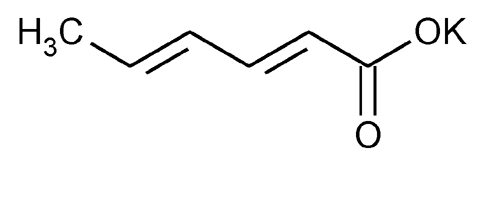
Potassium Sorbate
2,4-Hexadienoic acid, (E,E)-, potassium salt; 2,4-Hexadienoic acid, potassium salt.
Potassium (E,E)-sorbate; Potassium sorbate
» Potassium Sorbate contains not less than 98.0 percent and not more than 101.0 percent of C6H7KO2, calculated on the dried basis.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in tight containers, protected from light, and avoid exposure to excessive heat.
Identification—
A:
Dissolve 1 g in 10 mL of water: the solution responds to the test for Potassium  191
191 .
.
B:
Dissolve 0.2 g in 2 mL of water, and add a few drops of bromine TS: the color is discharged.
Acidity or alkalinity—
Dissolve 1.1 g in 20 mL of water, and add phenolphthalein TS. If the solution is colorless, titrate with 0.10 N sodium hydroxide to a pink color that persists for 15 seconds: not more than 1.1 mL is required. If the solution is pink in color, titrate with 0.10 N hydrochloric acid: not more than 0.80 mL is required to discharge the pink color.
Loss on drying  731
731 —
Dry it at 105
—
Dry it at 105 for 3 hours: it loses not more than 1.0% of its weight.
for 3 hours: it loses not more than 1.0% of its weight.
Heavy metals, Method II  231
231 :
0.001%.
:
0.001%.
Assay—
Dissolve about 300 mg of Potassium Sorbate, accurately weighed, in 40 mL of glacial acetic acid, warming, if necessary, to effect solution. Cool to room temperature, add 1 drop of crystal violet TS, and titrate with 0.1 N perchloric acid VS to a blue-green endpoint. Perform a blank determination, and make any necessary correction. Each mL of 0.1 N perchloric acid is equivalent to 15.02 mg of C6H7KO2.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
Chromatographic Column—
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
| Monograph | Robert H. Lafaver, B.A.
Scientist 1-301-816-8335 |
(EM105) Excipient Monographs 1 |
USP32–NF27 Page 1323
Chromatographic columns text is not derived from, and not part of, USP 32 or NF 27.