Potassium Bromide
KBr




 119.0
119.0
Potassium bromide.
Potassium bromide

 [7758-02-3].
[7758-02-3].
Potassium bromide.
Potassium bromide
» Potassium Bromide contains not less than 98.0 percent and not more than 100.5 percent of KBr, calculated on the dried basis. It contains no added substances.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in well-closed containers, and store at room temperature.
Appearance of solution:
clear and colorless.
Test solution—
Dissolve 10.0 g in carbon dioxide-free water, and dilute with the same solvent to 100 mL.
Identification—
B:
Responds to the test for Potassium  191
191 .
.
Acidity or alkalinity—
To 10 mL of the solution prepared for the test for Appearance of solution, add 0.1 mL of bromothymol blue TS: not more than 0.5 mL of 0.01 N hydrochloric acid or 0.01 N sodium hydroxide is required to change the color of this solution.
Bromates—
Starch–mercuric iodide solution—
Triturate 1.0 g of soluble starch with 5 mL of water and pour the mixture into 100 mL of boiling water, containing 10 mg of mercuric iodide.
Procedure—
To 10 mL of the solution prepared for the test for Appearance of solution add 1 mL of Starch–mercuric iodide solution, 0.1 mL of a 100 g per L solution of potassium iodide, and 0.25 mL of 0.5 M sulfuric acid. Allow to stand protected from light for 5 minutes: no blue or violet color develops.
Limit of chlorine:
not more than 0.6%.
Nitric acid solution and Ferric ammonium sulfate solution—
Proceed as directed in the Assay.
Procedure—
Dissolve 1.000 g of Potassium Bromide in 20 mL of Nitric acid solution in a conical flask, add and mix 5 mL of 30 percent hydrogen peroxide, and heat in a water bath until the solution is colorless. Rinse the sides of the flask with a small quantity of water, and heat in a water bath for 15 minutes. Allow to cool, dilute with water to 50 mL, and add 5.0 mL of silver nitrate VS and 1 mL of dibutyl phthalate. Mix, and back titrate the excess silver nitrate with ammonium thiocyanate VS (see Titrimetry  541
541 ), using 5 mL of Ferric ammonium sulfate solution as the indicator. Perform a blank titration. Not more than 1.7 mL of silver nitrate VS is used.
), using 5 mL of Ferric ammonium sulfate solution as the indicator. Perform a blank titration. Not more than 1.7 mL of silver nitrate VS is used.
Iodides—
To 5 mL of the solution prepared for the test for Appearance of solution add 0.15 mL of a 10.5 g per 100 mL ferric chloride solution, and 2 mL of dichloromethane. Shake, and allow to separate. The lower layer is colorless.
Sulfates  221
221 —
A 2.0-g portion shows no more sulfate than corresponds to 0.2 mL of 0.020 N sulfuric acid (0.01%).
—
A 2.0-g portion shows no more sulfate than corresponds to 0.2 mL of 0.020 N sulfuric acid (0.01%).
Limit of iron:
not more than 20 ppm.
Citric acid solution—
Prepare a 200 g citric acid per mL solution.
Iron standard solution—
Transfer 0.863 g of ferric ammonium sulfate to a 500-mL volumetric flask, and dissolve in 25 mL of dilute sulfuric acid. Dilute with water to volume. Transfer 1.0 mL of the resulting solution to a 10-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume. Transfer 2.5 mL of this resulting solution to a 50-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume. [note—Prepare immediately before use.]
Test solution—
Transfer 5 mL of the solution prepared for the test for Appearance of solution to a 10-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume.
Procedure—
To 10 mL each of the Iron standard solution and the Test solution add 2.0 mL of the Citric acid solution and 0.1 mL of thioglycolic acid. Make alkaline to litmus with ammonia water, and dilute with water to 20 mL. After 5 minutes, any pink color in the Test solution is not more intense than that in the Iron standard solution.
Magnesium and alkaline-earth metals—
To 200 mL of water add 0.1 g of hydroxylamine hydrochloride, 10 mL of pH 10.0 ammonia–ammonium chloride buffer (prepared by dissolving 5.4 g of ammonium chloride in 20 mL of water, adding 20 mL of ammonium hydroxide and diluting to 100 mL), 1 mL of 0.1 M zinc sulfate, and about 0.2 g of eriochrome black T trituration. Heat to about 40 . Titrate this solution (see Titrimetry
. Titrate this solution (see Titrimetry  541
541 ) with 0.01 M edetate disodium VS until the violet color changes to deep blue. To this solution add 10.0 g of Potassium Bromide dissolved in 100 mL of water. If the color changes to violet, titrate the solution with 0.01 M edetate disodium VS to a deep blue endpoint. The volume of 0.01 M edetate disodium consumed in the second titration does not exceed 5.0 mL (0.02%, calculated as Ca).
) with 0.01 M edetate disodium VS until the violet color changes to deep blue. To this solution add 10.0 g of Potassium Bromide dissolved in 100 mL of water. If the color changes to violet, titrate the solution with 0.01 M edetate disodium VS to a deep blue endpoint. The volume of 0.01 M edetate disodium consumed in the second titration does not exceed 5.0 mL (0.02%, calculated as Ca).
Heavy metals, Method I  231
231 :
not more than 10 ppm.
:
not more than 10 ppm.
Assay—
Nitric acid solution—
Dilute 14 mL of nitric acid with water to 100 mL.
Ferric ammonium sulfate solution—
Transfer 10 g of ferric ammonium sulfate to a 100-mL volumetric flask. Dissolve in and dilute with water to volume.
Procedure—
Dissolve 2.000 g of Potassium Bromide in water, and dilute with water to 100.0 mL. To 10.0 mL of the solution add 50 mL of water, 5 mL of Nitric acid solution, 25.0 mL of silver nitrate VS, and 2 mL of dibutyl phthalate. Mix, and back titrate the excess silver nitrate with ammonium thiocyanate VS (see Titrimetry  541
541 ), using 2 mL of Ferric ammonium sulfate solution as the indicator, shaking vigorously towards the endpoint. Each mL of 0.1 M silver nitrate is equivalent to 11.90 mg of KBr. Calculate the percent content of Potassium Bromide, corrected for the chloride content, by the formula:
), using 2 mL of Ferric ammonium sulfate solution as the indicator, shaking vigorously towards the endpoint. Each mL of 0.1 M silver nitrate is equivalent to 11.90 mg of KBr. Calculate the percent content of Potassium Bromide, corrected for the chloride content, by the formula:
a 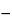 3.357b
3.357b
in which a is the percent content of KBr and KCl obtained, calculated as KBr; and b is the percent content of chlorides.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
| Monograph | Ian DeVeau, Ph.D.
Director, Veterinary Drugs and Radiopharmaceuticals 1-301-816-8178 |
(VET05) Veterinary Drugs 05 |
USP32–NF27 Page 3334
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 31(2) Page 441