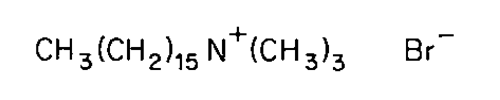Cetrimonium Bromide
» Cetrimonium Bromide contains not less than 96.0 percent and not more than 101.0 percent of hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide, calculated as C19H42BrN, on the dried basis.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in well-closed containers. No storage requirements specified.
USP Reference standards  11
11 —
—
USP Cetrimonium Bromide RS.
USP Cetrimonium Bromide RS.
Appearance of solution—
Transfer 2.0 g of Cetrimonium Bromide to a 100-mL flask, dissolve in and dilute with previously boiled and cooled water to volume: the solution is clear and colorless.
Identification—
A:
Transfer 250 mg of it to a 25-mL volumetric flask, and dissolve in and dilute with alcohol to volume. Determine the absorbance in a 1-cm cell with a suitable spectrophotometer, after correcting for the blank: between 260 nm and 280 nm, the absorbance is not greater than 0.05.
B:
Dissolve about 5 mg of it in 5 mL of phosphate buffer pH 8.0. Add a strip of methyl green–iodomercurate paper. After 5 minutes, the solution shows a more intense greenish-blue color than a blank solution prepared at the same time in the same manner.
C:
Transfer 2.0 g of it to a 100-mL flask, dissolve in and dilute with previously boiled and cooled water to volume: the solution froths copiously when shaken.
D:
Thin-Layer Chromatographic Identification Test  201
201 .
.
Test solution:
a solution in water containing about 20 mg of Cetrimonium Bromide per mL.
Sodium acetate solution—
Transfer 135 g of sodium acetate trihydrate to a 500-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in and dilute with water to volume, and mix.
Developing solvent:
a mixture of acetone, Sodium acetate solution, and methanol (20:35:45).
Procedure—
Proceed as directed in the chapter. Remove the plate from the developing chamber, and dry the plate in a current of hot air. Allow to cool. Expose the plate to iodine vapor, and examine in daylight: the principal spot obtained from the Test solution is similar in position, color, and size to that obtained from the Standard solution.
E:
A solution of it meets the requirements of the tests for Bromide  191
191 .
.
Microbial enumeration tests  61
61 and Tests for specified microorganisms
and Tests for specified microorganisms  62
62 —
The total aerobic microbial count is not more than 1000 cfu per g. The total combined molds and yeasts count is not more than 10 cfu per g.
—
The total aerobic microbial count is not more than 1000 cfu per g. The total combined molds and yeasts count is not more than 10 cfu per g.
Acidity or alkalinity—
To 50 mL of the solution obtained in the Appearance of solution test add 0.1 mL of bromocresol purple TS. Not more than 0.1 mL of 0.1 N sodium hydroxide or 0.1 N hydrochloric acid is required to change the color of the indicator.
Loss on drying  731
731 —
Dry about 1.0 g of it at 105
—
Dry about 1.0 g of it at 105 for 2 hours: it loses not more than 2.0% of its weight.
for 2 hours: it loses not more than 2.0% of its weight.
Residue on ignition  281
281 :
not more than 0.5%, determined on 1.0 g.
:
not more than 0.5%, determined on 1.0 g.
Limit of amines and amine salts—
Dissolve 5.0 g of Cetrimonium Bromide in 30 mL of a mixture of 1 N hydrochloric acid VS and methanol (1:99, v/v), and add 100 mL of isopropyl alcohol. Pass a stream of nitrogen slowly through the solution. Gradually add 15.0 mL of 0.1 N tetrabutylammonium hydroxide VS, recording the potentiometric titration curve. If the curve shows two inflection points, the volume of titrant added between the two points is not greater than 2.0 mL.
Assay—
Transfer 2.0 g of Cetrimonium Bromide, accurately weighed, to a 100-mL volumetric flask, and dissolve in and dilute with water to volume. Transfer 25.0 mL of this solution to a separatory funnel, and add 25 mL of chloroform, 10 mL of 0.1 N sodium hydroxide VS, and 10.0 mL of a freshly prepared solution of potassium iodide (1 in 20). Shake well, allow to separate, and discard the chloroform layer. Wash the aqueous layer with three 10-mL portions of chloroform, and discard the washings. Transfer the aqueous layer to a stoppered conical flask, add 40 mL of hydrochloric acid, allow to cool, and titrate with 0.05 M potassium iodate VS until the deep brown color is almost discharged. Add 2 mL of chloroform, and continue the titration, shaking vigorously, until the color of the chloroform layer no longer changes. Perform a blank titration on a mixture of 10.0 mL of a freshly prepared solution of potassium iodide (1 in 20), 20 mL of water, and 40 mL of hydrochloric acid, and make any necessary correction. Each mL of 0.05 M potassium iodate is equivalent to 36.45 mg of Cetrimonium Bromide (C19H42BrN).
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
| Monograph | Robert H. Lafaver, B.A.
Scientist 1-301-816-8335 |
(EM105) Excipient Monographs 1 |
| Reference Standards | Lili Wang, Technical Services Scientist 1-301-816-8129 RSTech@usp.org |
|
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Senior Scientist 1-301-816-8339 |
(MSA05) Microbiology and Sterility Assurance | |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Senior Scientist 1-301-816-8339 |
(MSA05) Microbiology and Sterility Assurance |
USP32–NF27 Page 1203
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 30(3) Page 970