Lactase
» Lactase (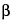 -d-galactoside galactohydrolase) is a hydrolytic enzyme derived from the mold Aspergillus oryzae. It contains not less than 30,000 USP Lactase Units in each g.
-d-galactoside galactohydrolase) is a hydrolytic enzyme derived from the mold Aspergillus oryzae. It contains not less than 30,000 USP Lactase Units in each g.
note—One USP Lactase Unit is the lactase activity contained in the amount of enzyme that hydrolyses one microequivalent of galactosidic linkage per minute at a pH of 4.5 and at 37 as directed in the Assay for lactase activity.
as directed in the Assay for lactase activity.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in tight containers at room temperature.
Labeling—
Label it to indicate lactase activity in USP Units.
Microbial enumeration tests  61
61 and Tests for specified microorganisms
and Tests for specified microorganisms  62
62 —
It meets the requirements of the test for absence of Salmonella species and Escherichia coli.
—
It meets the requirements of the test for absence of Salmonella species and Escherichia coli.
Loss on drying  731
731 —
Dry it in a vacuum at 60
—
Dry it in a vacuum at 60 for 4 hours: it loses not more than 6.0% of its weight.
for 4 hours: it loses not more than 6.0% of its weight.
Arsenic  211
211 :
not more than 3 µg per g.
:
not more than 3 µg per g.
Lead  251
251 :
not more than 5 µg per g.
:
not more than 5 µg per g.
Heavy metals  231
231 :
not more than 30 µg per g.
:
not more than 30 µg per g.
Assay for lactase activity—
pH 4.5 Acetate buffer—
Dilute 57.5 mL of glacial acetic acid with sufficient water to make 500 mL of solution. Transfer 50 mL of the glacial acetic acid solution into a 1000-mL volumetric flask, add 11.3 mL of 4 N sodium hydroxide, and dilute with water to volume. If necessary, adjust with the addition of either the glacial acetic acid solution or 4 N sodium hydroxide to a pH of 4.50 ± 0.05.
Substrate solution—
On the day of use, weigh 370.0 mg of o-nitrophenyl-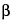 -d-galactopyranoside, and place in a 100-mL volumetric flask. Add about 50 mL of pH 4.5 Acetate buffer, swirl to dissolve, then dilute with pH 4.5 Acetate buffer to volume.
-d-galactopyranoside, and place in a 100-mL volumetric flask. Add about 50 mL of pH 4.5 Acetate buffer, swirl to dissolve, then dilute with pH 4.5 Acetate buffer to volume.
Standard preparation—
Transfer about 0.4 g of USP Lactase RS, accurately weighed, to a 1000-mL volumetric flask. Add about 600 mL of water, allow to stand for 15 minutes, swirl gently, and dilute with water to volume. Pipet 3.0 mL of this solution into a 200-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume.
Assay preparation—
Transfer an accurately weighed quantity of about 0.4 g of Lactase to a 1000-mL volumetric flask. Add about 600 mL of water, allow to stand for 15 minutes, swirl gently, and dilute with water to volume. Pipet 3.0 mL of this solution into a 200-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume.
Procedure—
Transfer 2.0 mL of the Substrate solution to 3 separate test tubes labeled S, U, and B. Transfer the tubes to a thermostated water bath maintained at 37.0 ± 0.1 , and incubate for 10 minutes. Following the incubation, add rapidly to tube S, 0.5 mL of the Standard preparation, to tube U, 0.5 mL of the Assay preparation, and to tube B (the reagent blank), 0.5 mL of water. Mix each tube on a vortex mixer for 1 second, and immediately return the tubes to the water bath, which has been maintained at 37.0 ± 0.1
, and incubate for 10 minutes. Following the incubation, add rapidly to tube S, 0.5 mL of the Standard preparation, to tube U, 0.5 mL of the Assay preparation, and to tube B (the reagent blank), 0.5 mL of water. Mix each tube on a vortex mixer for 1 second, and immediately return the tubes to the water bath, which has been maintained at 37.0 ± 0.1 . After 15 minutes of incubation, rapidly add 2.5 mL of a 10% sodium carbonate solution to each test tube to stop the enzyme reaction. Add 20.0 mL of water to each test tube, and mix. Concomitantly determine the absorbances of the three solutions at 420 nm in a 1-cm cell using a suitable spectrophotometer (see Spectrophotometry
. After 15 minutes of incubation, rapidly add 2.5 mL of a 10% sodium carbonate solution to each test tube to stop the enzyme reaction. Add 20.0 mL of water to each test tube, and mix. Concomitantly determine the absorbances of the three solutions at 420 nm in a 1-cm cell using a suitable spectrophotometer (see Spectrophotometry  851
851 ). Calculate the number of USP Lactase Units of the Lactase taken by the formula:
). Calculate the number of USP Lactase Units of the Lactase taken by the formula:
(P)(WS / WU)(AU 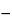 AB) / (AS
AB) / (AS 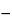 AB)
AB)
in which P is the potency of USP Lactase RS in USP Units per g; WS is the amount, in g, of USP Lactase RS taken; WU is the amount, in g, of the Lactase taken; and AU is the absorbance reading of tube U, AB is the absorbance reading of tube B, and AS is the absorbance reading of tube S.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
| Monograph | Larry N. Callahan, Ph.D.
Senior Scientist 1-301-816-8385 |
(BBPP05) Biologics and Biotechnology - Proteins and Polysaccharides |
| Reference Standards | Lili Wang, Technical Services Scientist 1-301-816-8129 RSTech@usp.org |
|
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Senior Scientist 1-301-816-8339 |
(MSA05) Microbiology and Sterility Assurance | |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Senior Scientist 1-301-816-8339 |
(MSA05) Microbiology and Sterility Assurance |
USP32–NF27 Page 2745