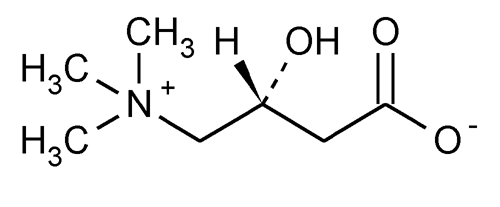
Levocarnitine
» Levocarnitine contains not less than 97.0 percent and not more than 103.0 percent of C7H15NO3, calculated on the anhydrous basis.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in tight containers.
USP Reference standards  11
11 —
—
USP Levocarnitine RS.
USP Levocarnitine RS.
Identification, Infrared Absorption  197K
197K —
The test specimen and the Reference Standard are dried previously in vacuum at 50
—
The test specimen and the Reference Standard are dried previously in vacuum at 50 for 5 hours.
for 5 hours.
pH  791
791 :
between 5.5 and 9.5 in a solution (1 in 20).
:
between 5.5 and 9.5 in a solution (1 in 20).
Water content  921
921 :
not more than 4.0%.
:
not more than 4.0%.
Residue on ignition  281
281 :
not more than 0.5%.
:
not more than 0.5%.
Chloride  221
221 —A 0.090-g portion shows no more chloride than corresponds to 0.50 mL of 0.020 N hydrochloric acid (0.4%).
—A 0.090-g portion shows no more chloride than corresponds to 0.50 mL of 0.020 N hydrochloric acid (0.4%).
Limit of potassium—
[note—The Standard solution and the Test solutions may be modified, if necessary, to obtain solutions of suitable concentrations, adaptable to the linear or working range of the instrument.]
Standard solution—
Transfer 5.959 g of potassium chloride, previously dried at 105 for 2 hours and accurately weighed, to a 250-mL volumetric flask, dilute with water to volume, and mix. This solution contains 12.5 mg of potassium per mL. Dilute an accurately measured volume of this solution quantitatively, and stepwise if necessary, with water to obtain a solution containing 31.25 µg of potassium per mL.
for 2 hours and accurately weighed, to a 250-mL volumetric flask, dilute with water to volume, and mix. This solution contains 12.5 mg of potassium per mL. Dilute an accurately measured volume of this solution quantitatively, and stepwise if necessary, with water to obtain a solution containing 31.25 µg of potassium per mL.
Test solutions—
Transfer 62.5 mg of Levocarnitine to a 100-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in and dilute with water to volume, and mix to obtain a stock solution. To three separate 25-mL volumetric flasks add 0, 2.0, and 4.0 mL of the Standard solution. To each flask add 20.0 mL of the stock solution, dilute with water to volume, and mix. These solutions contain 0 (Test solution A), 2.5 (Test solution B), and 5.0 (Test solution C) µg per mL of potassium.
Procedure—
Concomitantly determine the absorbances of the Test solutions at the potassium emission line at 766.7 nm with a suitable atomic absorption spectrophotometer (see Spectrophotometry and Light-Scattering  851
851 ) equipped with an air–acetylene flame, using water as the blank. Plot the absorbances of the Test solutions versus their contents of potassium, in µg per mL, draw the straight line best fitting the three points, and extrapolate the line until it intercepts the concentration axis. From the intercept determine the amount, in µg, of potassium in each mL of Test solution A. Calculate the percentage of potassium in the portion of Levocarnitine taken by multiplying the concentration, in µg per mL, of potassium found in Test solution A by 0.2: not more than 0.2% is found.
) equipped with an air–acetylene flame, using water as the blank. Plot the absorbances of the Test solutions versus their contents of potassium, in µg per mL, draw the straight line best fitting the three points, and extrapolate the line until it intercepts the concentration axis. From the intercept determine the amount, in µg, of potassium in each mL of Test solution A. Calculate the percentage of potassium in the portion of Levocarnitine taken by multiplying the concentration, in µg per mL, of potassium found in Test solution A by 0.2: not more than 0.2% is found.
Limit of sodium—
[note—The Standard solution and the Test solutions may be modified, if necessary, to obtain solutions of suitable concentrations, adaptable to the linear or working range of the instrument.]
Standard solution—
Transfer 6.355 g of sodium chloride, previously dried at 105 for 2 hours and accurately weighed, to a 250-mL volumetric flask, dilute with water to volume, and mix. This solution contains 10.0 mg of sodium per mL. Dilute an accurately measured volume of this solution quantitatively, and stepwise if necessary, with water to obtain a solution containing 250 µg of sodium per mL.
for 2 hours and accurately weighed, to a 250-mL volumetric flask, dilute with water to volume, and mix. This solution contains 10.0 mg of sodium per mL. Dilute an accurately measured volume of this solution quantitatively, and stepwise if necessary, with water to obtain a solution containing 250 µg of sodium per mL.
Test solutions—
Transfer 4.0 g of Levocarnitine to a 100-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in and dilute with water to volume, and mix to obtain a stock solution. To three separate 25-mL volumetric flasks add 0, 2.0, and 4.0 mL of the Standard solution. To each flask add 20.0 mL of the stock solution, dilute with water to volume, and mix. These solutions contain 0 (Test solution A), 20.0 (Test solution B), and 40.0 (Test solution C) µg per mL of sodium.
Procedure—
Concomitantly determine the absorbances of the Test solutions at the sodium emission line at 589.0 nm with a suitable atomic absorption spectrophotometer (see Spectrophotometry and Light-Scattering  851
851 ) equipped with an air–acetylene flame, using water as the blank. Plot the absorbances of the Test solutions versus their contents of sodium, in µg per mL, draw the straight line best fitting the three points, and extrapolate the line until it intercepts the concentration axis. From the intercept determine the amount, in µg, of sodium in each mL of Test solution A. Calculate the percentage of sodium in the portion of Levocarnitine taken by multiplying the concentration, in µg per mL, of sodium found in Test solution A by 0.003125: not more than 0.1% is found.
) equipped with an air–acetylene flame, using water as the blank. Plot the absorbances of the Test solutions versus their contents of sodium, in µg per mL, draw the straight line best fitting the three points, and extrapolate the line until it intercepts the concentration axis. From the intercept determine the amount, in µg, of sodium in each mL of Test solution A. Calculate the percentage of sodium in the portion of Levocarnitine taken by multiplying the concentration, in µg per mL, of sodium found in Test solution A by 0.003125: not more than 0.1% is found.
Heavy metals  231
231 :
not more than 0.002%.
:
not more than 0.002%.
Assay—
Transfer about 100 mg of Levocarnitine, accurately weighed, to a 250-mL flask, and dissolve in a mixture of 3 mL of formic acid and 50 mL of glacial acetic acid. Add 2 drops of crystal violet TS, and titrate with 0.1 N perchloric acid VS to an emerald green endpoint. Perform a blank determination, and make any necessary correction. Each mL of 0.1 N perchloric acid is equivalent to 16.12 mg of C7H15NO3.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
| Monograph | Curtis Phinney
1-301-816-8540 |
(DSN05) Dietary Supplements - Non-Botanicals |
| Reference Standards | Lili Wang, Technical Services Scientist 1-301-816-8129 RSTech@usp.org |
USP32–NF27 Page 2768
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 28(1) Page 71