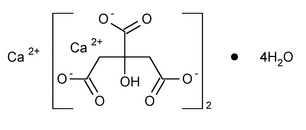Calcium Citrate
C12H10Ca3O14·4H2O 570.49
1,2,3-Propanetricarboxylic acid, 2-hydroxy-, calcium salt (2:3), tetrahydrate;
Calcium citrate (3:2), tetrahydrate

 [5785-44-4].
[5785-44-4].
(kal' see um si' trate).
C12H10Ca3O14·4H2O 570.49
1,2,3-Propanetricarboxylic acid, 2-hydroxy-, calcium salt (2:3), tetrahydrate;
Calcium citrate (3:2), tetrahydrate
DEFINITION
Calcium Citrate contains four molecules of water of hydration. When dried at 150 to constant weight, it contains NLT 97.5% and NMT 100.5% of Ca3(C6H5O7)2.
to constant weight, it contains NLT 97.5% and NMT 100.5% of Ca3(C6H5O7)2.
IDENTIFICATION
• A.
Analysis:
Dissolve 0.5 g in a mixture of 10 mL of water and 2.5 mL of 2 N nitric acid. Add 1 mL of mercuric sulfate TS, heat to boiling, and add 1 mL of potassium permanganate TS.
Acceptance criteria:
A white precipitate is formed.
• B.
Sample:
0.5 g of Calcium Citrate
Analysis:
Ignite completely the Sample at as low a temperature as possible, cool, and dissolve the residue in dilute glacial acetic acid (1:10). Filter, and add 10 mL of ammonium oxalate TS to the filtrate.
Acceptance criteria:
A voluminous white precipitate that is soluble in hydrochloric acid is formed.
ASSAY
• Procedure
Sample solution:
Dissolve 350 mg of Calcium Citrate, previously dried at 150 to constant weight, in 12 mL of 0.5 M hydrochloric acid, and dilute with water to about 100 mL.
to constant weight, in 12 mL of 0.5 M hydrochloric acid, and dilute with water to about 100 mL.
Analysis:
While stirring the Sample solution, add 30 mL of 0.05 M edetate disodium VS from a 50-mL buret. Add 15 mL of 1 N sodium hydroxide and 300 mg of hydroxy naphthol blue, and continue the titration to a blue endpoint. Each mL of 0.05 M edetate disodium is equivalent to 8.307 mg of calcium citrate (Ca3(C6H5O7)2).
Acceptance criteria:
97.5%–100.5% on the dried basis
IMPURITIES
• Arsenic, Method I  211
211
Test preparation:
Dissolve 1 g of Calcium Citrate in 5 mL of 3 N hydrochloric acid, and dilute with water to 35 mL.
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 3 ppm
• Heavy Metals, Method I  231
231
Test preparation:
Dissolve 1 g of Calcium Citrate in a mixture of hydrochloric acid and water (2:20). Add 1.5 mL of ammonium hydroxide, and dilute with water to 25 mL.
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 20 ppm
• Lead  251
251
Test preparation:
Dissolve 0.5 g of Calcium Citrate in 20 mL of 3 N hydrochloric acid. Evaporate this solution on a steam bath to 10 mL, dilute with water to 20 mL, and cool. Use 5 mL of Diluted Standard Lead Solution (5 µg of Pb) for the test.
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 10 ppm
• Limit of Fluoride
[Note—Prepare and store all solutions in plastic containers. ]
Standard stock solution:
1000 µg/mL of fluoride ion from USP Sodium Fluoride RS in water
Standard solution:
5 µg/mL of fluoride ion from Standard stock solution. [Note—Prepare on the day of use. ]
Linearity solution A:
Transfer 1.0 mL of the Standard solution to a 250-mL plastic beaker. Add 50 mL of water, 5 mL of 1 N hydrochloric acid, 10 mL of 1.0 M sodium citrate, and 10 mL of 0.2 M edetate disodium. If necessary, adjust with 1 N sodium hydroxide or 1 N hydrochloric acid to a pH of 5.5. Transfer to a 100-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume. This solution contains 0.05 µg/mL of fluoride.
Linearity solution B:
Transfer 5.0 mL of the Standard solution to a 250-mL plastic beaker, and proceed as directed for Linearity solution A beginning with “Add 50 mL of water,”. This solution contains 0.25 µg/mL of fluoride.
Linearity solution C:
Transfer 10.0 mL of the Standard solution to a 250-mL plastic beaker, and proceed as directed for Linearity solution A beginning with “Add 50 mL of water,”. This solution contains 0.50 µg/mL of fluoride.
Sample solution:
Transfer 1.0 g of Calcium Citrate to a 100-mL beaker. Add 10 mL of water and, while stirring, 10 mL of 1 N hydrochloric acid. When dissolved, boil rapidly for 1 min, transfer the solution to a 250-mL plastic beaker, and cool in ice water. Add 15 mL of 1.0 M sodium citrate and 10 mL of 0.2 M edetate disodium, and adjust with 1 N sodium hydroxide or 1 N hydrochloric acid to a pH of 5.5. Transfer this solution to a 100-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume.
Electrode system:
Use a fluoride-specific, ion-indicating electrode and a silver–silver chloride reference electrode connected to a pH meter capable of measuring potentials with a minimum reproducibility of ±0.2 mV (see pH  791
791 ).
).
Analysis
Samples:
Linearity solution A, Linearity solution B, Linearity solution C, and Sample solution
Transfer 50 mL of each Linearity solution A, Linearity solution B, and Linearity solution C to separate 250-mL plastic beakers, and measure the potential of each solution with the Electrode system. Between each reading wash the electrodes with water, and absorb any residual water by blotting the electrodes dry. Plot the logarithms of the fluoride concentrations (0.05, 0.25, and 0.50 µg/mL, respectively) versus potential to obtain a Standard response line.
Transfer 50 mL of the Sample solution to a 250-mL plastic beaker, and measure the potential with the Electrode system. From the measured potential and the Standard response line determine the concentration, C, in µg/mL, of fluoride ion in the Sample solution. Calculate the percentage of fluoride in the specimen taken by multiplying C by 0.01.
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 0.003%
• Limit of Acid-Insoluble Substances
Sample solution:
Dissolve 5 g of Calcium Citrate by heating with a mixture of hydrochloric acid and water (10:50) for 30 min.
Analysis:
Filter, wash, and dry at 105 for 2 h the residue so obtained.
for 2 h the residue so obtained.
Acceptance criteria:
The weight of the residue is NMT 10 mg (0.2%).
SPECIFIC TESTS
• Loss on Drying  731
731 :
Dry a sample at 150
:
Dry a sample at 150 for 4 h: it loses from 10.0% to 13.3% of its weight.
for 4 h: it loses from 10.0% to 13.3% of its weight.
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
• Packaging and Storage:
Preserve in well-closed containers.
• USP Reference Standards  11
11
USP Sodium Fluoride RS
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Domenick Vicchio, Ph.D.
Senior Scientific Liaison 1-301-998-6828 |
(SM42010) Monographs - Small Molecules 4 |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP35–NF30 Page 2451
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 27(6) Page 3257