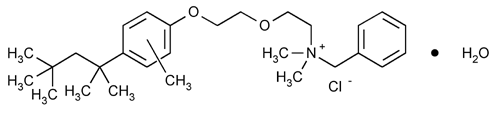
Methylbenzethonium Chloride
Benzenemethanaminium, N,N-dimethyl-N-[2-[2-[methyl-4-(1,1,3,3-tetramethylbutyl)phenoxy]ethoxy]ethyl]-, chloride, monohydrate.
Benzyldimethyl[2-[2-[[4-(1,1,3,3-tetramethylbutyl)tolyl]oxy]ethoxy]ethyl]ammonium chloride monohydrate
Anhydrous 462.12
» Methylbenzethonium Chloride contains not less than 97.0 percent and not more than 103.0 percent of C28H44ClNO2, calculated on the dried basis.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in tight containers.
Identification—
A:
To 1 mL of a solution (1 in 100) add 2 mL of alcohol, 0.5 mL of 2 N nitric acid, and 1 mL of silver nitrate TS: a white precipitate, which is insoluble in 2 N nitric acid and soluble in 6 N ammonium hydroxide, is formed.
B:
Treat separate portions of a solution (1 in 100) with 2 N nitric acid and with mercuric chloride TS, respectively: precipitates are formed that dissolve upon the addition of alcohol.
C:
To 10 mL of a solution (1 in 20,000) add 0.1 g of sodium carbonate, 1 mL of bromophenol blue TS, and 10 mL of chloroform, and shake the mixture: the chloroform layer is blue.
D:
Dissolve 100 mg in 1 mL of sulfuric acid, add 1.0 g of potassium nitrate, and heat on a steam bath for 3 minutes. Cautiously dilute the solution with water to 10 mL, add 0.5 g of granulated zinc, and warm the mixture for 10 minutes. Cool, add 0.2 g of sodium nitrite to 1 mL of the clear liquid, and add this mixture to 20 mg of naphthol dipotassium disulfonate or naphthol disodium disulfonate in 1 mL of ammonium hydroxide: the solution turns orange-red, and a brown precipitate may be formed.
Loss on drying  731
731 —
Dry it at 105
—
Dry it at 105 for 4 hours: it loses not more than 5.0% of its weight.
for 4 hours: it loses not more than 5.0% of its weight.
Residue on ignition  281
281 :
not more than 0.1%.
:
not more than 0.1%.
Limit of ammonium compounds—
To 5 mL of a solution (1 in 50) add 3 mL of 1 N sodium hydroxide, and heat to boiling: the odor of ammonia is not perceptible.
Assay—
Accurately weigh a quantity of Methylbenzethonium Chloride, equivalent to about 500 mg of dried methylbenzethonium chloride, and transfer, with the aid of 35 mL of water, to a glass-stoppered, 250-mL conical separator containing 25 mL of chloroform. Add 10.0 mL of freshly prepared potassium iodide solution (1 in 20), insert the stopper in the separator, shake, allow the layers to separate, and discard the chloroform layer. Wash the aqueous layer with three 10-mL portions of chloroform, and discard the washings. Transfer the aqueous layer to a glass-stoppered, 250-mL conical flask, and rinse the separator with three 5-mL portions of water, adding the washings to the flask. Add 40 mL of cold hydrochloric acid to the flask, mix, and titrate with 0.05 M potassium iodate VS until the solution becomes light brown in color. Add 5 mL of chloroform, insert the stopper in the flask, and shake vigorously. Continue the titration, dropwise, with shaking after each addition, until the chloroform layer becomes colorless and the aqueous layer is clear yellow. Perform a blank determination, using 20 mL of water as the test specimen (see Residual Titrations under Titrimetry  541
541 ). Each mL of 0.05 M potassium iodate is equivalent to 46.21 mg of C28H44ClNO2.
). Each mL of 0.05 M potassium iodate is equivalent to 46.21 mg of C28H44ClNO2.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
| Monograph | Behnam Davani, Ph.D., M.B.A.
Senior Scientist 1-301-816-8394 |
(MDAA05) Monograph Development-Antivirals and Antimicrobials |
USP32–NF27 Page 2937
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 27(1) Page 1802