Dibasic Sodium Phosphate
Na2HPO4·xH2O (anhydrous)




 141.96
141.96
Phosphoric acid, disodium salt, dodecahydrate.
Disodium hydrogen phosphate, dodecahydrate 358.14
Phosphoric acid, disodium salt, heptahydrate.
Disodium hydrogen phosphate heptahydrate 268.07
Phosphoric acid, disodium salt, dihydrate.
Disodium hydrogen phosphate, dihydrate 177.99
Phosphoric acid, sodium salt, monohydrate.
Disodium hydrogen phosphate, monohydrate 159.94
Phosphoric acid, disodium salt, hydrate.
Disodium hydrogen phosphate hydrate
Anhydrous
» Dibasic Sodium Phosphate is dried or contains one, two, seven, or twelve molecules of water of hydration. It contains not less than 98.0 percent and not more than 100.5 percent of Na2HPO4, calculated on the dried basis.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in tight containers.
Labeling—
Label it to indicate whether it is dried or is the monohydrate, the dihydrate, the heptahydrate, or the dodecahydrate.
Identification—
A solution (the equivalent of 1 part of Na2HPO4 in 30) responds to the tests for Sodium  191
191 and for Phosphate
and for Phosphate  191
191 .
.
Loss on drying  731
731 —
Dry it at 130
—
Dry it at 130 to constant weight: the dried form loses not more than 5.0% of its weight, the monohydrate loses between 10.3% and 12.0% of its weight, the dihydrate loses between 18.5% and 21.5% of its weight, the heptahydrate loses between 43.0% and 50.0% of its weight, and the dodecahydrate loses between 55.0% and 64.0% of its weight.
to constant weight: the dried form loses not more than 5.0% of its weight, the monohydrate loses between 10.3% and 12.0% of its weight, the dihydrate loses between 18.5% and 21.5% of its weight, the heptahydrate loses between 43.0% and 50.0% of its weight, and the dodecahydrate loses between 55.0% and 64.0% of its weight.
Insoluble substances—
Dissolve the equivalent of 5.0 g of Na2HPO4 in 100 mL of hot water, filter through a tared filtering crucible, wash the insoluble residue with hot water, and dry at 105 for 2 hours: the weight of the residue so obtained does not exceed 20 mg (0.4%).
for 2 hours: the weight of the residue so obtained does not exceed 20 mg (0.4%).
Chloride  221
221 —
A portion equivalent to 0.5 g of Na2HPO4 shows no more chloride than corresponds to 0.42 mL of 0.020 N hydrochloric acid (0.06%).
—
A portion equivalent to 0.5 g of Na2HPO4 shows no more chloride than corresponds to 0.42 mL of 0.020 N hydrochloric acid (0.06%).
Sulfate  221
221 —
A portion equivalent to 0.1 g of Na2HPO4 shows no more sulfate than corresponds to 0.2 mL of 0.020 N sulfuric acid (0.2%).
—
A portion equivalent to 0.1 g of Na2HPO4 shows no more sulfate than corresponds to 0.2 mL of 0.020 N sulfuric acid (0.2%).
Arsenic, Method I  211
211 —
Prepare a Test Preparation by dissolving a portion equivalent to 187.5 mg of Na2HPO4 in 35 mL of water: the limit is 16 ppm.
—
Prepare a Test Preparation by dissolving a portion equivalent to 187.5 mg of Na2HPO4 in 35 mL of water: the limit is 16 ppm.
Heavy metals  231
231 —
Dissolve a portion equivalent to 2.1 g of Na2HPO4 in enough water to make 50 mL of stock solution. Transfer 12 mL of this stock solution to a 50-mL color-comparison tube (Test Preparation). Transfer 11 mL of the stock solution to a second color-comparison tube containing 1.0 mL of Standard Lead Solution (Monitor Preparation). Transfer 1.0 mL of Standard Lead Solution and 11 mL of water to a third color-comparison tube (Standard Preparation). Proceed as directed for Procedure, omitting the dilution to 50 mL: the limit is 0.002%.
—
Dissolve a portion equivalent to 2.1 g of Na2HPO4 in enough water to make 50 mL of stock solution. Transfer 12 mL of this stock solution to a 50-mL color-comparison tube (Test Preparation). Transfer 11 mL of the stock solution to a second color-comparison tube containing 1.0 mL of Standard Lead Solution (Monitor Preparation). Transfer 1.0 mL of Standard Lead Solution and 11 mL of water to a third color-comparison tube (Standard Preparation). Proceed as directed for Procedure, omitting the dilution to 50 mL: the limit is 0.002%.
Assay—
Transfer 40.0 mL of 1 N hydrochloric acid to a 250-mL beaker, add 50 mL of water, and titrate potentiometrically with 1 N sodium hydroxide VS to the endpoint. Record the volume of 1 N sodium hydroxide VS consumed as the blank. Transfer a portion of Dibasic Sodium Phosphate, accurately weighed, equivalent to about 2.5 g of Na2HPO4, to a 250-mL beaker, add 40.0 mL of the 1 N hydrochloric acid and 50 mL of water, and stir until dissolved. Titrate the excess acid potentiometrically with 1 N sodium hydroxide VS to the inflection point at about pH 4, and record the buret reading. Subtract this buret reading from that of the blank, and designate the volume of 1 N sodium hydroxide VS resulting from this subtraction as A. Continue the titration with 1 N sodium hydroxide VS to the inflection point at about pH 8.8, record the buret reading, and calculate the volume (B) of 1 N sodium hydroxide required in the titration between the two inflection points (pH 4 to pH 8.8). Where A is equal to or less than B, each mL of the volume A of 1 N sodium hydroxide is equivalent to 142.0 mg of Na2HPO4. Where A is greater than B, each mL of the volume 2B 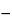 A of 1 N sodium hydroxide is equivalent to 142.0 mg of Na2HPO4.
A of 1 N sodium hydroxide is equivalent to 142.0 mg of Na2HPO4.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
| Monograph | Elena Gonikberg, Ph.D.
Senior Scientist 1-301-816-8251 |
(MDGRE05) Monograph Development-Gastrointestinal Renal and Endocrine |
USP32–NF27 Page 3581
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 29(5) Page 1578