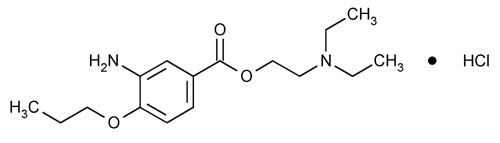
Proparacaine Hydrochloride
Benzoic acid, 3-amino-4-propoxy-, 2-(diethylamino)ethyl ester, monohydrochloride.
2-(Diethylamino)ethyl 3-amino-4-propoxybenzoate monohydrochloride
» Proparacaine Hydrochloride contains not less than 97.0 percent and not more than 103.0 percent of C16H26N2O3·HCl, calculated on the dried basis.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in well-closed containers.
Identification—
A:
It meets the requirements under Identification—Organic Nitrogenous Bases  181
181 .
.
B:
Dissolve 50 mg, accurately weighed, in water to make 250.0 mL, and mix. Pipet 10 mL of this solution into a 100-mL volumetric flask, add 2 mL of 10 percent, pH 6.0 phosphate buffer (see Buffer Solutions in the section Reagents, Indicators, and Solutions), add water to volume, and mix: the UV absorption spectrum of the solution exhibits maxima and minima at the same wavelengths as that of a similar solution of USP Proparacaine Hydrochloride RS, concomitantly measured, and the respective absorptivities, calculated on the dried basis, at the wavelength of maximum absorbance at about 310 nm do not differ by more than 3.0%.
C:
A solution (1 in 50) responds to the tests for Chloride  191
191 , the procedure for alkaloidal hydrochlorides being used.
, the procedure for alkaloidal hydrochlorides being used.
Melting range  741
741 :
between 178
:
between 178 and 185
and 185 , but the range between beginning and end of melting does not exceed 2
, but the range between beginning and end of melting does not exceed 2 .
.
Loss on drying  731
731 —
Dry it at 105
—
Dry it at 105 for 3 hours: it loses not more than 0.5% of its weight.
for 3 hours: it loses not more than 0.5% of its weight.
Residue on ignition  281
281 :
not more than 0.15%.
:
not more than 0.15%.
Ordinary impurities  466
466 —
—
Test solution:
methanol.
Standard solution:
methanol.
Eluant:
a mixture of butyl alcohol, water, and glacial acetic acid (5:3:1).
Visualization:
1; 17.
Assay—
Place 250 mg of Proparacaine Hydrochloride, accurately weighed, in a 250-mL conical flask, add 80 mL of a 1 in 20 solution of acetic anhydride in glacial acetic acid, and heat on a steam bath for 10 minutes. Cool to room temperature, add 10 mL of mercuric acetate TS and 1 or 2 drops of crystal violet TS, and titrate with 0.1 N perchloric acid VS to a blue-green endpoint. Perform a blank determination, and make any necessary correction. Each mL of 0.1 N perchloric acid is equivalent to 33.09 mg of C16H26N2O3·HCl.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
| Monograph | Daniel K. Bempong, Ph.D.
Senior Scientist 1-301-816-8143 |
(MDPS05) Monograph Development-Pulmonary and Steroids |
| Reference Standards | Lili Wang, Technical Services Scientist 1-301-816-8129 RSTech@usp.org |
USP32–NF27 Page 3410