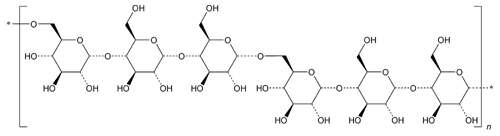
Pullulan
Poly[6)-
» Pullulan is a neutral, simple polysaccharide produced by the growth of Aureobasidium pullulans. It has a chain structure of repeated 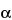 -1,6-bonds of maltotriose composed of three glucoses in
-1,6-bonds of maltotriose composed of three glucoses in 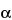 -1,4-bonds. It may contain some maltotetraosyl units. It contains not less than 90 percent of glucan, calculated on the dried basis.
-1,4-bonds. It may contain some maltotetraosyl units. It contains not less than 90 percent of glucan, calculated on the dried basis.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in well-closed containers. No storage requirements specified.
Labeling—
Label it to indicate the viscosity, giving the type of viscosity parameter, concentration of the solution, and the type of equipment used.
Identification—
A:
Dissolve 10 g of Pullulan in 100 mL of water by adding in small portions with stirring: a viscous solution is produced.
B:
Mix 10 mL of the viscous solution obtained in Identification test A with 0.1 mL of Pullulanase test solution prepared as described below, and allow to incubate at 25 for about 20 minutes: a substantial loss of viscosity is observed.
for about 20 minutes: a substantial loss of viscosity is observed.
Pullulanase test solution—Prepare a solution of pullulanase containing 10 units per mL.
C:
To 10 mL of a solution of Pullulan (1 in 50) add 2 mL of polyethylene glycol 600: a white precipitate is formed immediately.
Viscosity  911
911 —
Weigh exactly 10.0 g of Pullulan, previously dried, dissolve in water to make exactly 100 g, and perform the test at 30 ± 0.1
—
Weigh exactly 10.0 g of Pullulan, previously dried, dissolve in water to make exactly 100 g, and perform the test at 30 ± 0.1 using a Ubbelohde-type viscometer: the kinematic viscosity is between 100 and 180 mm2·s-1.
using a Ubbelohde-type viscometer: the kinematic viscosity is between 100 and 180 mm2·s-1.
Microbial enumeration tests  61
61 and Tests for specified microorganisms
and Tests for specified microorganisms  62
62 —
The total aerobic microbial count does not exceed 100 cfu per g, and the total combined molds and yeasts count does not exceed 100 cfu per g.
—
The total aerobic microbial count does not exceed 100 cfu per g, and the total combined molds and yeasts count does not exceed 100 cfu per g.
pH  791
791 —
Dissolve 1.0 g of Pullulan in 10 mL of freshly boiled and cooled water: the pH is between 4.5 and 6.5.
—
Dissolve 1.0 g of Pullulan in 10 mL of freshly boiled and cooled water: the pH is between 4.5 and 6.5.
Loss on drying  731
731 —
Dry it at 90
—
Dry it at 90 in vacuum for 6 hours: it loses not more than 6.0% of its weight.
in vacuum for 6 hours: it loses not more than 6.0% of its weight.
Residue on ignition  281
281 :
not more than 0.3%, determined on 2.0 g.
:
not more than 0.3%, determined on 2.0 g.
Heavy metals, Method II  231
231 :
not more than 5 µg per g.
:
not more than 5 µg per g.
Content of monosaccharide, disaccharide, and oligosaccharides—
Test stock solution—
Transfer 0.8 g of Pullulan, previously dried and accurately weighed, to a 100-mL volumetric flask, dilute with water to volume, and mix.
Standard solution—
Transfer 1.0 mL of the Test stock solution to a 50-mL volumetric flask, dilute with water to volume, and mix.
Test solution—
To 1.0 mL of the Test stock solution add 0.1 mL of saturated potassium chloride solution, and shake vigorously with 3 mL of methyl alcohol. Centrifuge, and use the supernatant.
Blank solution—
Use water.
Procedure—
Transfer 0.2 mL each of the Standard solution, the Test solution, and the Blank solution to a test tube containing 5 mL of a 1 in 500 solution of anthrone in 75% (v/v) sulfuric acid, with the test tube placed in ice water. Mix each tube immediately, and then heat the test tube at 90 for 10 minutes. Remove the tube, and allow it to cool in cold running water. Perform the test with the solutions so obtained using a suitable UV/visible spectrophotometer (see Spectrophotometry and Light-Scattering
for 10 minutes. Remove the tube, and allow it to cool in cold running water. Perform the test with the solutions so obtained using a suitable UV/visible spectrophotometer (see Spectrophotometry and Light-Scattering  851
851 ), and using water as a blank. Determine the absorbances AT, AB, and AS, at 620 nm, for the Test solution, the Blank solution, and the Standard solution, respectively. Determine the percentage of monosaccharide, disaccharide, and oligosaccharides in the portion of dried Pullulan taken by the formula:
), and using water as a blank. Determine the absorbances AT, AB, and AS, at 620 nm, for the Test solution, the Blank solution, and the Standard solution, respectively. Determine the percentage of monosaccharide, disaccharide, and oligosaccharides in the portion of dried Pullulan taken by the formula:
100(4.1/50)(AT – AB) / (AS – AB)]
in which 4.1 is the dilution factor for the Test solution, and 50 is the dilution factor for the Standard solution. The total content of monosaccharide, disaccharide, and oligosaccharides is not more than 10.0%, corresponding to not less than 90% of glucan, on the dried basis.
Nitrogen content  461
461 —
Weigh accurately about 3 g of Pullulan, previously dried, and perform the test as directed in Method II under Nitrogen Determination
—
Weigh accurately about 3 g of Pullulan, previously dried, and perform the test as directed in Method II under Nitrogen Determination  461
461 : the amount of nitrogen is not more than 0.05%, 12 mL of sulfuric acid being used for the decomposition, and 40 mL of a solution of sodium hydroxide (2 in 5) being added.
: the amount of nitrogen is not more than 0.05%, 12 mL of sulfuric acid being used for the decomposition, and 40 mL of a solution of sodium hydroxide (2 in 5) being added.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
| Monograph | Hong Wang, Ph.D.
Scientist 1-301-816-8351 |
(EM205) Excipient Monographs 2 |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Senior Scientist 1-301-816-8339 |
(MSA05) Microbiology and Sterility Assurance | |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Senior Scientist 1-301-816-8339 |
(MSA05) Microbiology and Sterility Assurance |
USP32–NF27 Page 1330
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 33(5) Page 975