 :
NMT 0.3%, calculated on the dried basis
:
NMT 0.3%, calculated on the dried basis
• Heavy Metals, Method II  231
231 :
NMT 10 ppm
:
NMT 10 ppm
SPECIFIC TESTS
• Microbial Enumeration Tests  61
61 and Tests for Specified Microorganisms
and Tests for Specified Microorganisms  62
62 :
The total aerobic microbial count does not exceed 1000 cfu/g, the total combined molds and yeasts count does not exceed 100 cfu/g, and it meets the requirements of the tests for absence of Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa and for absence of Escherichia coli and Salmonella species.
:
The total aerobic microbial count does not exceed 1000 cfu/g, the total combined molds and yeasts count does not exceed 100 cfu/g, and it meets the requirements of the tests for absence of Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa and for absence of Escherichia coli and Salmonella species.
• pH  791
791 :
The pH of the supernatant is 5.0–7.5. Mix 10 g with 90 mL of water, and allow to stand with occasional stirring for 1 h.
:
The pH of the supernatant is 5.0–7.5. Mix 10 g with 90 mL of water, and allow to stand with occasional stirring for 1 h.
• Loss on Drying  731
731 :
Dry a sample at 105
:
Dry a sample at 105 for 3 h: it loses NMT 6.5% of its weight.
for 3 h: it loses NMT 6.5% of its weight.
• Water-Soluble Substances
Sample:
6.0 g
Analysis:
Mix the Sample with 90 mL of recently boiled and cooled water, and allow to stand with occasional stirring for 10 min. Filter, with the aid of vacuum, discard the first 10 mL of the filtrate, and pass the filtrate through the same filter a second time, if necessary, to obtain a clear filtrate. Evaporate a 15.0-mL portion of the filtrate in a tared evaporating dish to dryness without charring, dry at 105 for 1 h, cool in a desiccator, and weigh.
for 1 h, cool in a desiccator, and weigh.
Acceptance criteria:
The difference between the weight of the residue and the weight obtained from a blank determination does not exceed 15.0 mg (1.5%).
• Ether-Soluble Substances
Sample:
10.0 g
Analysis:
Place the Sample in a chromatography column having an internal diameter of about 20 mm, and pass 50 mL of peroxide-free ether through the column. Evaporate the eluate to dryness in a previously dried and tared evaporating dish with the aid of a current of air in a fume hood. After all the ether has evaporated, dry the residue at 105 for 30 min, cool in a desiccator, and weigh.
for 30 min, cool in a desiccator, and weigh.
Acceptance criteria:
The difference between the weight of the residue and the weight obtained from a blank determination does not exceed 15.0 mg (0.15%).
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
• Packaging and Storage:
Preserve in tight containers.
• Labeling:
The labeling indicates the nominal degree of polymerization value. Degree of polymerization compliance is determined using Identification test B.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Robert H. Lafaver, M.S.
Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8335 |
(EXC2010) Monographs - Excipients |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8339 |
(GCM2010) General Chapters - Microbiology | |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8339 |
(GCM2010) General Chapters - Microbiology |
USP35–NF30 Page 1749
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 31(5) Page 1421