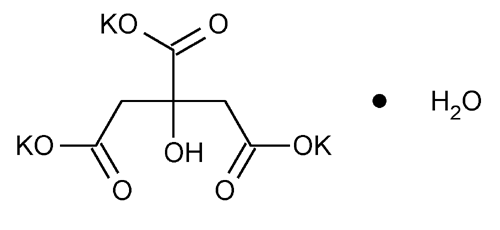
Potassium Citrate
1,2,3-Propanetricarboxylic acid, 2-hydroxy-, tripotassium salt, monohydrate.
Tripotassium citrate monohydrate
Anhydrous 306.40
» Potassium Citrate contains not less than 99.0 percent and not more than 100.5 percent of C6H5K3O7, calculated on the dried basis.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in tight containers.
Alkalinity—
A solution of 1.0 g in 20 mL of water is alkaline to litmus, but after the addition of 0.20 mL of 0.10 N sulfuric acid, no pink color is produced by the addition of 1 drop of phenolphthalein TS.
Loss on drying  731
731 —
Dry it at 180
—
Dry it at 180 for 4 hours: it loses between 3.0% and 6.0% of its weight.
for 4 hours: it loses between 3.0% and 6.0% of its weight.
Tartrate—
To a solution of 1 g in 1.5 mL of water in a test tube add 1 mL of 6 N acetic acid, and scratch the walls of the test tube with a glass rod: no crystalline precipitate is formed.
Heavy metals, Method I  231
231 —
Dissolve 2 g in 25 mL of water, and proceed as directed for Test Preparation, except to use glacial acetic acid to adjust the pH: the limit is 0.001%.
—
Dissolve 2 g in 25 mL of water, and proceed as directed for Test Preparation, except to use glacial acetic acid to adjust the pH: the limit is 0.001%.
Assay—
Dissolve about 200 mg of Potassium Citrate, accurately weighed, in 25 mL of glacial acetic acid. Add 2 drops of crystal violet TS, and titrate with 0.1 N perchloric acid VS to a green endpoint. Perform a blank determination, and make any necessary correction. Each mL of 0.1 N perchloric acid is equivalent to 10.21 mg of C6H5K3O7.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
Chromatographic Column—
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
| Monograph | Curtis Phinney
1-301-816-8540 |
(DSN05) Dietary Supplements - Non-Botanicals |
USP32–NF27 Page 3342
Chromatographic columns text is not derived from, and not part of, USP 32 or NF 27.